Canada’s Shifting Climate Zones: Köppen-Geiger Maps from 1930 to 2099
Canada stretches from the polar ice caps of the High Arctic down to the humid summers of the Great Lakes. Between those extremes, you’ll find tundra across the northern mainland, boreal forest covering the middle latitudes, oceanic climates along the Pacific coast, and even some semi-arid pockets in interior valleys where mountains block the rain.
I used the high-resolution Köppen-Geiger dataset from Beck et al. (2023), which covers 1901 through 2099 at 1-kilometer resolution, to visualize Canada’s climate zones. (My previous post on global climate zones includes the full table explaining what each climate code means, if you want the details.)
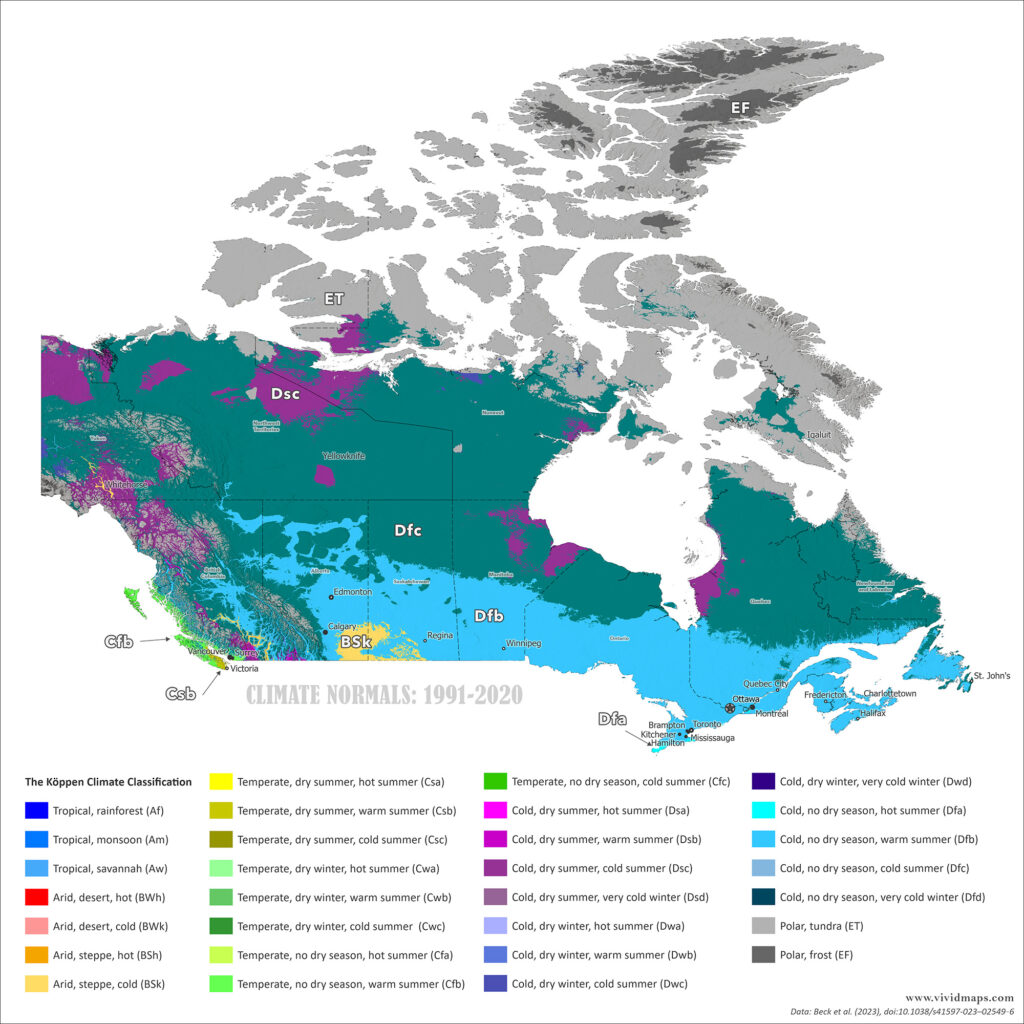
On the map above, the high Arctic islands appear in gray: ice caps (EF) and tundra (ET). Below that sits an enormous belt of subarctic (Dfc) and hemiboreal (Dfb) climates covering most of Canada’s forested area from Yukon to Labrador.
