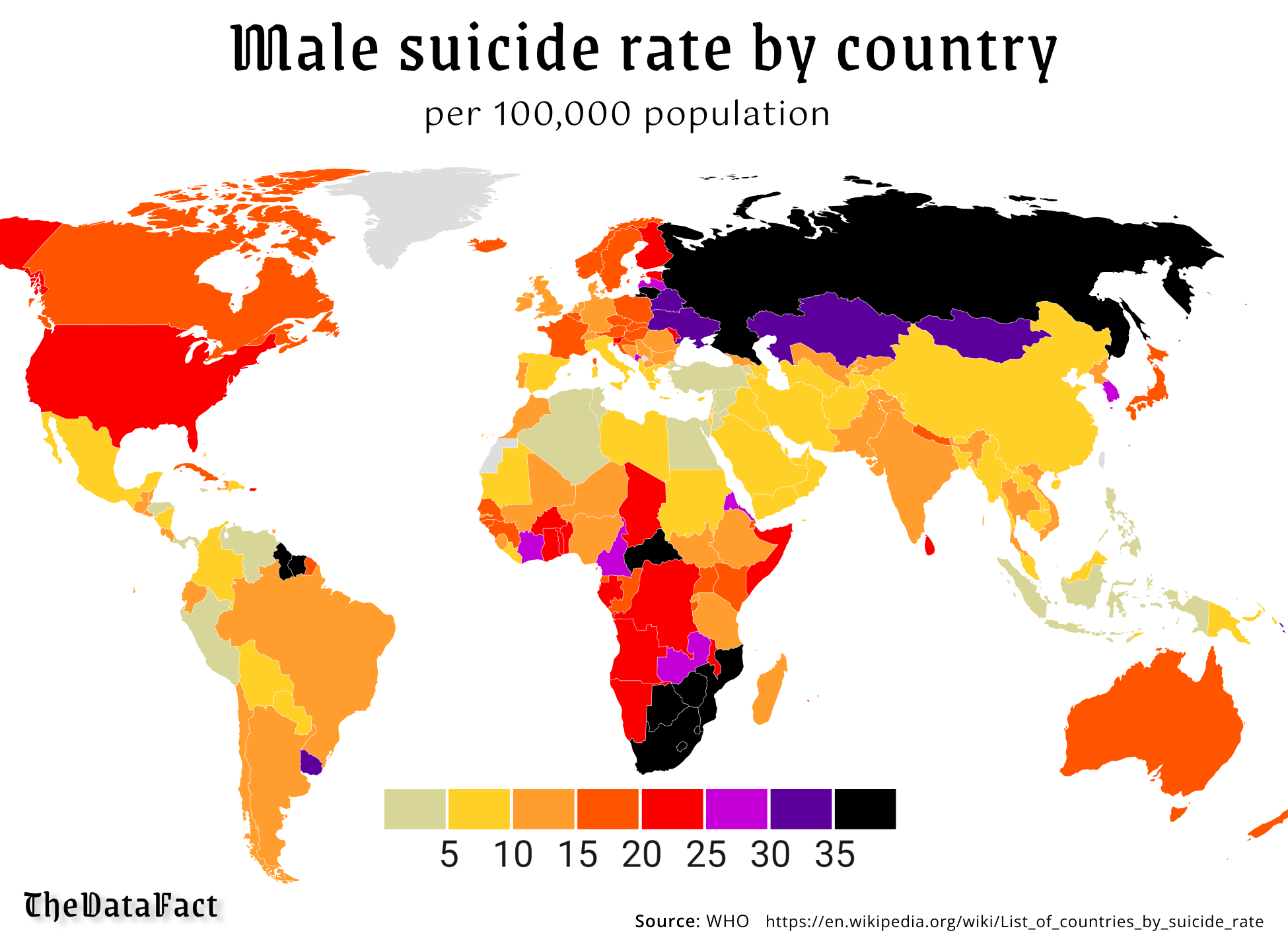
Midlife “Deaths Of Despair” in the United States (2000 vs 2014)
“Deaths of despair” refer to fatalities stemming from stress-related conditions such as suicide, drug overdoses, and alcohol-related diseases. These deaths are interconnected, reflecting the severe impact of mental and emotional distress on individuals’ lives. The term gained prominence as researchers observed rising death rates among certain demographics in the United States, particularly between 1999 and 2013. These increases were largely concentrated among White Americans, who reported higher levels of mental distress in surveys.
