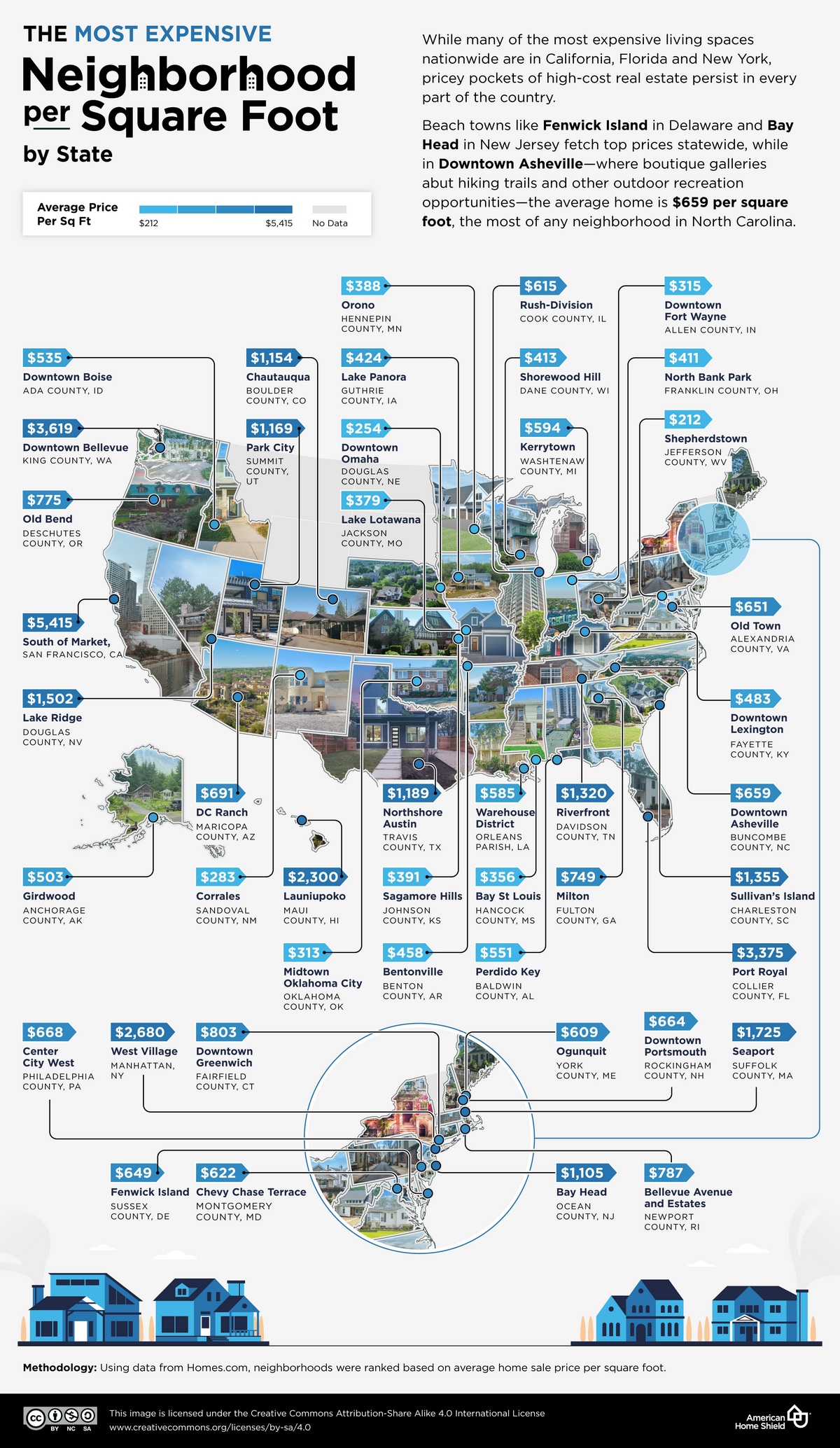
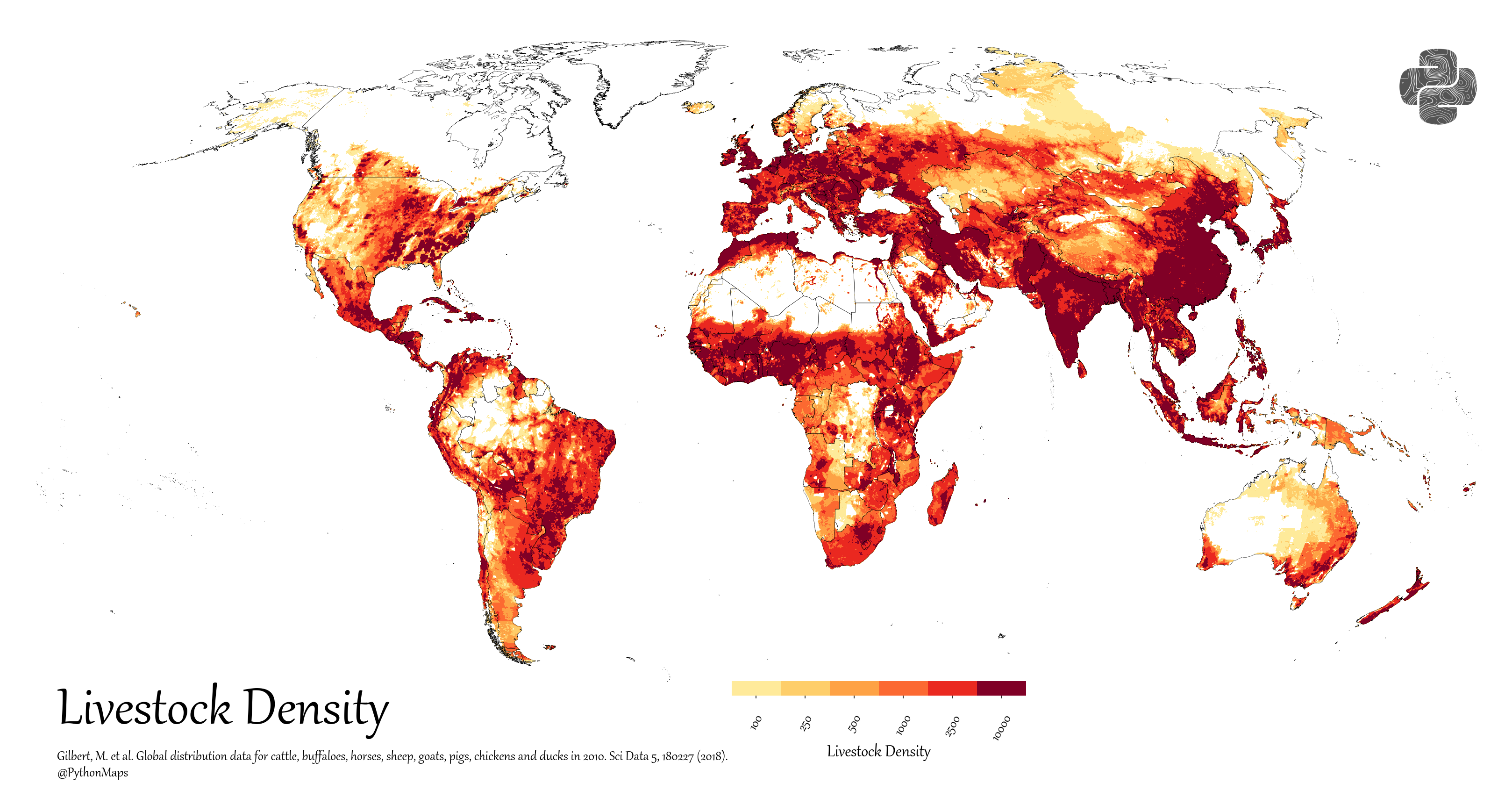
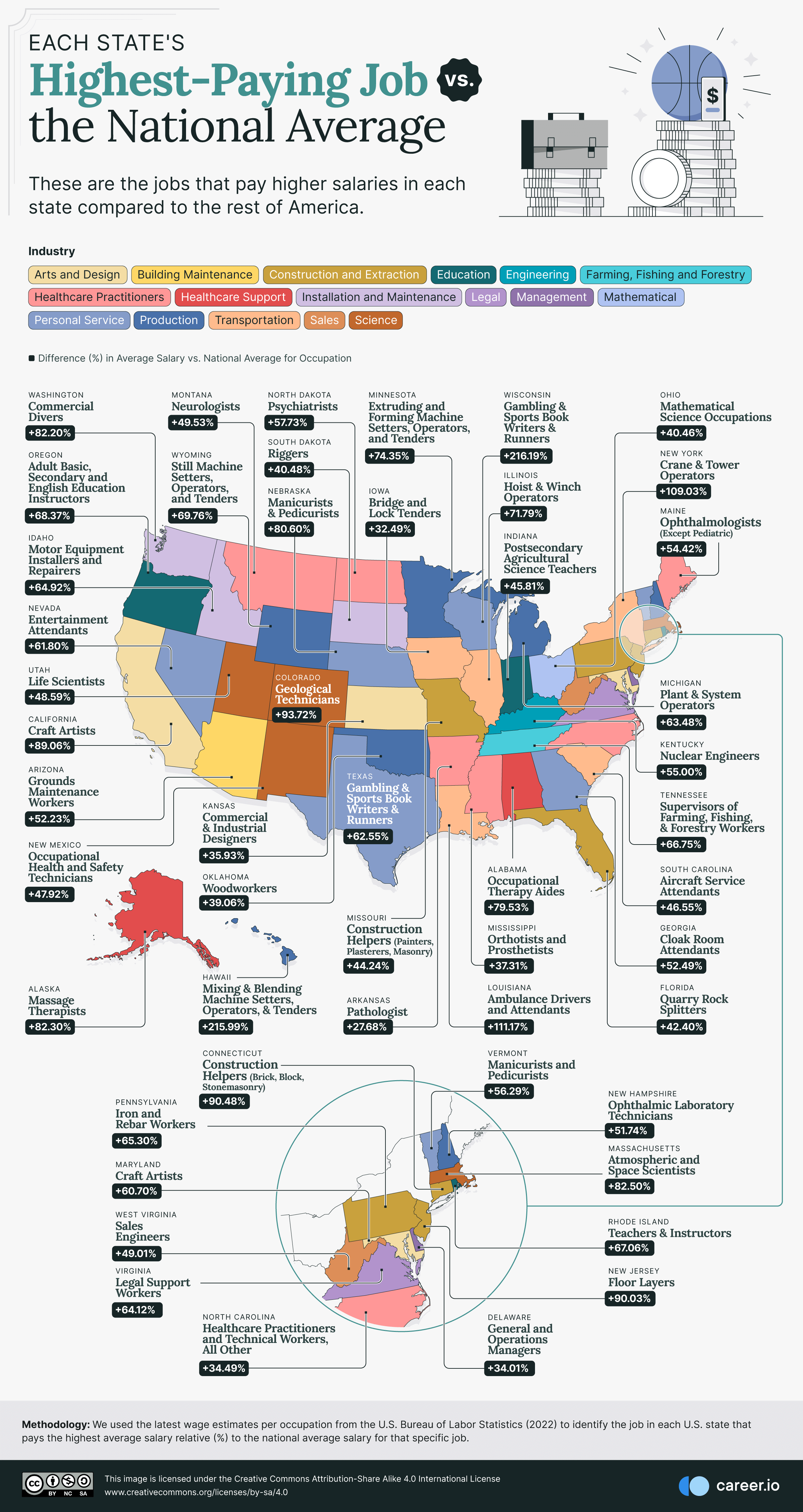
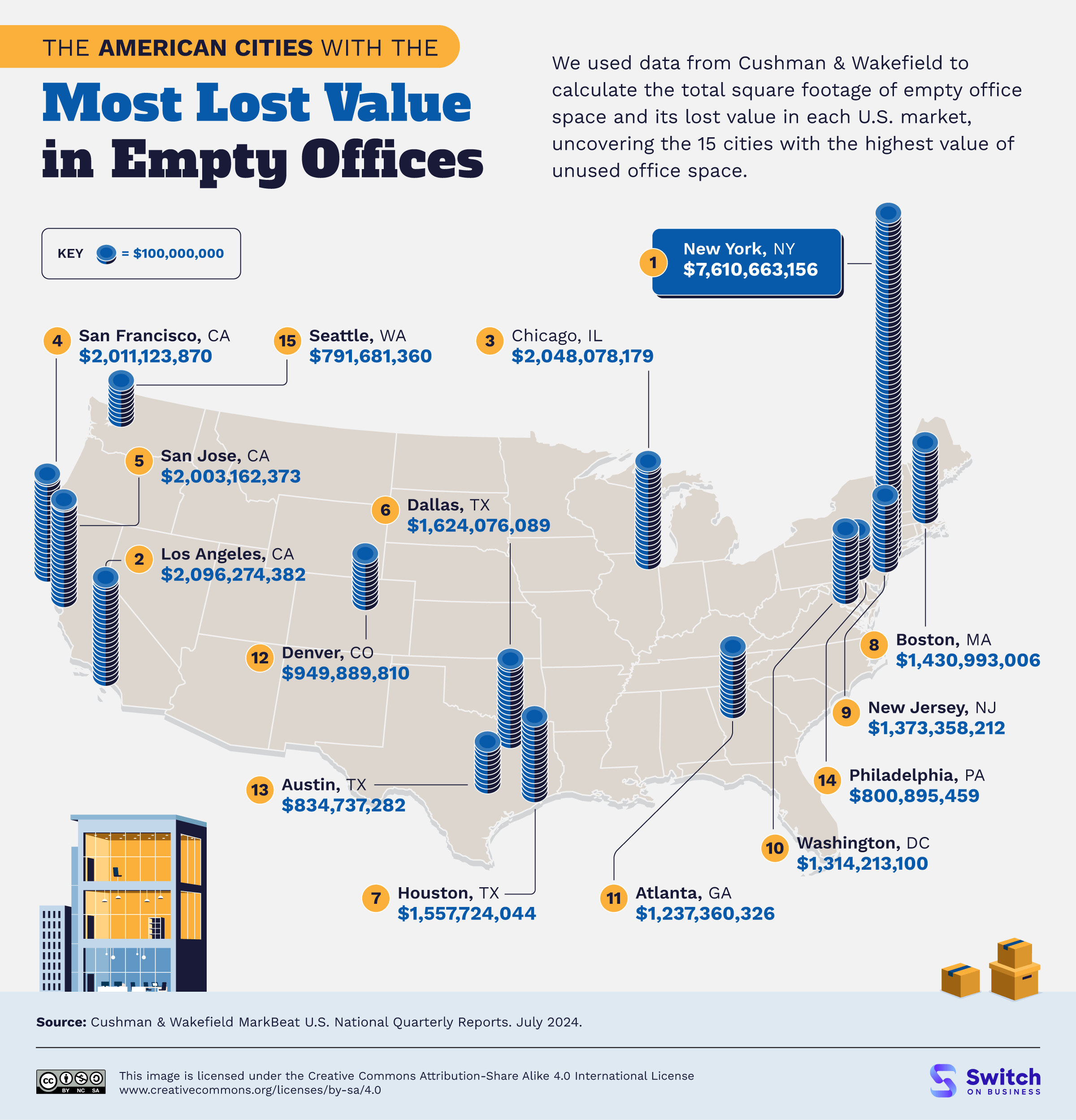
Unpacking Population Density in the Netherlands: A Land of Compact Living
The Netherlands, known for its picturesque landscapes, bustling cities, and efficient use of space, is also one of the most densely populated countries in Europe.
As of 2024, the Netherlands has a population of approximately 17.5 million people, packed into an area of just over 41,500 square kilometers. This results in an average population density of about 421 people per square kilometer, making it one of the most densely populated countries in the world.
The map below shows population density in the Netherlands.