The southern part of the country shows more variety. The Great Lakes region and southern Quebec range from Dfb to Dfa in the warmest areas. British Columbia’s coast stays mild year-round thanks to the influence of the Pacific (Cfb). Interior valleys in Alberta hold some of Canada’s only semi-arid pockets (BSk), found in rain shadows.
Changes Since 1930
Over the past century, Canada’s climate zones have moved north.
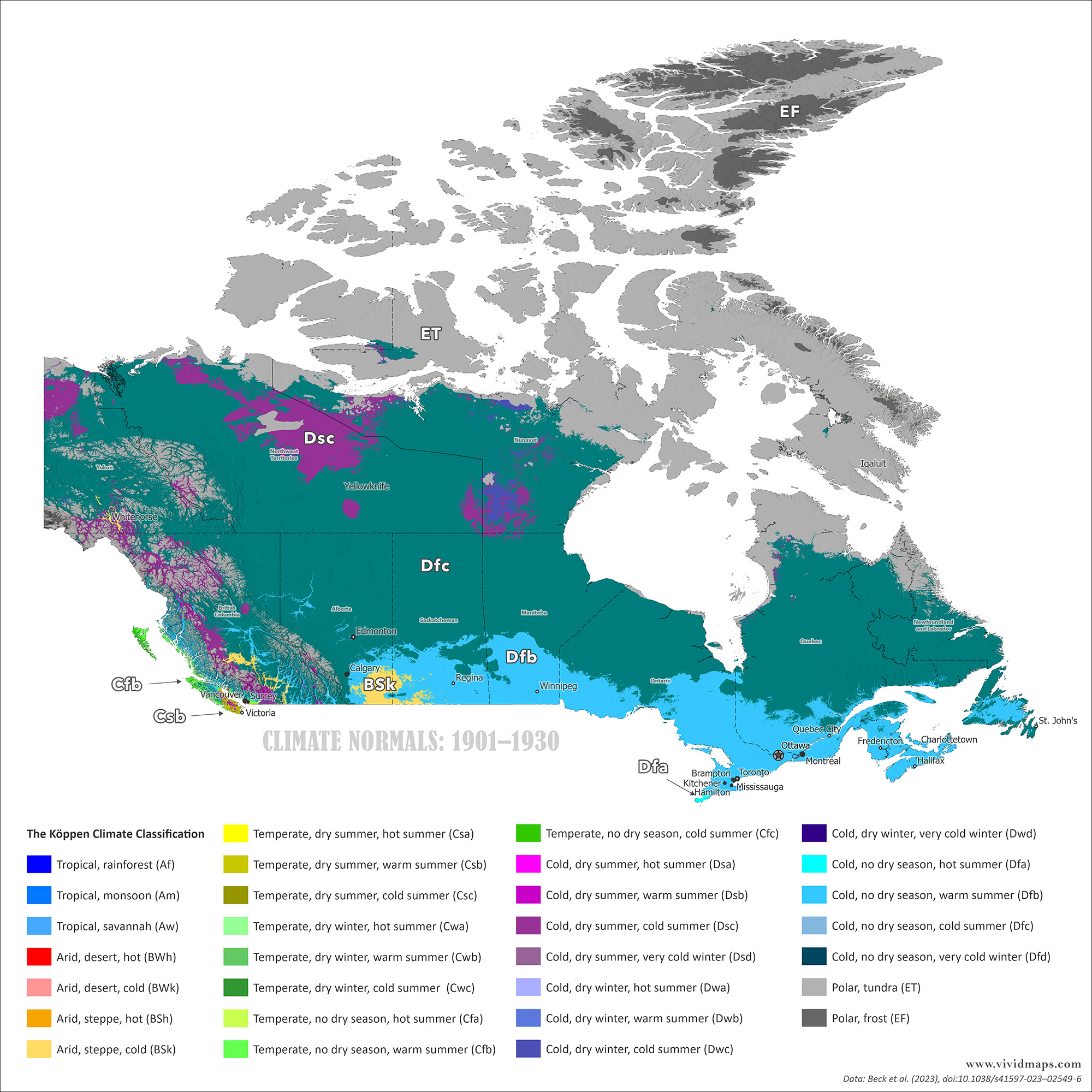