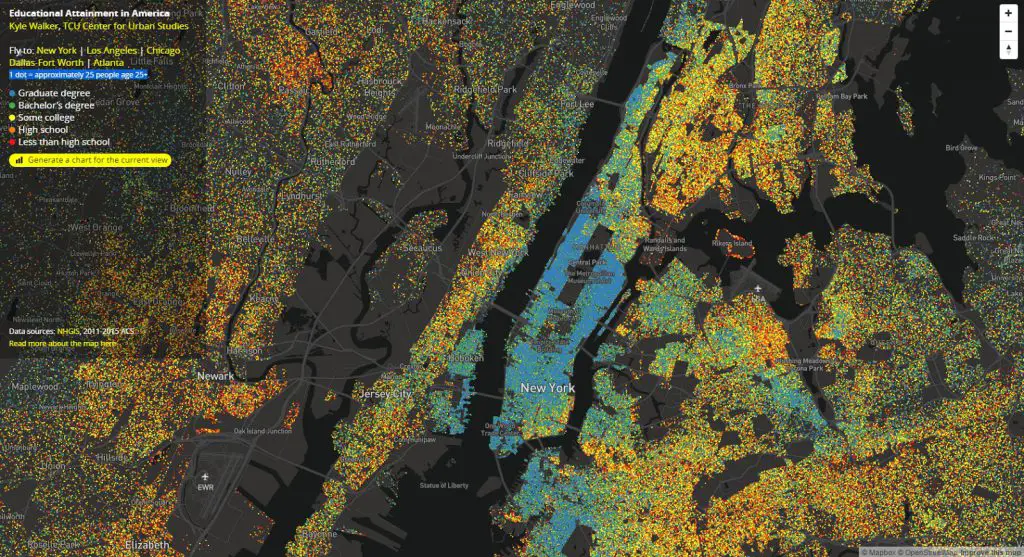
The prevalence of deaths of despair is notably higher among individuals with lower educational attainment. This correlation may be attributed to diminishing economic and labor opportunities, which exacerbate feelings of hopelessness and stress. Research has further delved into underlying factors contributing to this mortality trend, including economic insecurity at the county level.
Table of Contents
Spatial Characteristics of Deaths Of Despair
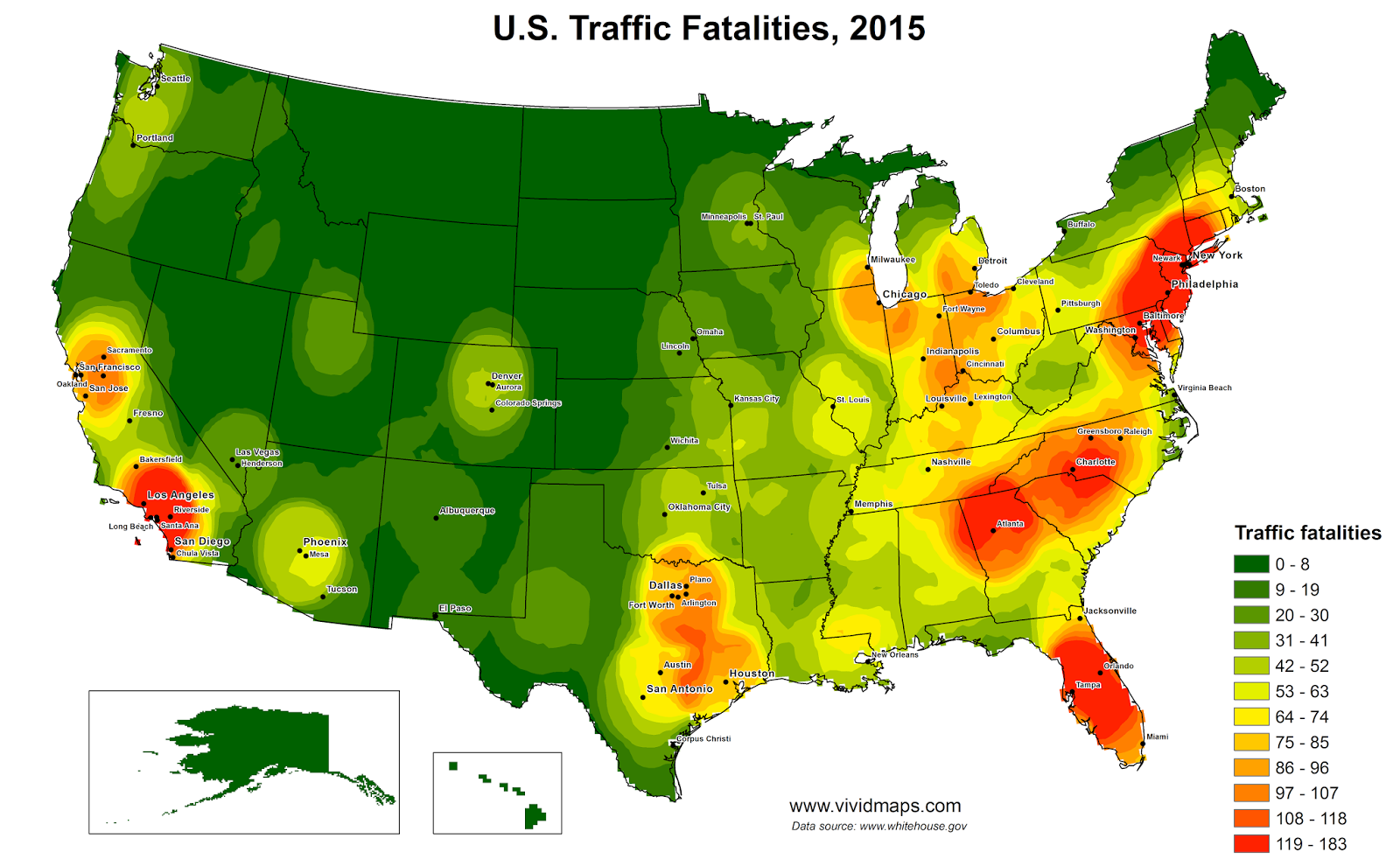
Research by Jong Hyung Lee and colleagues has shed light on the spatial distribution of deaths of despair across the United States. By analyzing social determinants of health at the county level, the researchers identified significant variations in mortality rates. Their study, which compiled population and mortality data from the National Center for Health Statistics, mapped changes from 2004 to 2016 and highlighted counties with higher risks of deaths of despair than the national average.
