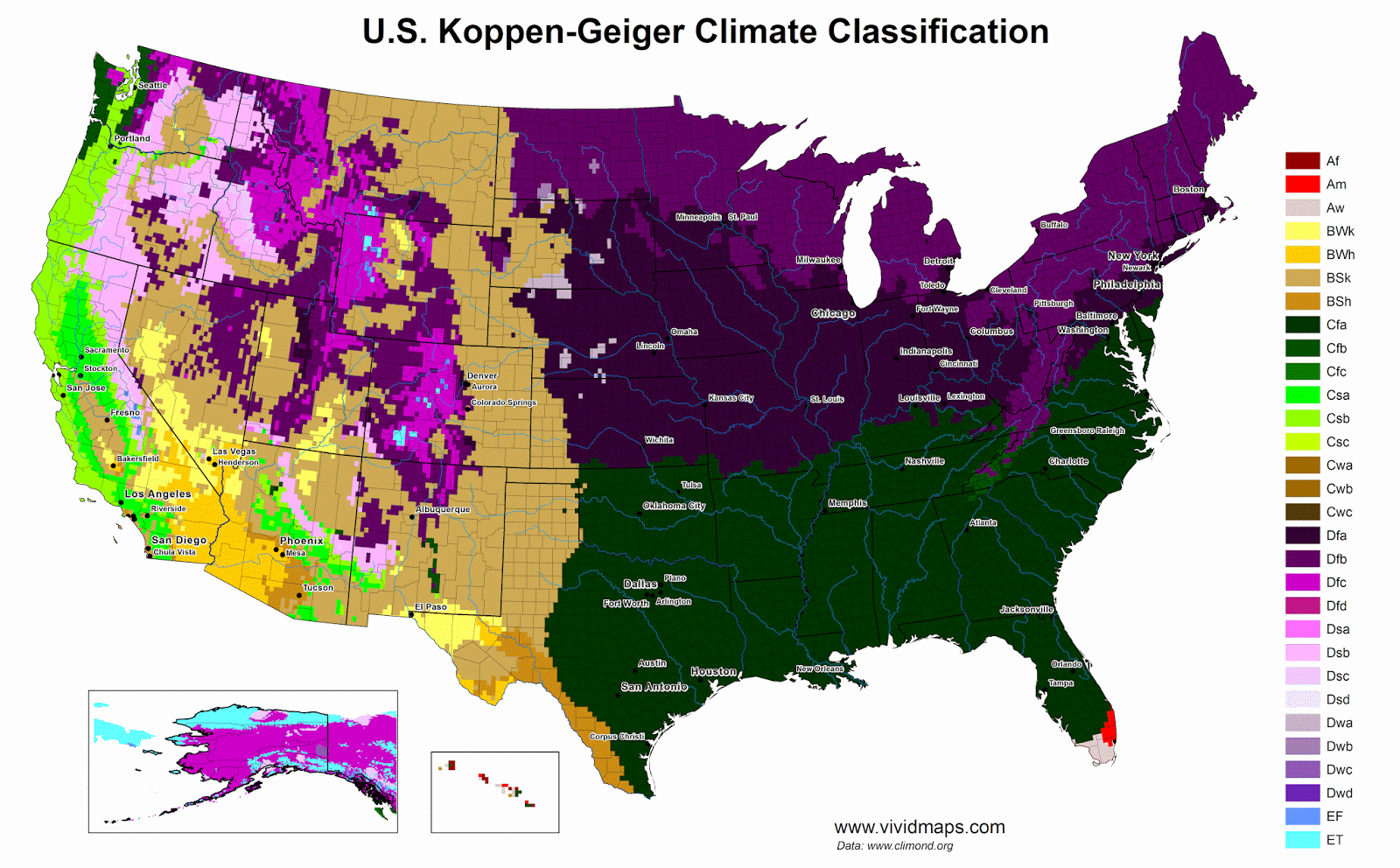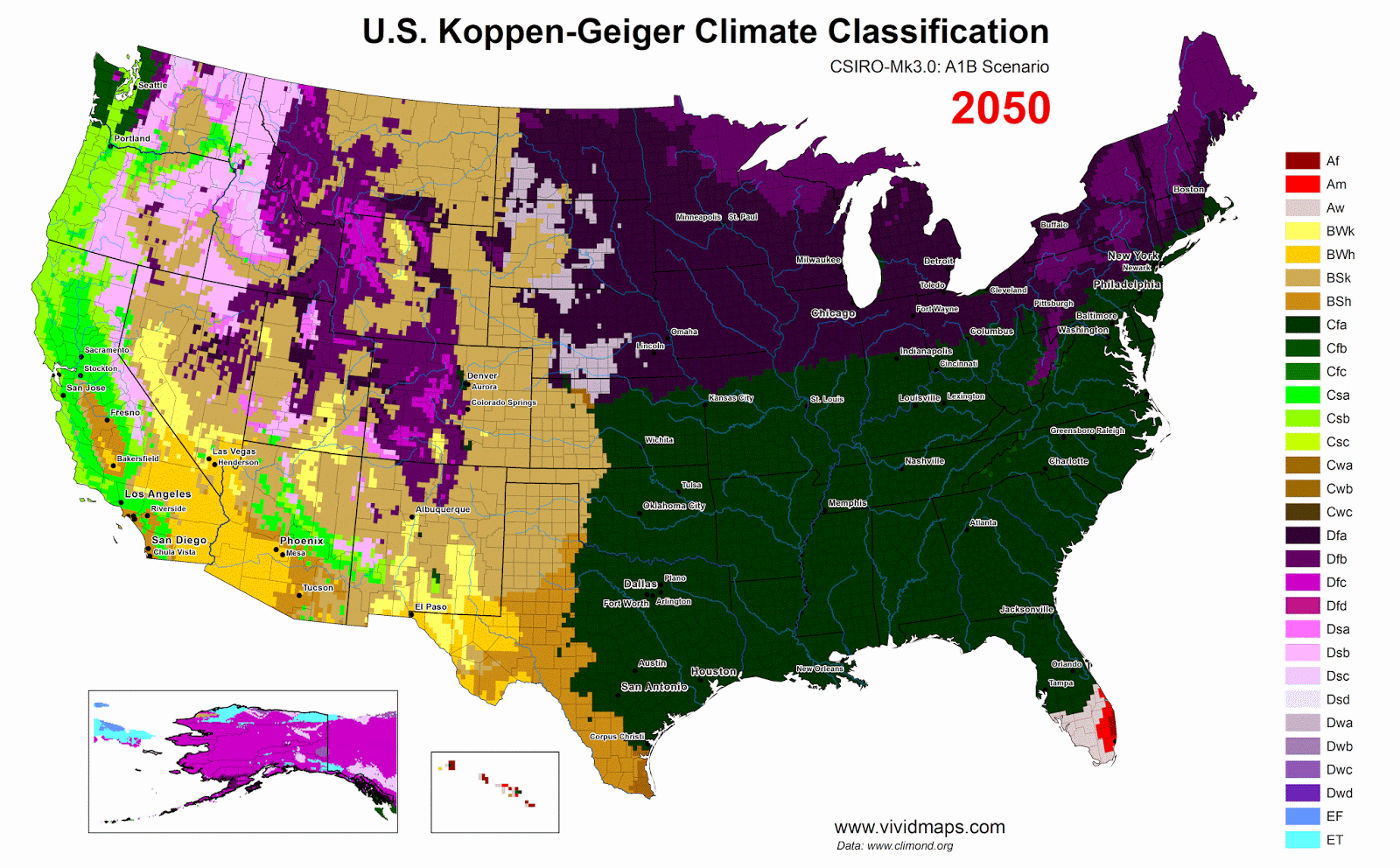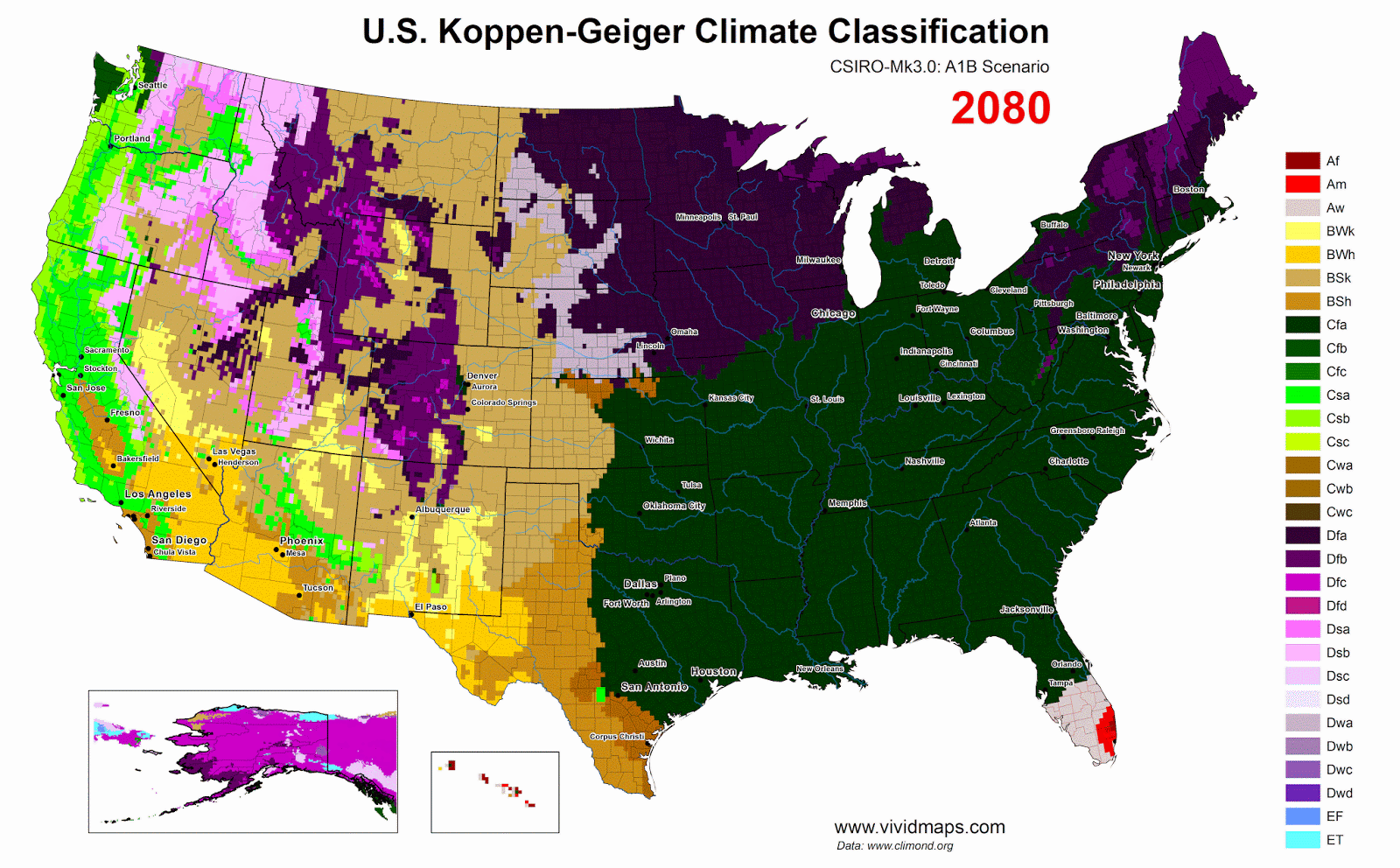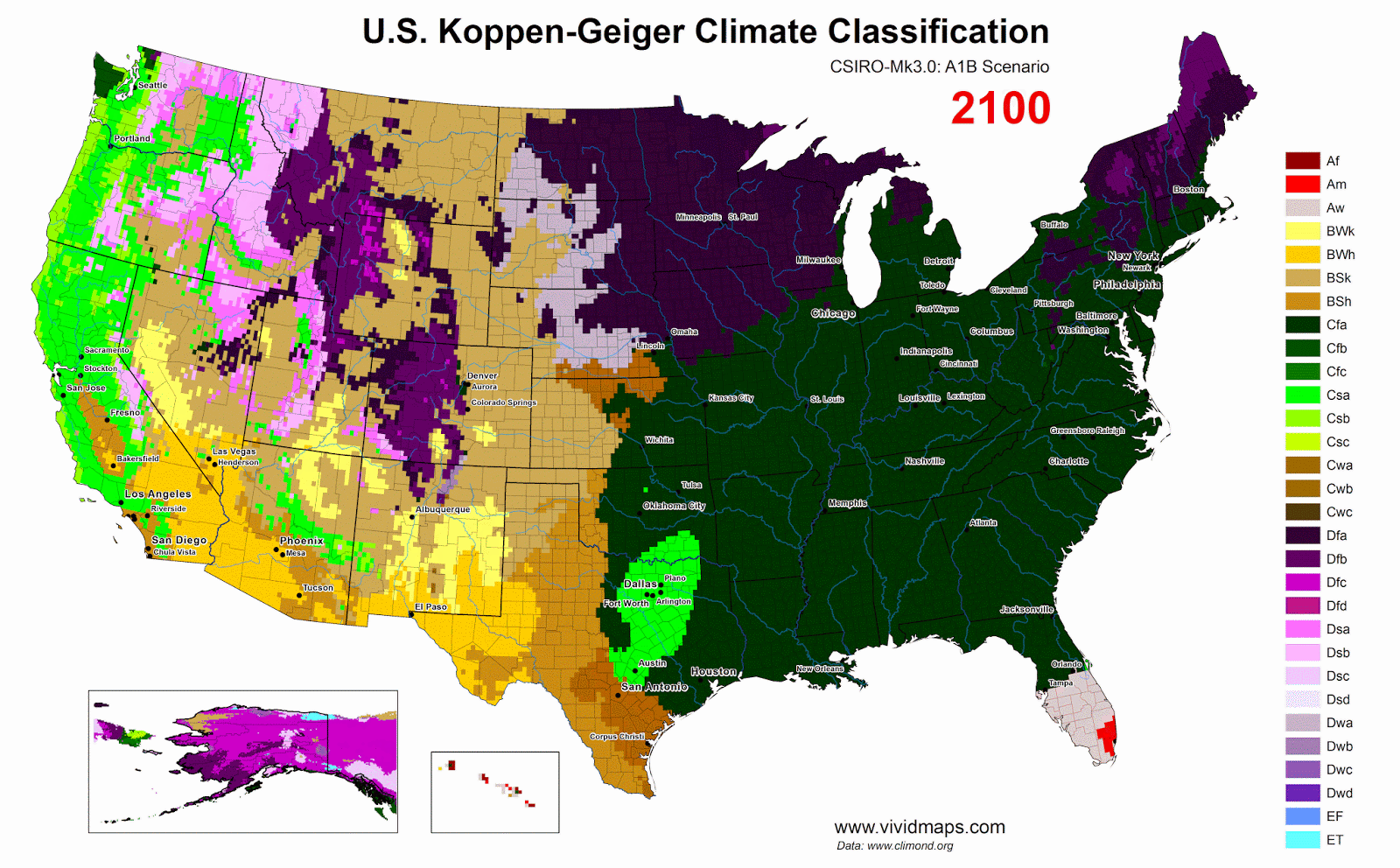
