Life Expectancy Worldwide Mapped (2000-2022)
Life expectancy is a statistical measure representing the average number of years a person can expect to live, typically at birth, based on current mortality rates. It is a key indicator of a population’s overall health and well-being. Factors such as healthcare quality, sanitation, nutrition, and socio-economic conditions influence life expectancy.
Additionally, cultural practices and governmental policies play roles in shaping health outcomes, highlighting the multifaceted nature of the factors influencing life expectancy disparities among nations.
The world map of life expectancy by country below was created using World Health Organization and World Bank data.
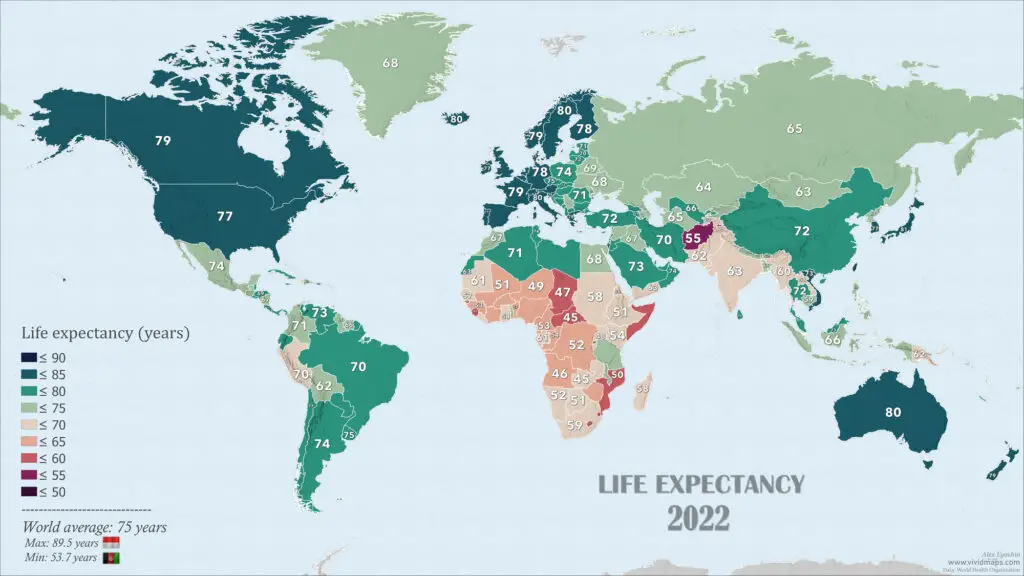
According to the map countries with the highest life expectancy are often found in Western Europe and East Asia. Below is the list of countries with the highest life expectancy and some key factors that contribute to the high life expectancy in these countries.
Top 10 countries with the highest life expectancy
| Rank | Country | Life expectancy | Key factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Monaco | 89.52 | Healthcare Excellence: Monaco boasts a state-of-the-art healthcare system, providing residents with access to top-tier medical facilities and services. Wealth and Living Standards: The principality’s affluence ensures high living standards, with access to nutritious food, recreational activities, and a low-stress lifestyle. |
| 2 | Singapore | 86.35 | Comprehensive Healthcare: Singapore invests heavily in healthcare infrastructure and preventive measures, contributing to a well-functioning healthcare system. Public Health Initiatives: Robust public health campaigns focus on disease prevention, early detection, and health education. |
| 3 | Macao | 84.98 | Economic Prosperity: Macao’s economic success contributes to overall well-being, providing citizens with the means to access quality healthcare and maintain healthy lifestyles. Low Crime Rates: Safety and security contribute to a stress-free living environment. |
| 4 | Japan | 84.83 | Healthy Lifestyles: Japan emphasizes a traditional diet rich in fish, vegetables, and green tea, contributing to lower rates of heart disease and longer life expectancy. Social Support Networks: Strong family and community ties contribute to mental well-being. |
| 5 | San Marino | 83.86 | Access to Healthcare: San Marino provides universal healthcare, ensuring citizens receive timely medical attention. Small Population: The country’s small size facilitates effective healthcare delivery and public health initiatives. |
| 6 | Canada | 83.8 | Universal Healthcare: Canada’s publicly funded healthcare system ensures access to medical services for all residents. Educational Attainment: High levels of education contribute to health awareness and positive lifestyle choices. |
| 7 | Iceland | 83.64 | Clean Environment: Iceland’s pristine environment and access to clean water contribute to a low prevalence of waterborne diseases. Low Pollution: Minimal pollution and a strong focus on environmental conservation contribute to overall health. |
| 8 | Hong Kong | 83.61 | Efficient Healthcare: Hong Kong’s healthcare system is efficient and accessible, contributing to early diagnosis and treatment. Urban Planning: The city’s well-designed urban spaces promote physical activity, contributing to residents’ overall health. |
| 9 | Andorra | 83.42 | Mountainous Environment: Andorra’s mountainous terrain offers opportunities for outdoor activities, contributing to a healthier lifestyle. Economic Prosperity: High living standards and economic stability positively impact health outcomes. |
| 10 | Israel | 83.35 | Innovative Healthcare: Israel is known for medical research and innovation, contributing to advancements in healthcare. Diverse Diet: A Mediterranean-influenced diet, rich in fruits and vegetables, contributes to heart health and longevity |
While these factors provide insights into each country’s high life expectancy, it’s crucial to recognize that these are complex outcomes influenced by a combination of historical, cultural, economic, and social factors. Ongoing efforts in healthcare, education, and public health contribute to the sustained well-being of populations in these countries.