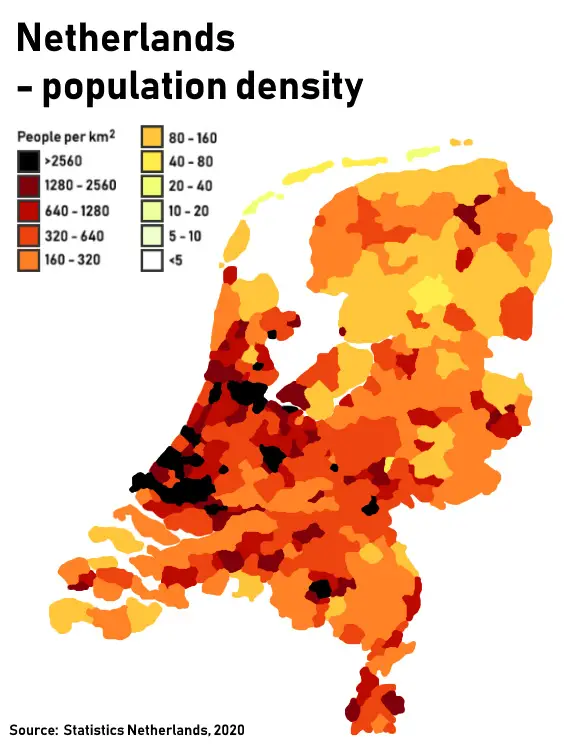
Table of Contents
Key Facts:
- Urban Concentration: The highest population densities are found in urban areas, particularly in the Randstad, which includes major cities like Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, and Utrecht. This metropolitan region has a density exceeding 1,500 people per square kilometer.
- Rural Areas: In contrast, rural areas, especially in the northern provinces of Friesland and Drenthe, have much lower densities, sometimes fewer than 100 people per square kilometer.
- Smallest Municipality: The smallest municipality by population is Schiermonnikoog, a small island in the Wadden Sea, with just over 900 residents.
Historical Perspective
The Netherlands’ high population density is not a recent phenomenon. Several historical factors have contributed to this:
- Agricultural Efficiency: The Dutch have a long history of efficient agriculture, which supported high population densities even in pre-industrial times. Innovations such as crop rotation and land reclamation allowed for sustained population growth.
- Urbanization: The Industrial Revolution spurred rapid urbanization, with cities expanding to accommodate workers. This trend has continued, with a significant portion of the population living in urban areas.
- Immigration: The Netherlands has been a destination for immigrants for centuries, from Spanish and Portuguese Jews in the 17th century to labor migrants and refugees in the 20th and 21st centuries.
Innovative Solutions for High Density
The Dutch have developed several innovative solutions to manage their high population density effectively:
- Vertical Living: High-rise buildings are common in urban areas, maximizing the use of limited space. The Zuidas district in Amsterdam, for example, is a hub of modern high-rise architecture.
- Public Transportation: The Netherlands boasts an extensive and efficient public transportation network, reducing the need for personal vehicles and easing congestion.
- Green Spaces: Despite the high density, Dutch cities are known for their green spaces. Parks, green roofs, and urban gardens are integrated into city planning to enhance the quality of life.
- Water Management: With a significant portion of the country below sea level, the Dutch have perfected water management. Canals, polders, and advanced drainage systems not only prevent flooding but also create habitable land.
Interesting Facts
- Bicycle Capital: The Netherlands has more bicycles than people, with around 23 million bikes for its 17.5 million residents. Cycling infrastructure is extensive, promoting sustainable and efficient urban mobility.
- Floating Homes: In response to space constraints and rising water levels, floating homes are becoming increasingly popular. These homes are designed to rise and fall with water levels, providing a unique living experience.
- Efficient Use of Space: The Dutch are experts in space optimization. For example, multi-use buildings that combine residential, commercial, and recreational spaces are common, maximizing functionality in limited areas.
- Population Density by Province: The most densely populated province is South Holland, with over 1,300 people per square kilometer. In contrast, the least densely populated province is Drenthe, with around 180 people per square kilometer.
Challenges and Future Outlook
High population density brings several challenges, including housing shortages, traffic congestion, and environmental pressures. However, the Netherlands continues to address these issues through innovative urban planning and sustainable practices.
- Housing: The government is investing in affordable housing projects and promoting the development of new residential areas.
- Sustainability: There is a strong focus on sustainability, with initiatives to reduce carbon emissions, promote renewable energy, and enhance green spaces.
- Smart Cities: Dutch cities are adopting smart technologies to improve urban living. Smart grids, efficient waste management, and intelligent transportation systems are part of the future landscape.
Interested in learning more about the Netherlands and its people? Check out these recommended books.