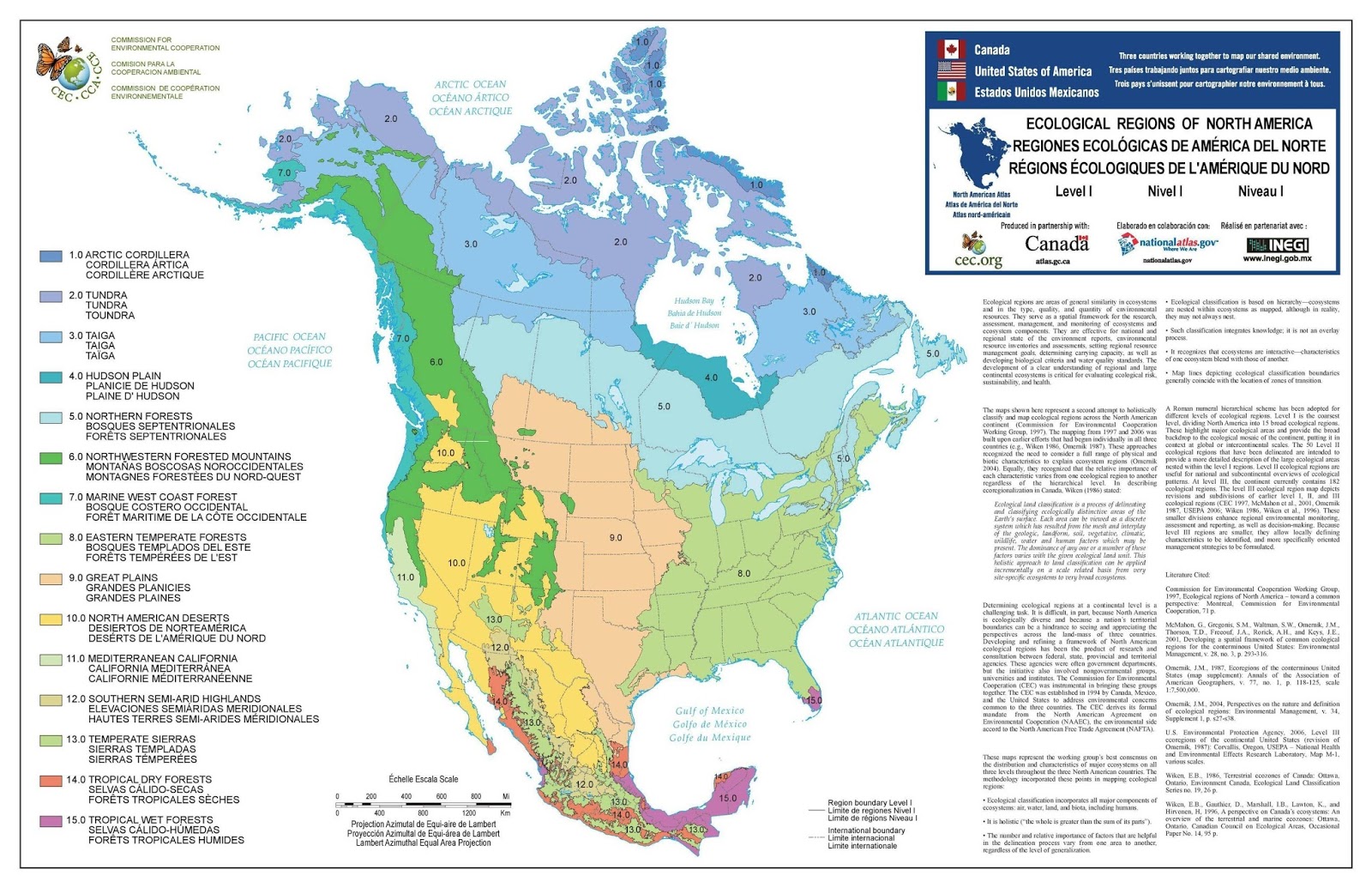
Ecological regions of North America
North America is a continent of incredible ecological diversity, spanning from the frigid Arctic to the tropical rainforests. The map of North America created by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation highlights its unique ecological regions, each characterized by distinct climates, flora, and fauna. Let’s explore these regions and understand their significance, extent, and the impact of climate change.
Table of Contents
- Arctic Cordillera
- Tundra
- Taiga
- Hudson Plains
- Northern Forests
- Northwestern Forested Mountains
- Marine West Coast Forest
- Eastern Temperate Forests
- Great Plains
- North American Deserts
- Mediterranean California
- Temperate Sierras
- Tropical Dry Forests
- Tropical Wet Forests
- Climate Change Impacts
- Explore More Maps of North America

Arctic Cordillera
The Arctic Cordillera is a narrow strip of mountainous terrain along the northeastern edge of Canada, encompassing areas like Baffin Island and Ellesmere Island. This region is known for its rugged mountains, ice caps, and glaciers, covering approximately 242,400 square kilometers.
Tundra
The Tundra extends across northern Canada, Alaska, and Greenland, characterized by its permafrost and lack of trees. This vast, treeless plain spans around 3.5 million square kilometers.
Taiga
Also known as the boreal forest, the Taiga stretches across Canada and Alaska, covering about 17 million square kilometers. It is dominated by coniferous forests.
Hudson Plains
The Hudson Plains, or Plaine D’Hudson, is a low-lying region around Hudson Bay, covering approximately 374,000 square kilometers. This region’s wetlands are crucial for migratory birds.
Northern Forests
Stretching from eastern Canada to the northeastern United States, the Northern Forests cover about 1.2 million square kilometers. These mixed forests are home to a variety of wildlife.
Northwestern Forested Mountains
This region includes the mountainous areas of western Canada and the western United States, covering around 1.6 million square kilometers. Known for its diverse coniferous forests.
Marine West Coast Forest
Found along the Pacific coast from northern California to southern Alaska, this region covers about 264,000 square kilometers. These temperate rainforests receive abundant rainfall.
Eastern Temperate Forests
The Eastern Temperate Forests span from the Gulf of Mexico to southern Canada, covering around 2.6 million square kilometers. This region’s deciduous forests are experiencing shifts in growing seasons.
Great Plains
The Great Plains stretch from Canada through the central United States into Mexico, covering about 3.2 million square kilometers. This vast grassland is crucial for agriculture.
North American Deserts
This region includes the deserts of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico, covering around 2.5 million square kilometers. These arid landscapes are experiencing more intense droughts.
Mediterranean California
Located in coastal California, this region covers about 160,000 square kilometers. Known for its unique Mediterranean climate.
Temperate Sierras
This region encompasses the Sierra Nevada and the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, covering around 374,000 square kilometers. These mountainous areas are crucial for water supply.
Tropical Dry Forests
Found in southwestern Mexico, this region covers about 103,000 square kilometers. These forests are adapted to seasonal droughts.
Tropical Wet Forests
The tropical rainforests of Central America and southern Mexico cover approximately 1 million square kilometers. These biodiversity hotspots are facing deforestation and habitat fragmentation.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change is reshaping all these ecological regions. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are affecting biodiversity and ecosystems. Glacial melt, thawing permafrost, shifts in species composition, and more frequent wildfires are some of the general impacts seen across these diverse landscapes. Addressing climate change is crucial to preserving the unique ecological regions of North America.
Explore More Maps of North America
Interested in discovering more about North America’s geography? Check out these maps available on Amazon:




Beautiful detailed map. But I can’t read the legend. Where can I find it?
Click the map