Top 10 countries with the lowest life expectancy
Countries with the lowest life expectancy often face challenges related to healthcare access, poverty, political instability, and high disease burdens. Some of the countries that historically have had lower life expectancies include certain sub-Saharan African nations, such as Chad, Central African Republic, Lesotho, and Sierra Leone.
| Rank | Country | Life expectancy |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Afghanistan | 53.65 |
| 2 | Central African Republic | 55.52 |
| 3 | Somalia | 55.72 |
| 4 | Mozambique | 57.1 |
| 5 | Sierra Leone | 58.76 |
| 6 | Chad | 59.15 |
| 7 | South Sudan | 59.16 |
| 8 | Lesotho | 59.57 |
| 9 | Eswatini | 59.69 |
| 10 | Niger | 60.09 |
Globally, life expectancy has increased over the years due to advancements in medical science and public health initiatives. In developed countries, longer life expectancies often correlate with better healthcare systems and living standards. However, regional disparities persist, with some areas facing challenges like infectious diseases, poverty, or inadequate healthcare access that impact life expectancy.
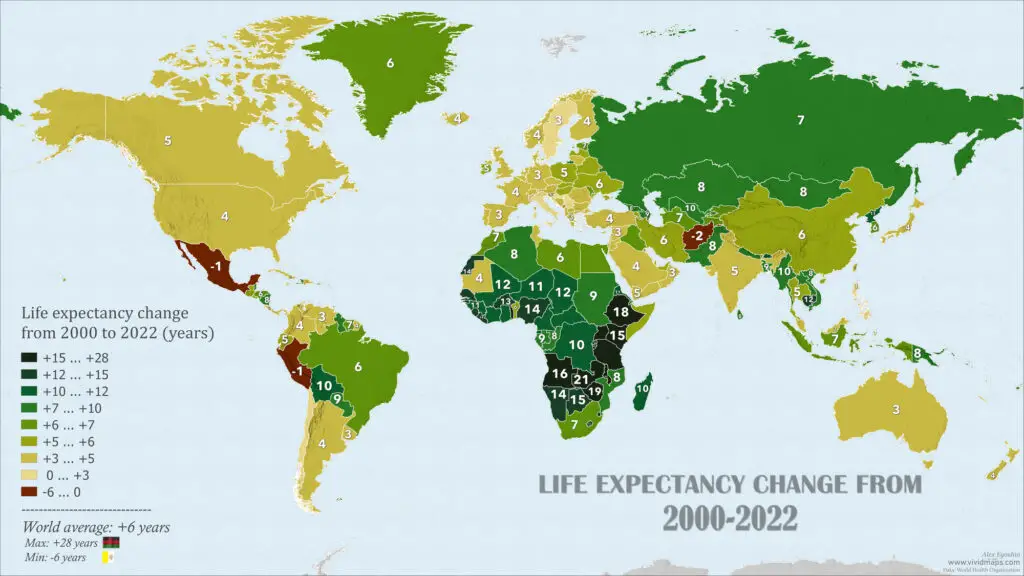
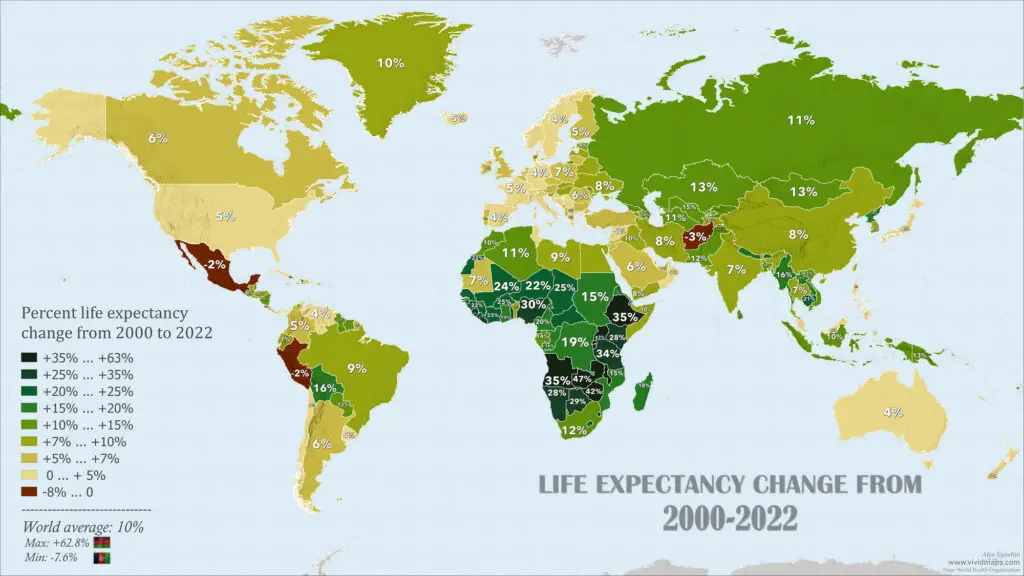
The 10 countries with the largest increases in life expectancy from 2000 to 2020
The notable increase in life expectancy in countries such as Malawi, Zambia, Uganda, Burundi, Zimbabwe, Rwanda, Ethiopia, Angola, Tanzania, and Togo from 2000 to the present can be attributed to multifaceted efforts addressing key health and socio-economic factors.