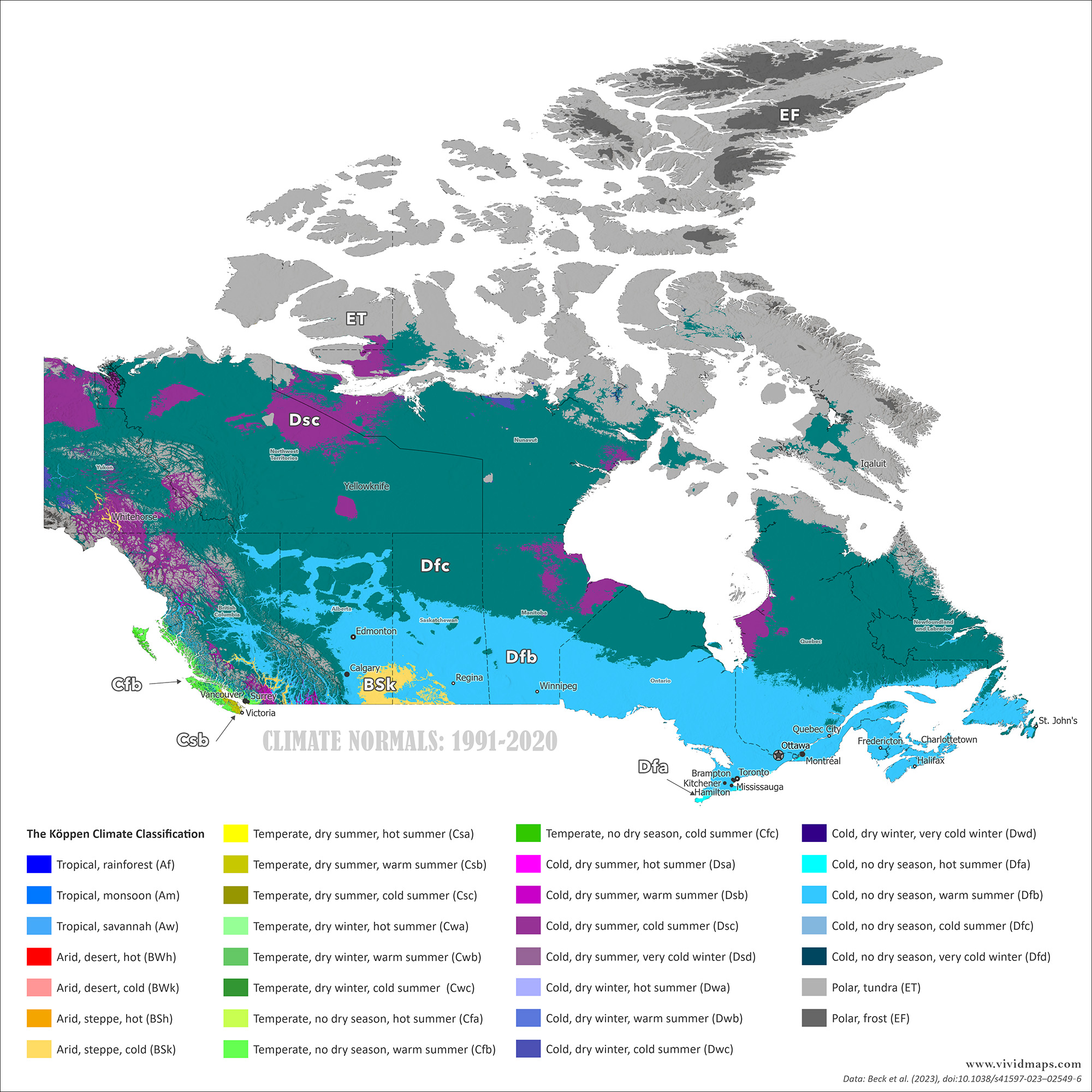
Early 20th century climate (1901–1930) versus modern climate (1991–2020).
Tundra has pulled back from the mainland. Areas that were treeless a century ago now support scattered spruce. The tree line has crept northward in many places, though not uniformly. Subarctic zones have shifted too. Parts of northern Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Ontario that were firmly subarctic a hundred years ago now edge into warmer classifications.