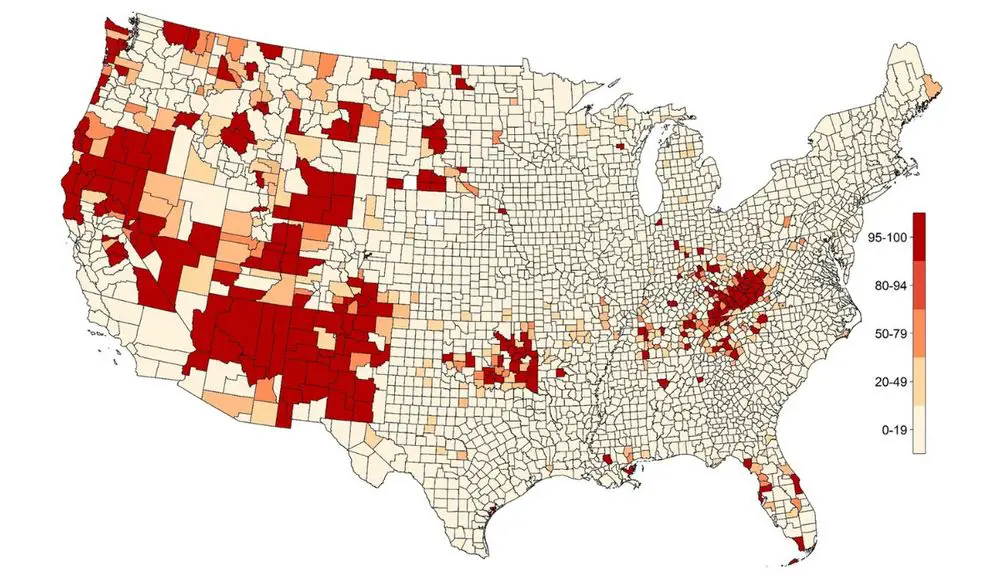
Hotspots of deaths of despair were identified in regions such as Appalachia, California, Florida, the Southwest, Oklahoma, and the Pacific Northwest. These areas demonstrated a higher concentration of stress-related fatalities, particularly in rural counties and those experiencing greater economic distress. Factors such as limited access to health insurance, lower educational attainment, and high unemployment rates were linked to increased mortality risks.
Conversely, counties with larger populations of Hispanic and Black individuals and higher levels of educational attainment exhibited lower risks of deaths of despair. This finding aligns with prior research suggesting that communal and social support, including access to healthcare and education, can mitigate the effects of stress. Additionally, understanding substance use as a coping mechanism for stress is crucial in addressing the issue.