| Rank | Country | Life expectancy change (years) | Percent life expectancy change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Malawi | +28 | +63% |
| 2 | Zambia | +21 | +47% |
| 3 | Uganda | +21 | +43% |
| 4 | Burundi | +20 | +42% |
| 5 | Zimbabwe | +19 | +42% |
| 6 | Rwanda | +19 | +40% |
| 7 | Ethiopia | +18 | +35% |
| 8 | Tanzania | +18 | +34% |
| 9 | Togo | +17 | +30% |
| 10 | Angola | +16 | +35% |
These nations have seen improvements in healthcare infrastructure, successful disease control initiatives, enhanced access to medical services, and advancements in maternal and child health. Additionally, economic development, improved living standards, investments in sanitation and water access, as well as educational programs and international collaborations, have collectively contributed to the positive trajectory in life expectancy. These efforts reflect a holistic approach to public health, aiming to address a range of determinants that influence overall well-being and longevity.
A decrease in life expectancy from 2022 to 2022 caused by a combination of health, social, economic, and environmental factors is noted for Vatican City (6 years), Afghanistan (-1.7 years), Peru (-1.5 years), Mexico (-1.3 years), French Polynesia (-1 year), Gibraltar (-1 year), and Mayotte (-0.7 year).
Below is an animated world map showing the change in life expectancy by country around the world.
Fascinating Facts About Life Expectancy
We’re living longer—by a lot
Just over a hundred years ago, the average person didn’t make it past 31. That’s hard to imagine now, with the global average life expectancy pushing past 70. Improvements in public health, medicine, and living standards have added decades to the average human life.
The world’s longevity hotspots
Some places just seem built for long life. In areas called Blue Zones—like Okinawa (Japan), Sardinia (Italy), and a small town in California called Loma Linda—people regularly live into their 90s and 100s. The common thread? Simple food, daily movement, strong social ties, and a slower pace of life.
Why women usually live longer
It’s a consistent trend almost everywhere: women tend to outlive men. The reasons are a mix of biology and behavior—estrogen seems to offer some protection against heart disease, and men often take more risks, whether in work, driving, or lifestyle choices.
History hasn’t always been kind
Life expectancy hasn’t risen in a straight line. Wars, pandemics, and food shortages have all caused sharp dips. The 1918 flu pandemic, for example, wiped out millions and caused a temporary collapse in global life expectancy.
Medicine changed the game
Modern healthcare—especially vaccines, antibiotics, and surgery—has played a massive role in helping people live longer. We’ve gone from a time when a simple infection could be fatal to one where many once-deadly diseases are now preventable or treatable.
Wealth helps—but doesn’t explain everything
Richer countries generally have higher life expectancies, but that doesn’t tell the whole story. Within the same country, people in wealthier neighborhoods often live years longer than those in poorer ones, highlighting the impact of inequality.
Education and health go hand in hand
People with more education tend to live longer. It’s not just about income—it’s also about health knowledge, problem-solving skills, and access to better healthcare options. Education influences everything from diet to exercise habits.
Longevity loves company
Loneliness doesn’t just feel bad—it can actually shorten your life. People with strong relationships and community support tend to live longer. A regular chat with friends or a close-knit family can be as important as a healthy diet.
More people are reaching 100
Centenarians—people who live to 100—are no longer a rare sight. Their numbers are growing every year, especially in places with good healthcare and low-stress lifestyles.
Japan’s secret sauce
Japan consistently ranks at the top for life expectancy. Their diet (think fish, rice, vegetables), combined with a culture of walking and strong social bonds, plays a big part. So does their access to universal healthcare.
Weight and health span
A healthy body weight isn’t just about appearance—it’s tied to how long and how well we live. Being very overweight or underweight can raise the risk of chronic illnesses and shorten your life.
It’s not just about years, but quality
These days, people are talking more about healthspan—the number of years you live in good health. After all, what’s the point of living to 90 if the last 20 years are spent feeling unwell? The real goal is to live long and feel good doing it.