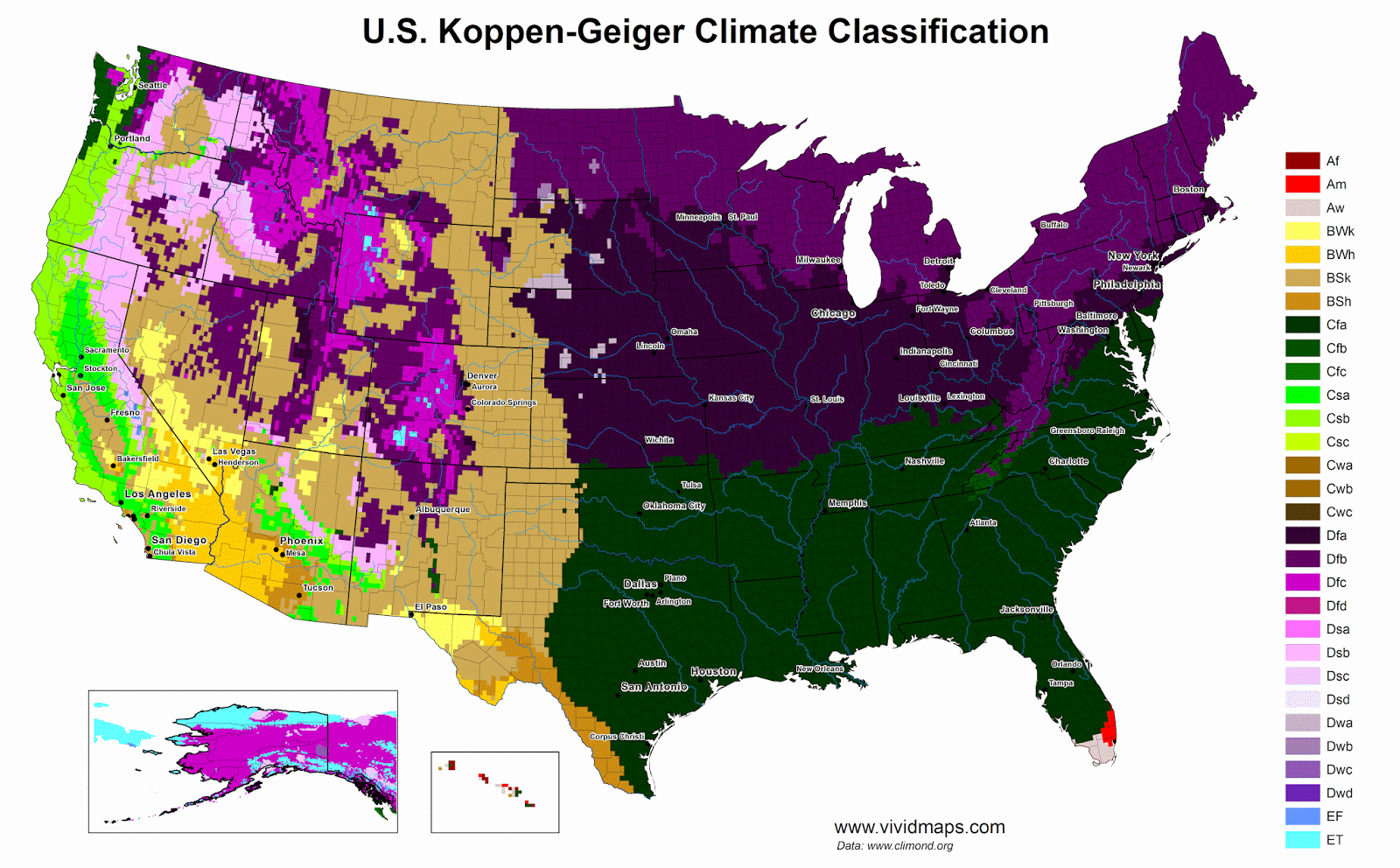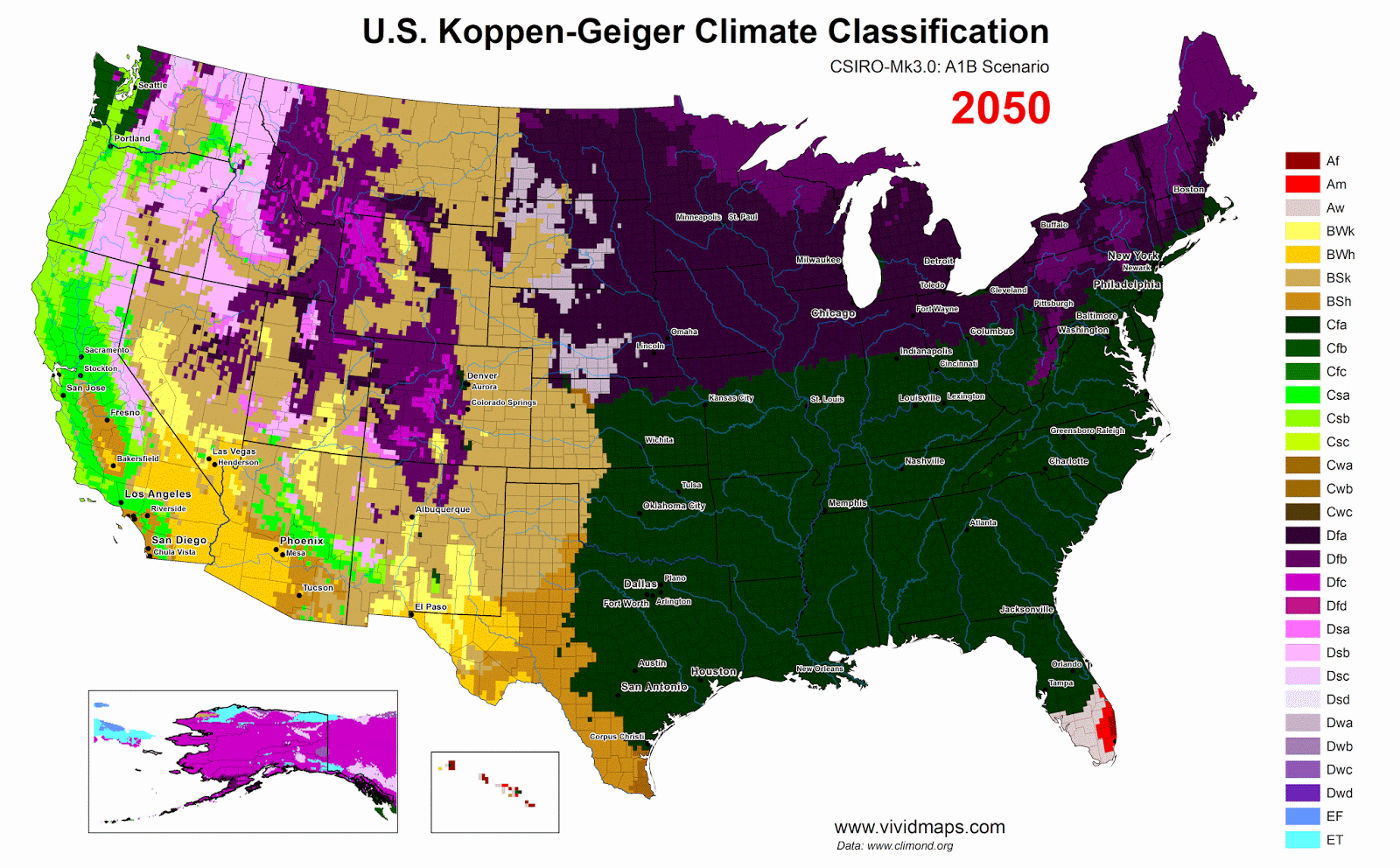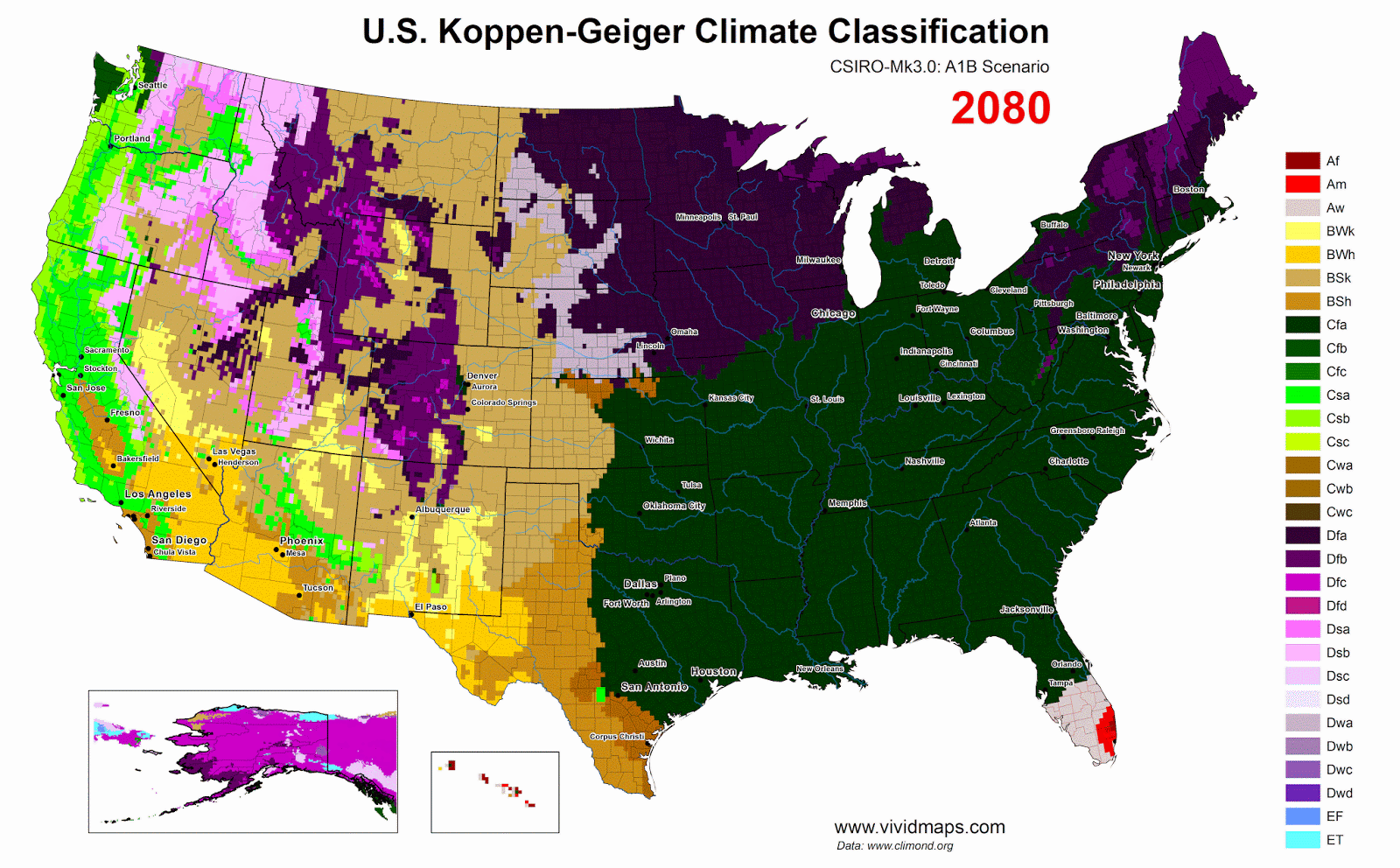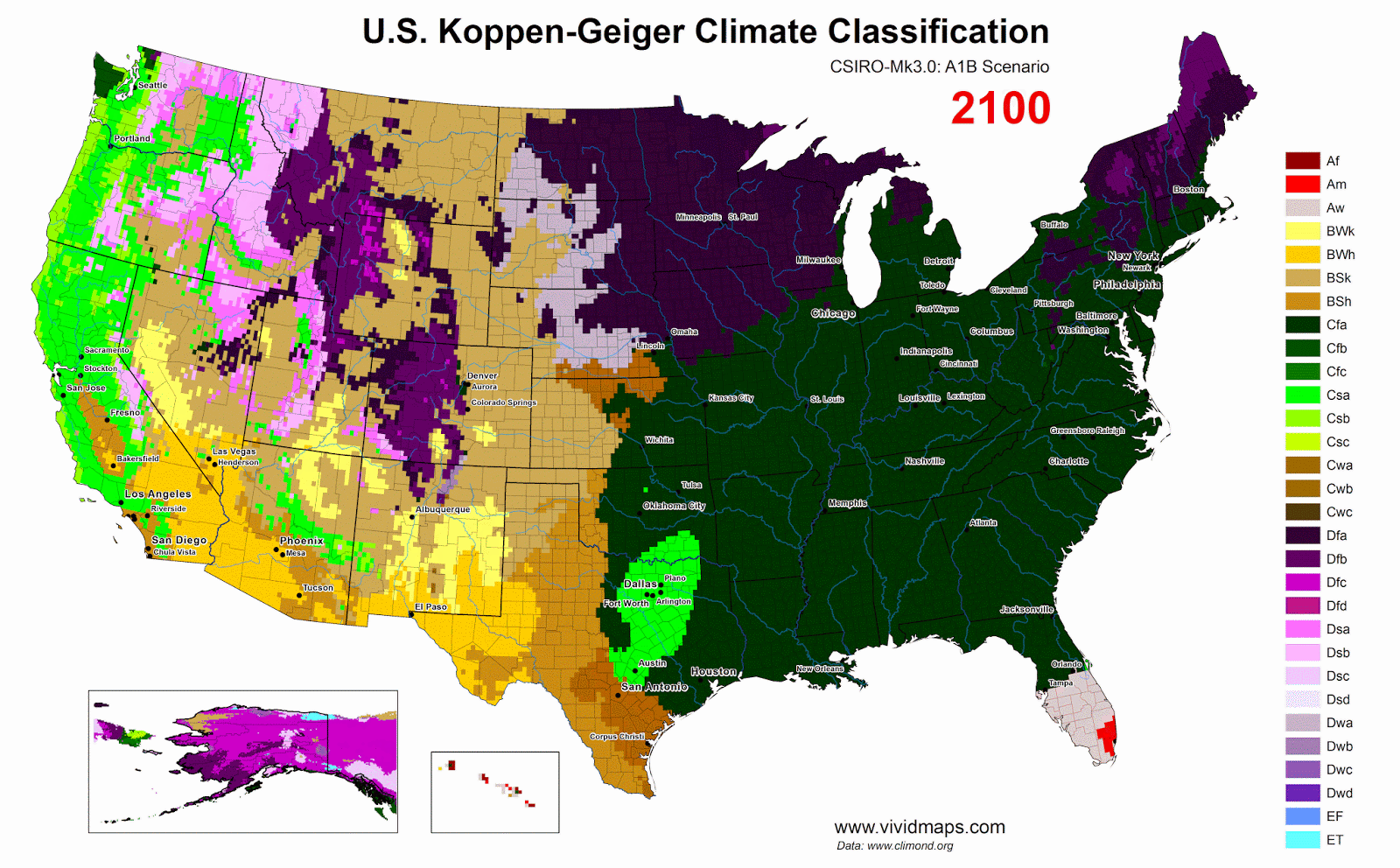
Projections to Century’s End
For future projections, I used the SSP2-4.5 scenario (the most likely scenario), in which emissions rise until mid-century and then level off.

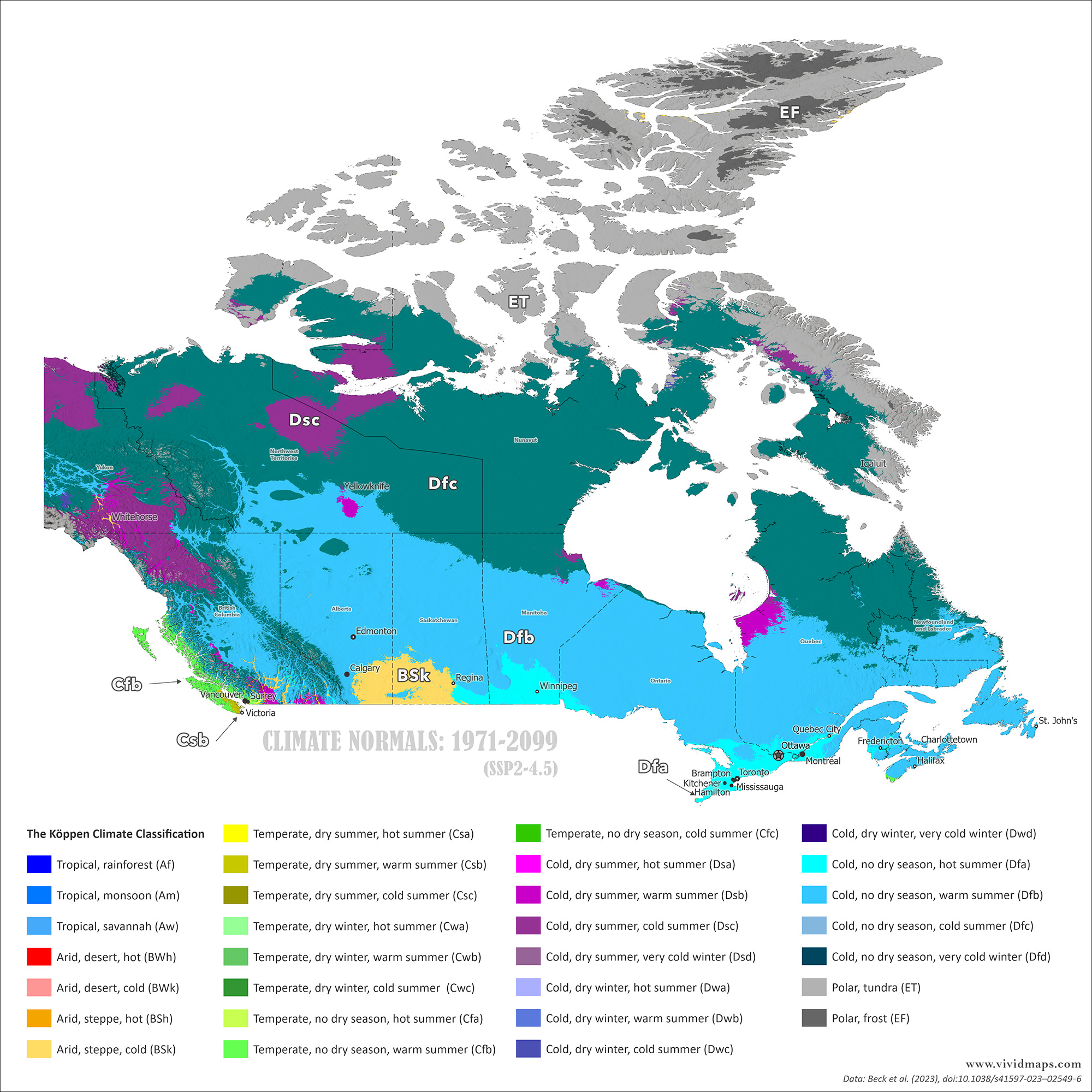
Current climate versus late-century projections (after 2077, ssp2-4.5).
By the late 21st century, changes become dramatic. The subarctic zone moves hundreds of kilometers north. reaches the High Arctic islands.
The tree line advances north. Permafrost thaws across huge areas. Hudson Bay’s ice-free season lengthens. Southern Canada warms considerably. The Great Lakes and St. Lawrence regions would see longer summers and less severe winters.


From 1930 to the end of the 21st century.
From 1930 to 2099, zones travel substantial distances. What’s tundra in 1930 becomes subarctic forest by 2099. What’s subarctic in 1930 becomes continental (hemiboreal) by 2099.
I also created maps for 1931–1960 and 2041–2070. The full animation shows the progression:
Data and Methods: All maps use the 1 km Köppen-Geiger dataset from Beck, H.E., et al. (2023), “High-resolution (1 km) Köppen-Geiger maps for 1901–2099 based on constrained CMIP6 projections.





great tool and visuals. Koppen is much more informative than Hardiness Zones but very unmemnomic; hard to recall the name or the class. What’s Dfa you say?
Great question – Köppen looks super cryptic until you know what each letter is doing.
Very roughly, the system uses 1–3 letters:
First letter = main climate group
A – tropical
B – dry
C – temperate
D – continental (cold winter)
E – polar
Second letter = precipitation pattern
f – no dry season
s – dry summer
w – dry winter
Third letter = temperature detail
a – hot summer
b – warm summer
c – cool short summer
d – very cold winter
So your example, Dfa, breaks down like this:
D – continental climate (big difference between warm and cold seasons)
f – precipitation in all seasons, no pronounced dry season
a – hot summer
One mnemonic trick 🙂
Think “D = Deep winters”,
“f = full‑year moisture (no dry season)”,
“a = awesome heat in summer”.