Trends Over Time
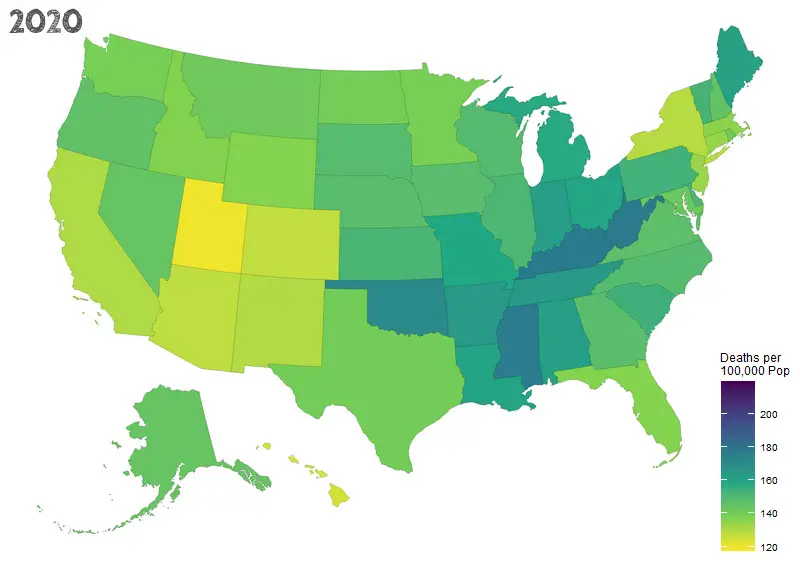
The increase in midlife mortality in the United States from 1999 to 2013 was primarily driven by deaths of despair. This trend has sparked significant concern and prompted further investigation into the root causes and potential solutions. The maps below, created by the NPR team using Brookings data, show midlife ‘Deaths of Despire’ in counties in 2000 vs. 2014.
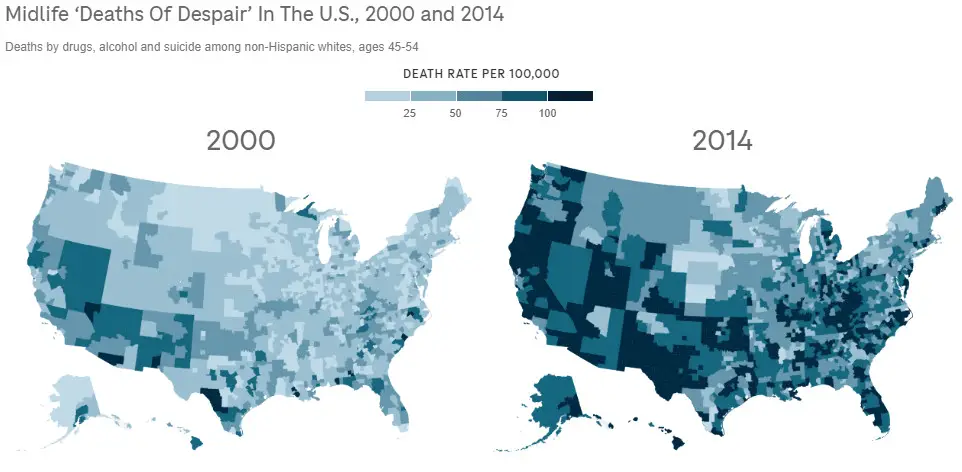
In recent years, the situation has continued to evolve. While there have been efforts to address the underlying causes, deaths of despair remain a critical public health issue. According to recent data, the opioid epidemic has significantly contributed to the continued rise in drug overdose deaths, particularly in rural and economically distressed areas. Suicide rates have also remained alarmingly high, reflecting ongoing mental health challenges faced by many Americans.
Tips to Avoid Deaths Of Despair
- Seek Professional Help: Mental health professionals can provide support and treatment for stress, anxiety, depression, and substance abuse.
- Build a Support Network: Surround yourself with family, friends, and community members who can offer emotional and practical support.
- Engage in Healthy Activities: Regular exercise, hobbies, and activities that bring joy can help reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Understanding the signs of mental distress and substance abuse can help in early intervention and support.
- Advocate for Community Resources: Support initiatives that improve access to healthcare, education, and employment opportunities in your community.
If you’re interested in mental health issues, these books will capture your attention.