Who were the ancient Egyptians?
The ancient Egyptians were a civilization that flourished along the banks of the Nile River in northeastern Africa for thousands of years, with a history spanning from around 3100 BCE to 30 BCE. They left an indelible mark on human history through achievements in architecture, art, science, and governance. The ancient Egyptian society was structured, and its cultural and religious practices played a significant role in shaping daily life.
The question of the genetic and cultural continuity between ancient Egyptians and the modern population of Egypt is complex. While modern Egyptians are the descendants of the ancient Egyptians to some extent, the population of Egypt has been influenced by a multitude of migrations, invasions, and cultural exchanges over the millennia. The Arab conquest in the 7th century and subsequent interactions with various cultures have contributed to the diverse genetic and cultural landscape of modern Egypt.
Genetic studies suggest that modern Egyptians exhibit a blend of ancestral lineages, including indigenous North African components and influences from the Middle East. Historical events and population movements have contributed to the dynamic nature of the Egyptian population, making it challenging to establish a direct and unbroken genetic link between the ancient and modern populations.
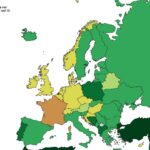
The map below shows genetic distances between DNA 90 ancient Egyptian mummies and DNA of modern populations.
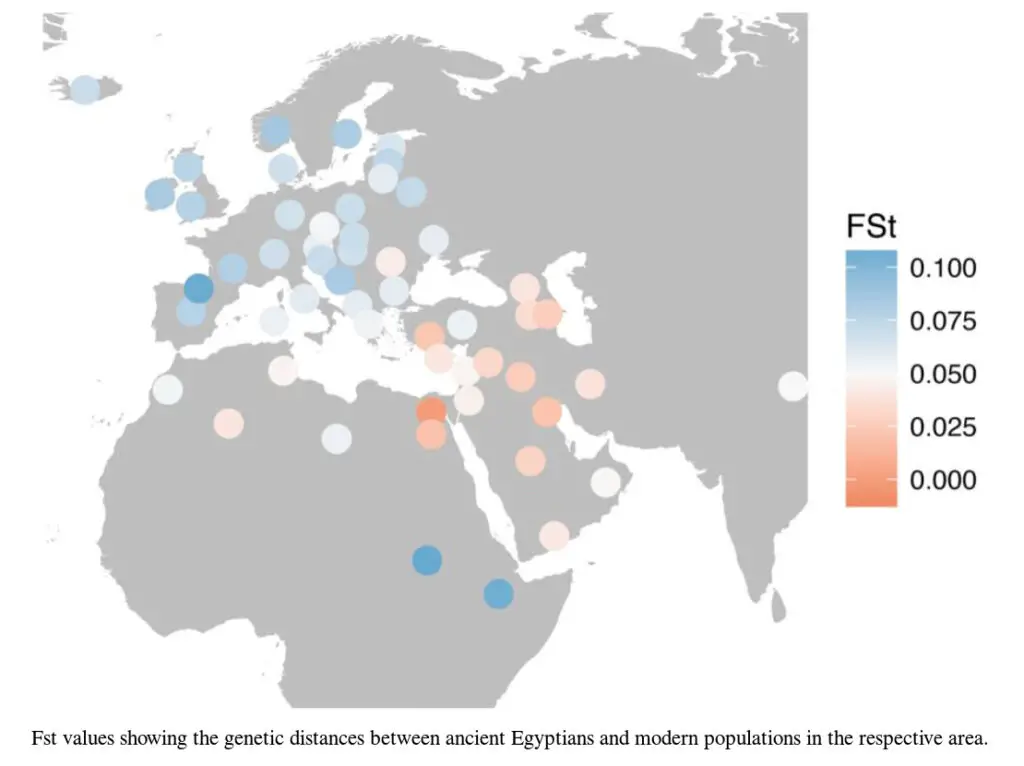
The Sahara acts as a vast and formidable barrier to human migration. As a result, according to the map, people living in Poland are closer to ancient Egyptians than some Sub-Saharan populations.
To learn more about ancient Egypt have a look at the following books: