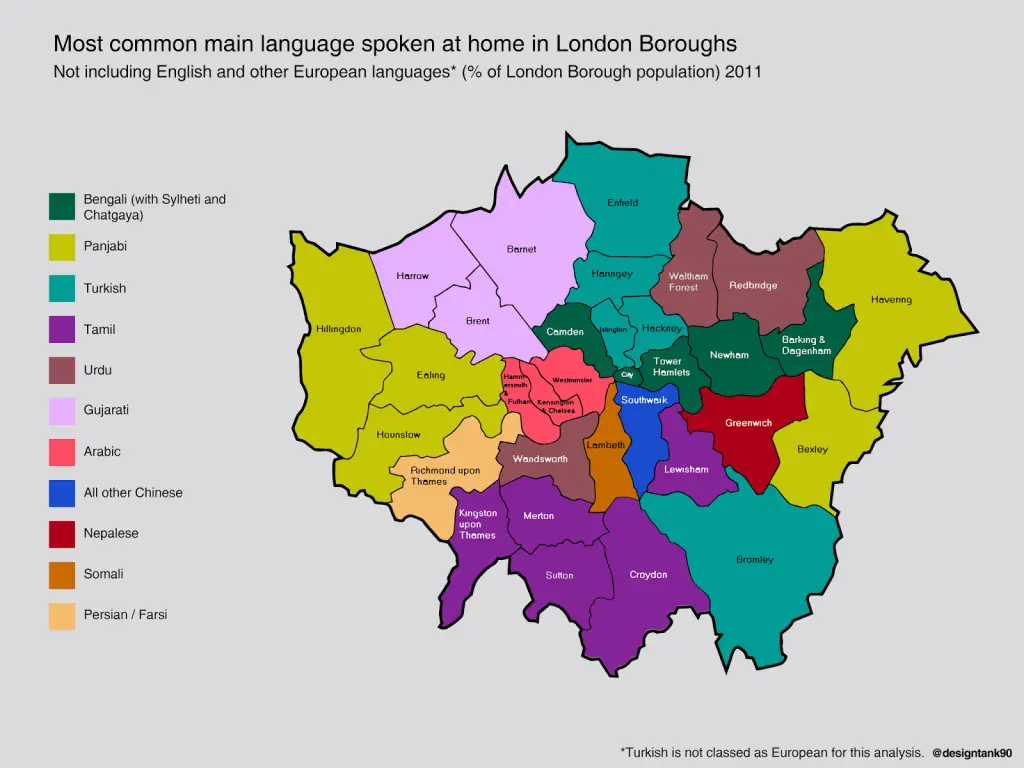
World Map of Language Diversity
Language diversity is the variety of languages spoken in a particular region or country. Greenberg’s diversity index is one method used to calculate linguistic diversity. It measures the probability that two randomly selected individuals in a population speak different languages. The formula for Greenberg’s diversity index is:
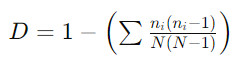
Where:
- D is the diversity index.
- ni is the number of speakers of each language in the population.
- N is the total population size.
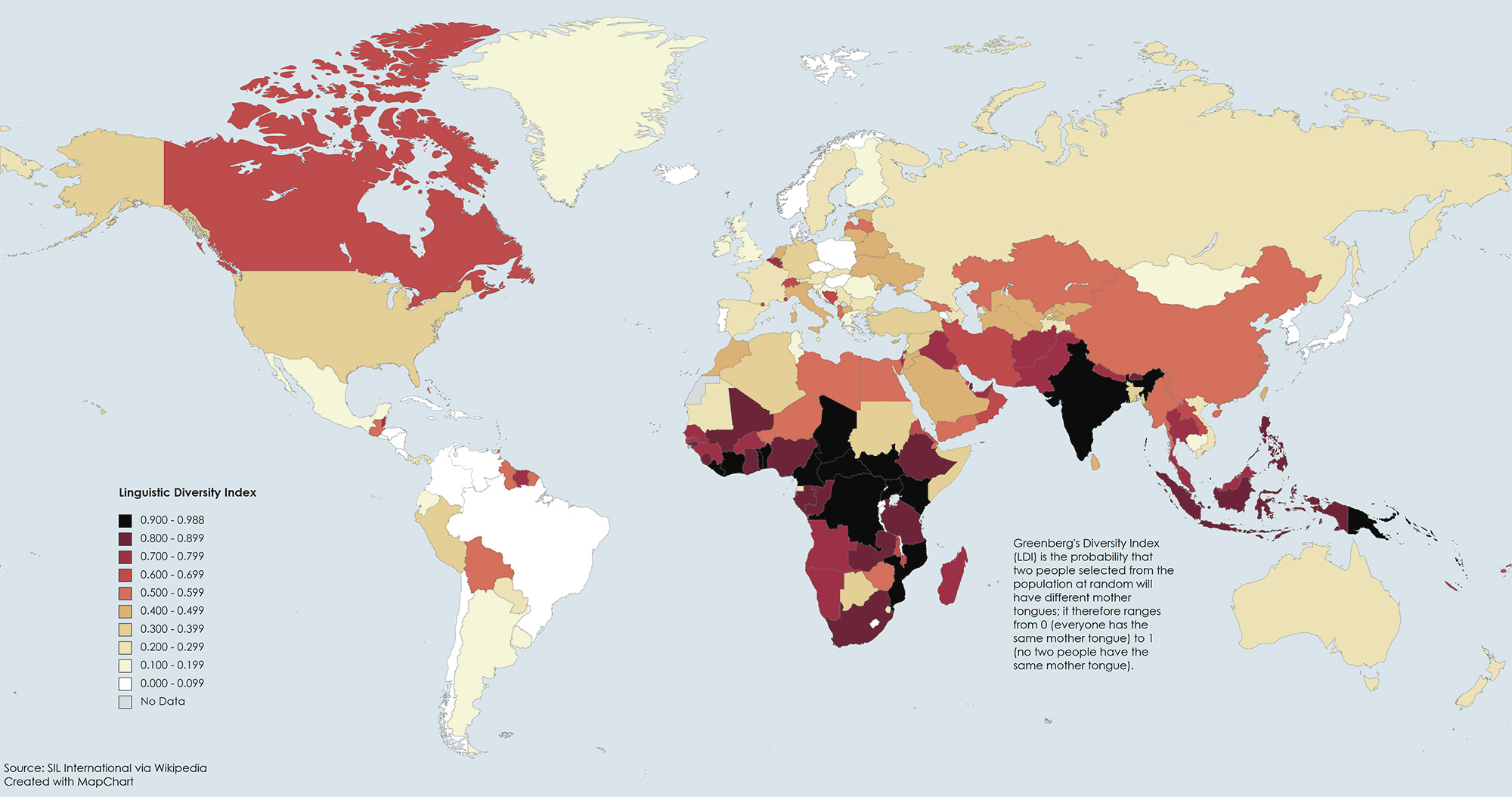
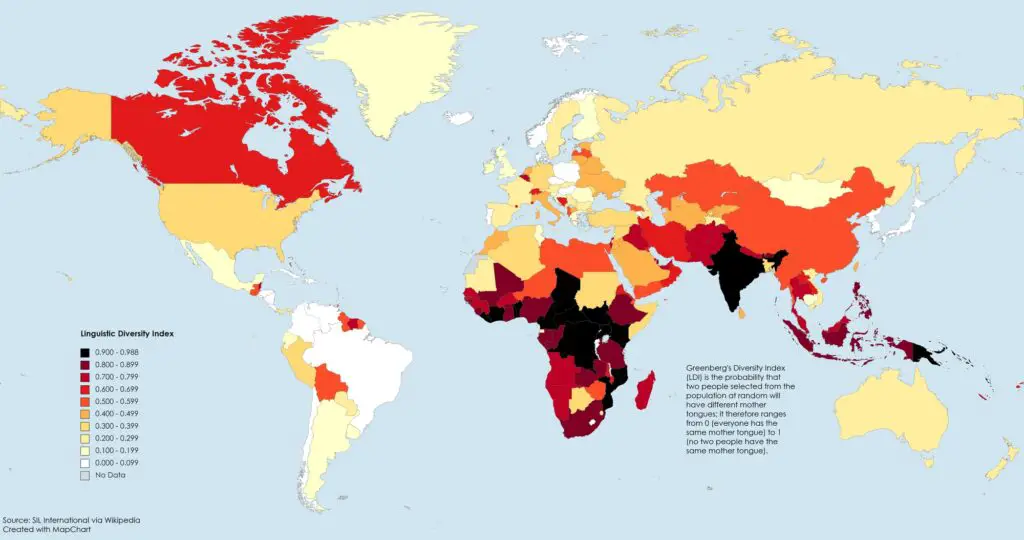
Countries with the highest linguistic diversity indexes tend to have numerous languages spoken among relatively small populations. Papua New Guinea is often cited as having the highest linguistic diversity index, with over 800 languages spoken in a population of approximately 8 million.
The top 10 countries with the highest linguistic diversity indexes include Papua New Guinea, Indonesia, Nigeria, India, Cameroon, Australia, Mexico, Brazil, Vanuatu, and Malaysia. These countries have a wide range of languages spoken, with Papua New Guinea having the highest number of languages, followed by Indonesia, Nigeria, and India.
The top 10 countries with the highest linguistic diversity
| Rank | Country | Number of languages |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | New Guinea | ~800 |
| 2 | Indonesia | ~700 |
| 3 | Nigeria | ~500 |
| 4 | India | ~450 |
| 5 | Mexico | ~290 |
| 6 | Cameroon | ~270 |
| 7 | Australia | ~260 |
| 8 | Brazil | ~220 |
| 9 | Malaysia | ~140 |
| 10 | Vanuatu | ~110 |
Conversely, countries with the lowest linguistic diversity indexes typically speak fewer languages among larger populations. These countries often have dominant or official languages that are widely spoken. For example, countries like Iceland, Denmark, and Norway have low linguistic diversity indexes due to the dominance of their respective languages (Icelandic, Danish, and Norwegian) within their populations.
The top 10 countries with the lowest linguistic diversity indexes include countries like Iceland, Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Malta, Portugal, Belgium, Sweden, the Netherlands, and Finland.
The Decline of Linguistic Diversity: A Global Concern
Linguistic diversity is declining at an alarming rate worldwide. This decline is primarily driven by globalization, urbanization, and the dominance of a few major languages. As people migrate to urban areas or adopt dominant languages for economic and social reasons, many languages are being lost. UNESCO estimates that one language dies every two weeks, leading to a gradual homogenization of languages and cultures. This loss of linguistic diversity not only erases unique ways of communication but also endangers traditional knowledge, cultural heritage, and biodiversity. Efforts to document and revitalize endangered languages are crucial to preserving the rich tapestry of human expression and ensuring the survival of diverse cultural identities for future generations.