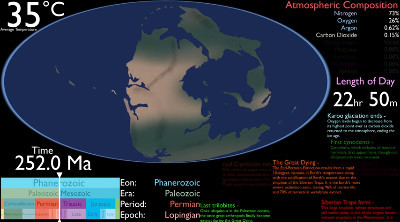
The breakup of Pangaea
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
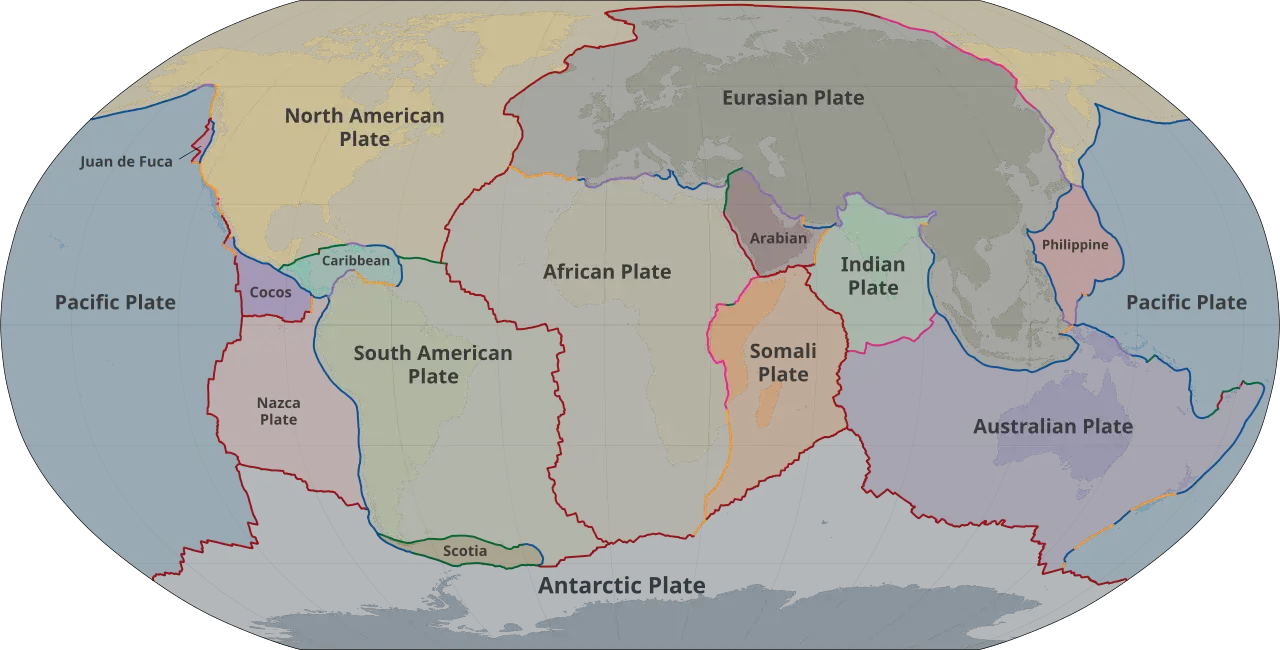
The breakup of Pangaea, a supercontinent that existed around 335 million years ago, is a significant event in Earth’s geological history. Pangaea began to break apart during the Mesozoic Era, forming the continents as we recognize them today. The process of breakup and continental drift occurred due to the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth’s surface.
Around 200 million years ago, during the Jurassic Period, Pangaea started to rift and split into two smaller supercontinents, Laurasia to the north and Gondwana to the south. Laurasia eventually fragmented into North America, Europe, and Asia, while Gondwana broke apart to form South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia, and the Indian subcontinent.
