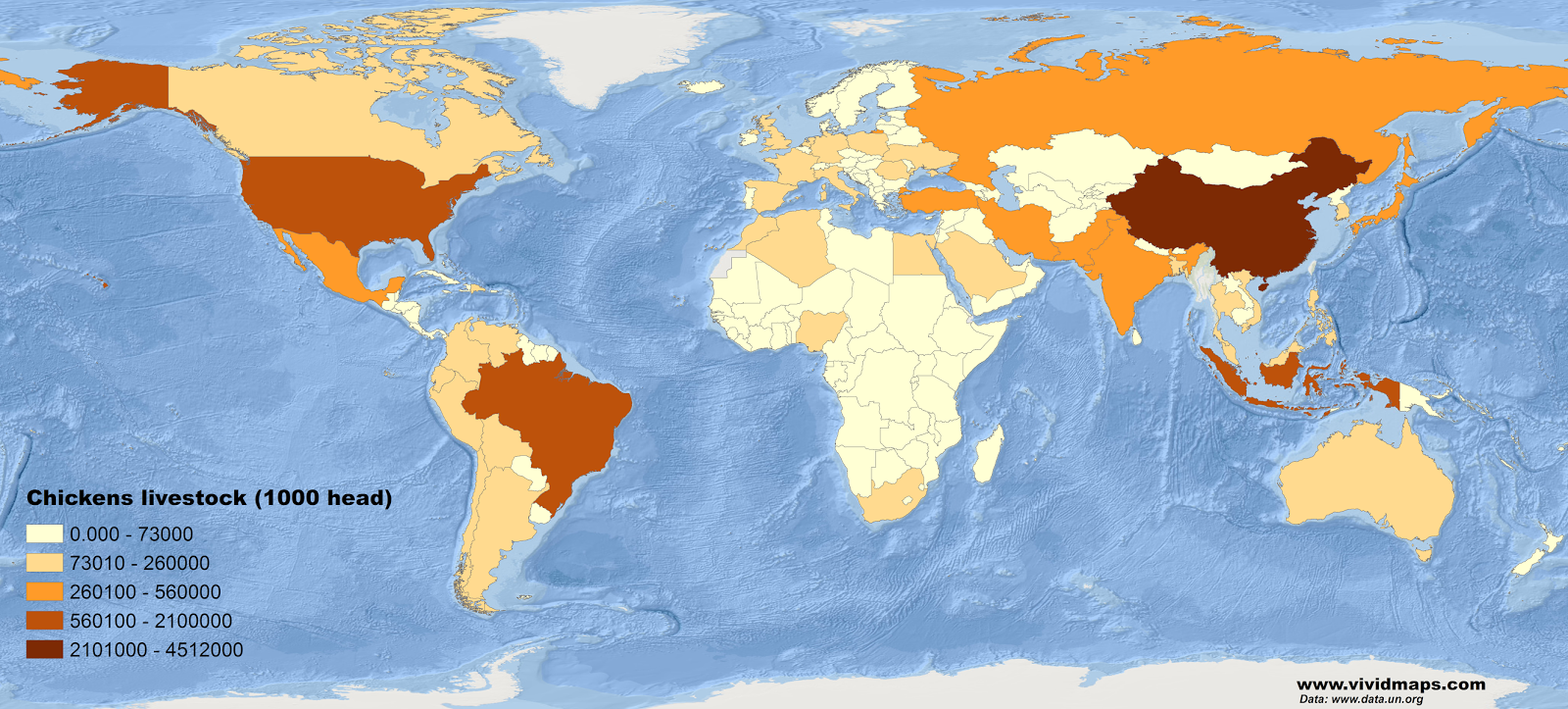
Blonde Hair Map
Blond or fair hair is a hair color characterized by low levels of the dark pigment eumelanin. The resultant visible hue depends on many factors but always has some yellowish color. The color can be from the very pale blond (induced by a patchy, infrequent distribution of pigment) to reddish “strawberry” blond colors or golden-brownish (“sandy”) blond colors (the latter with more eumelanin). On the Fischer-Saller scale, blond color ranges from A to J (blond brown).

Natural lighter hair colors occur most often in Europe and less frequently in other areas. In Northern European populations, the occurrence of blond hair is widespread.
The hair gene MCIR has at least seven varieties in Europe, giving the continent a broad range of hair and eye colors. Based on a recent genetic analysis carried out at three Japanese universities, the age of the genetic modification that emerged in blond hair in Europe has been separate to about eleven thousand years ago during the last ice age.
A typical explanation found in the scientific research for the evolution of light hair is linked to the demand for vitamin D synthesis and northern Europe’s seasonal lack of sunlight.
Lighter skin is due to a low concentration in pigmentation, thus enabling more sunlight to trigger the generation of vitamin D.
In this way, high rates of light hair in northern latitudes are the result of the light hair in northern latitudes are a consequence of the light skin change to lower levels of sunlight, which decreases the prevalence of rickets induced by vitamin D deficiency.
The darker pigmentation at higher latitudes in some ethnic groups such as the Inuit is explained by a more significant proportion of seafood in their diet. As seafood is high in vitamin D, vitamin D deficiency would not create a selective pressure for lighter pigmentation in that population.
Related posts:
– Average Body Hair Distributions
– Human skin and hair world map (1892)