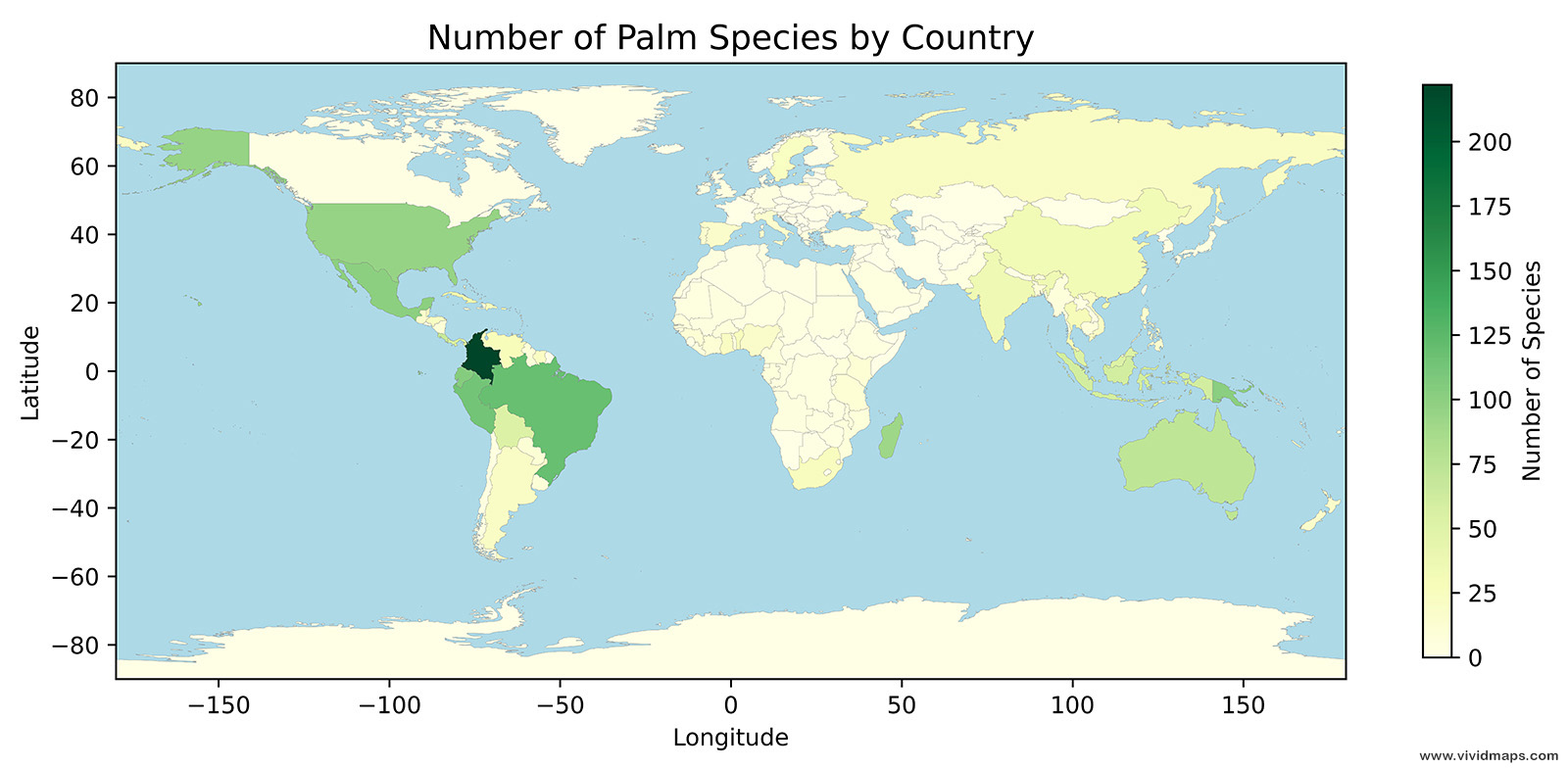
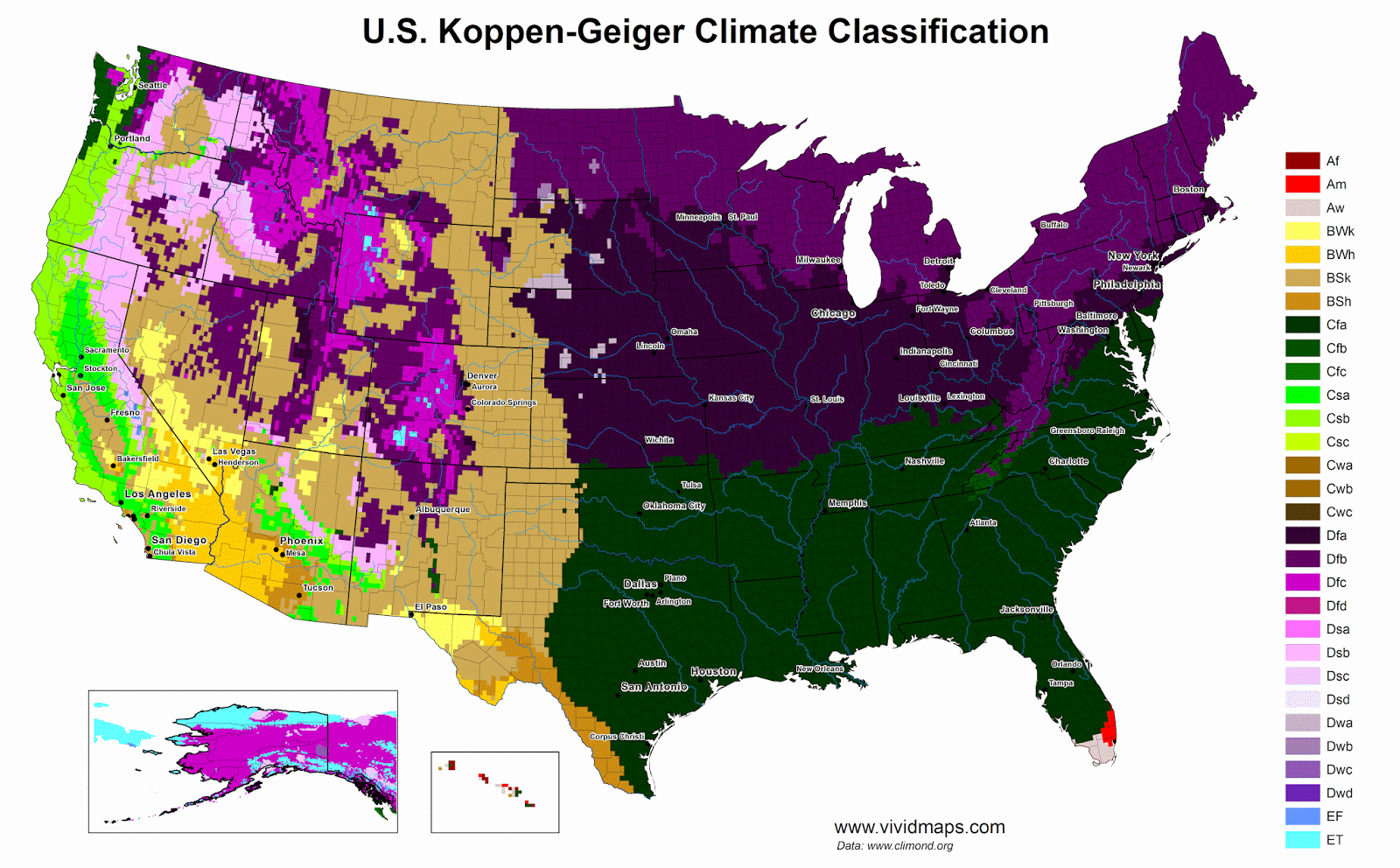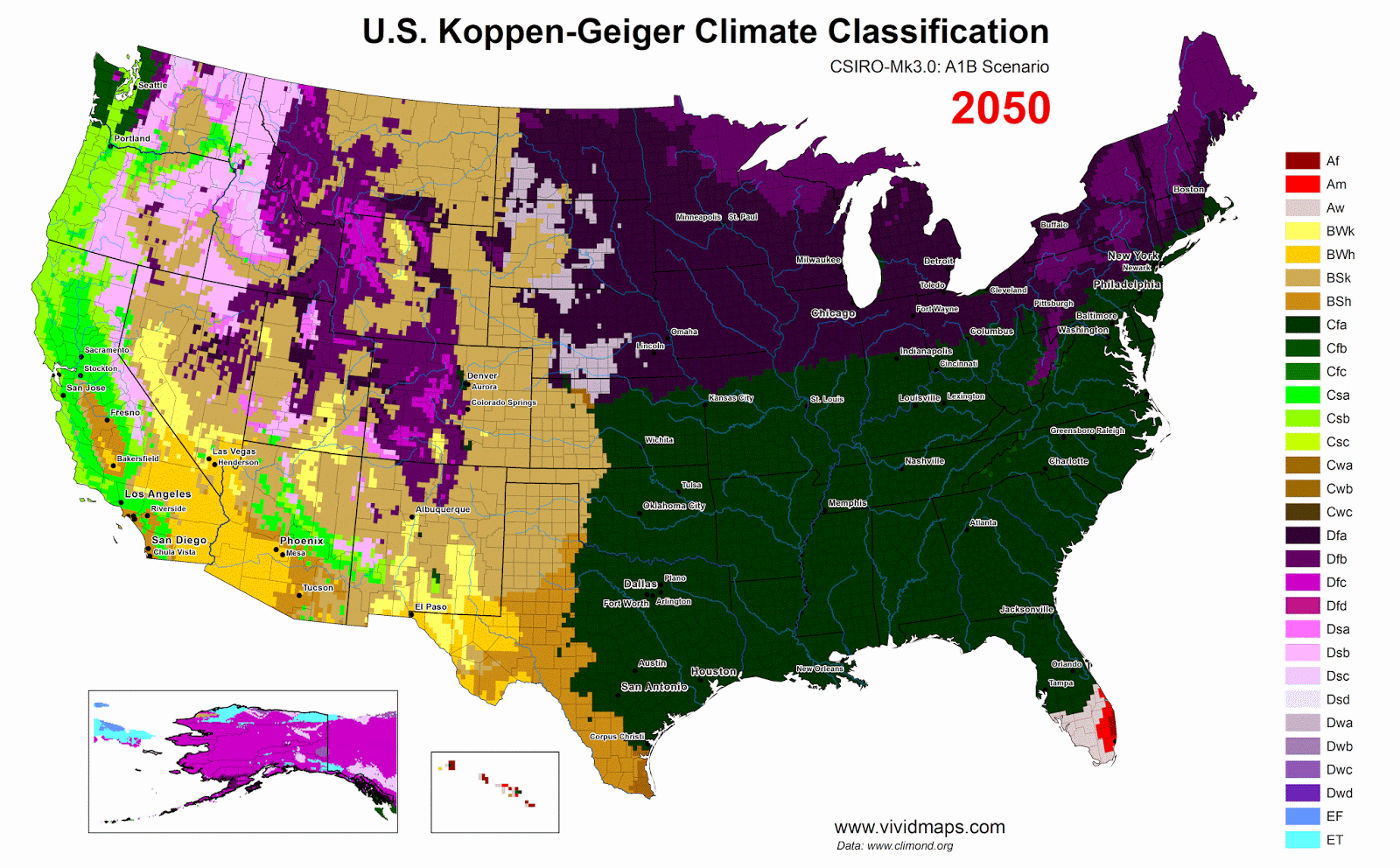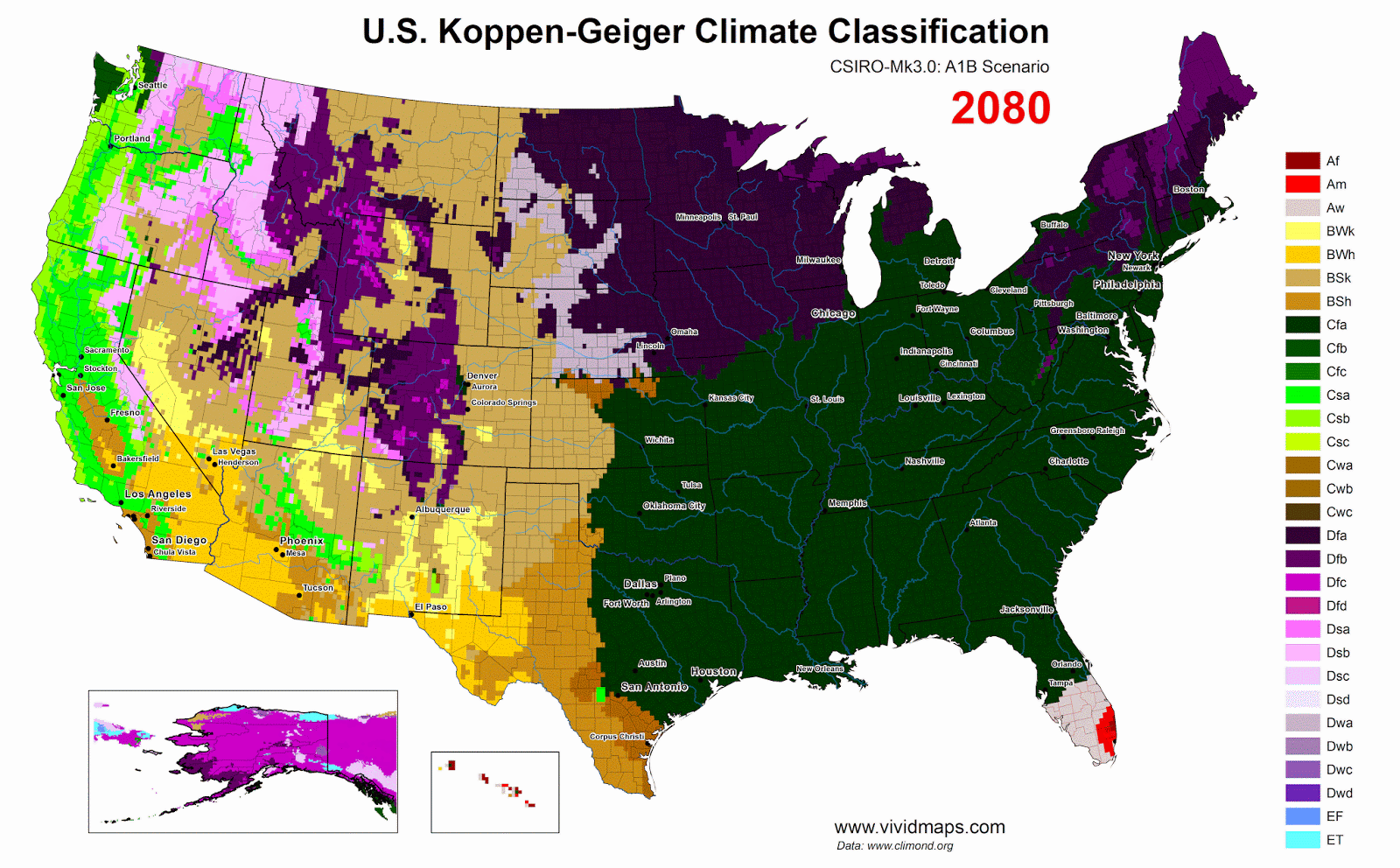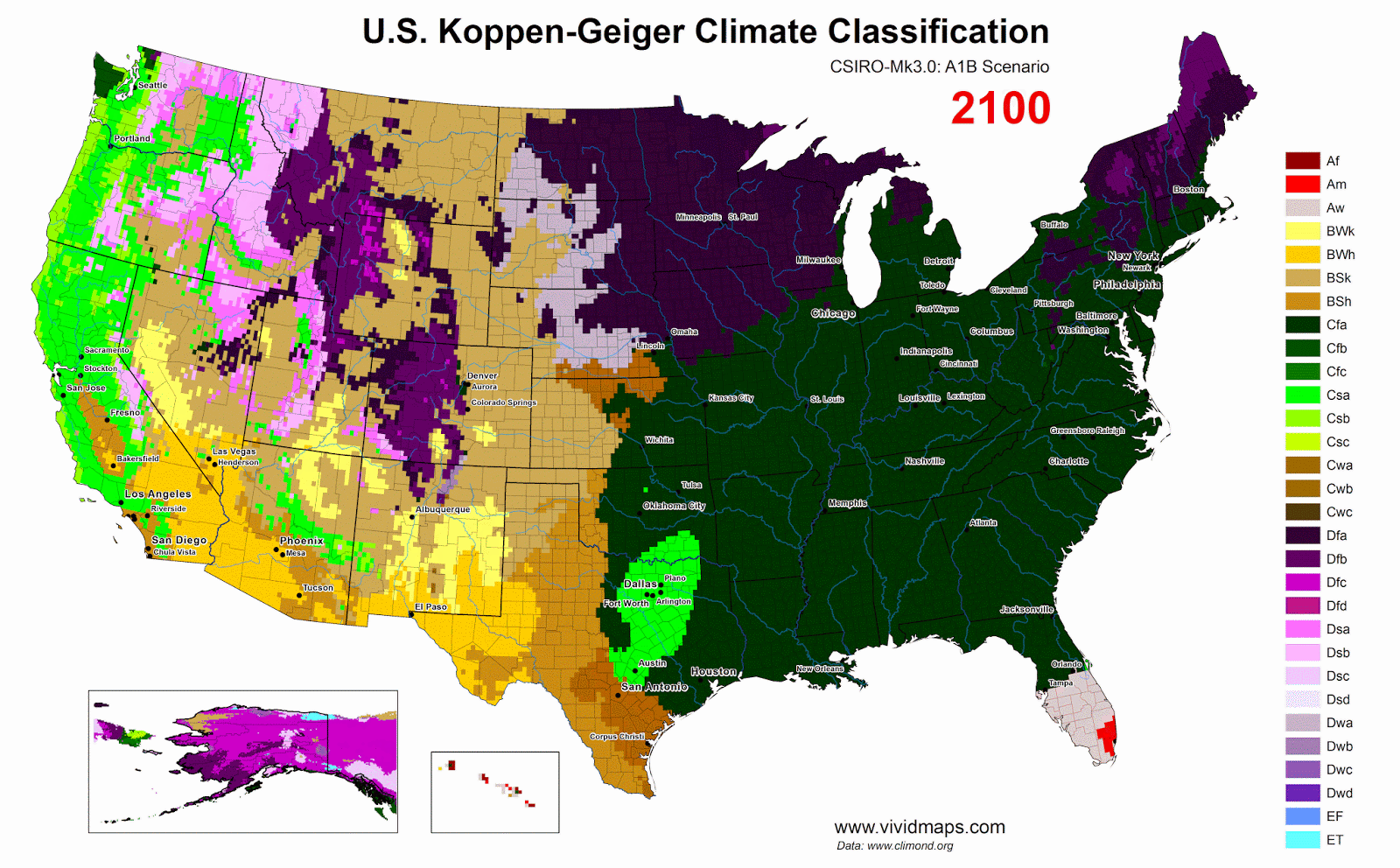
Zone of potential subtropical broadleaf evergreen forest in the United States
Despite a warm-temperate climate similar to that of southern Japan, the coastal plain of the southeastern USA is usually described as a region of mostly deciduous “Southern mixed hardwoods” forests. Evergreen broad-leaved canopy trees and some evergreen forest patches do remain, however, suggesting that evergreen broad-leaved forest may be the potential natural vegetation. Forests on sand and uplands would be dominated by evergreen Quercus species, while more mesomorphic “laurel forests” comparable to those of East Asia are generally restricted to more moist sites in depressions and floodplains. The evergreen Quercus region extends from the Atlantic coast as far west as central Texas, where low evergreen Quercus- Juniperus woodlands occur on dry limestone hills. Most American evergreen genera occur also in Japan. Interpretation of vegetation dynamics and potential natural vegetation is made more complicated in the southeastern USA, however, by the important role of recurring forest disturbance (fire, plus summer and winter storms). These American evergreen broad-leaved forests are being studied ecologically and phytosociologically for analysis of vegetation dynamics and comparison with similar forests in East Asia.
Via researchgate.net
Related post:
– Find cities with a similar climate