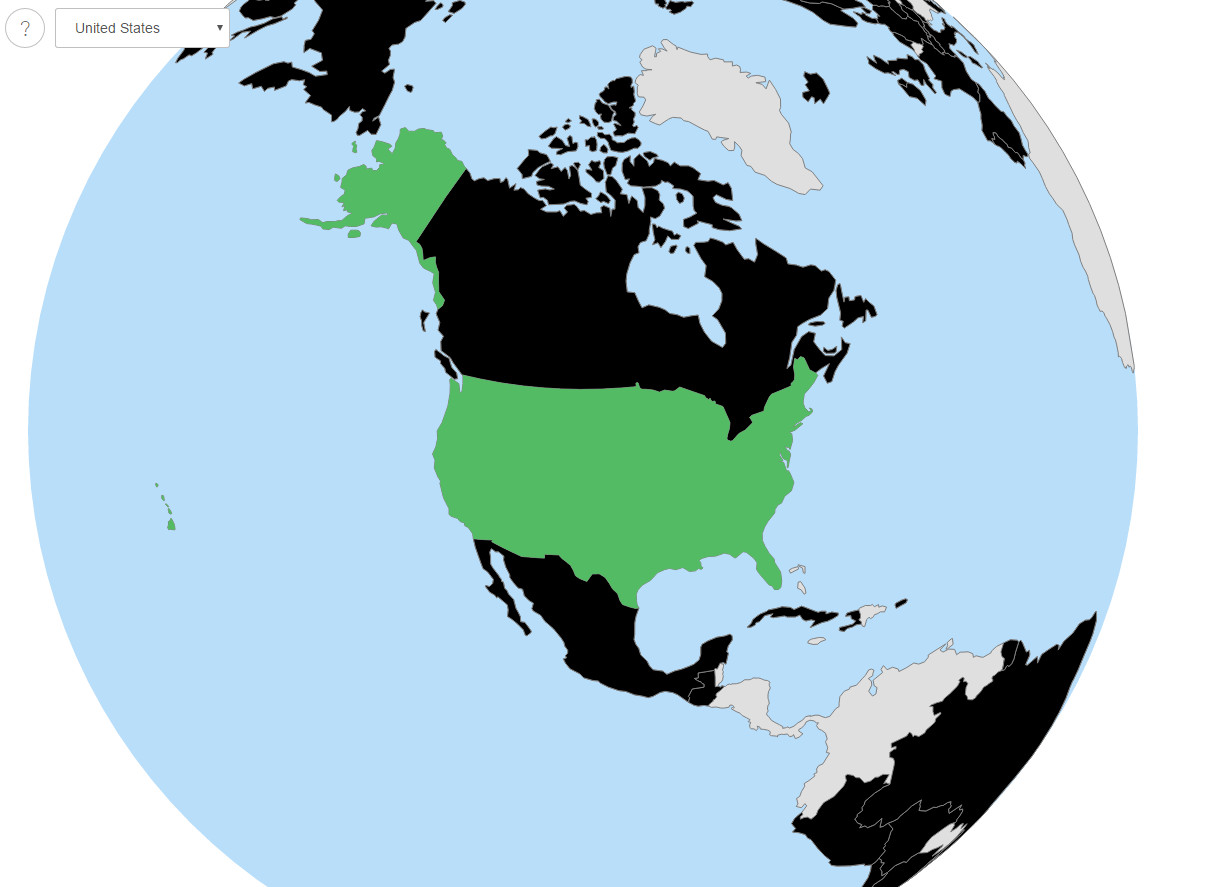
The globe below, created by Lazaro Gamio, shows the breakup of Pangea.

This gradual separation of landmasses profoundly affected Earth’s climate, ocean currents, and the evolution of life. It played a crucial role in shaping the distribution of flora and fauna across the continents. The breakup of Pangaea is a cornerstone in understanding the dynamic nature of Earth’s crust and the interconnectedness of geological and biological processes over millions of years. It laid the groundwork for the diverse landscapes and ecosystems that we observe on the planet today.
We recommend checking out the following books if you’re eager to learn more about Earth’s past.




This helped me out a lot, Thanks.
thats trippy man
thats crazy
this makes my head hurt