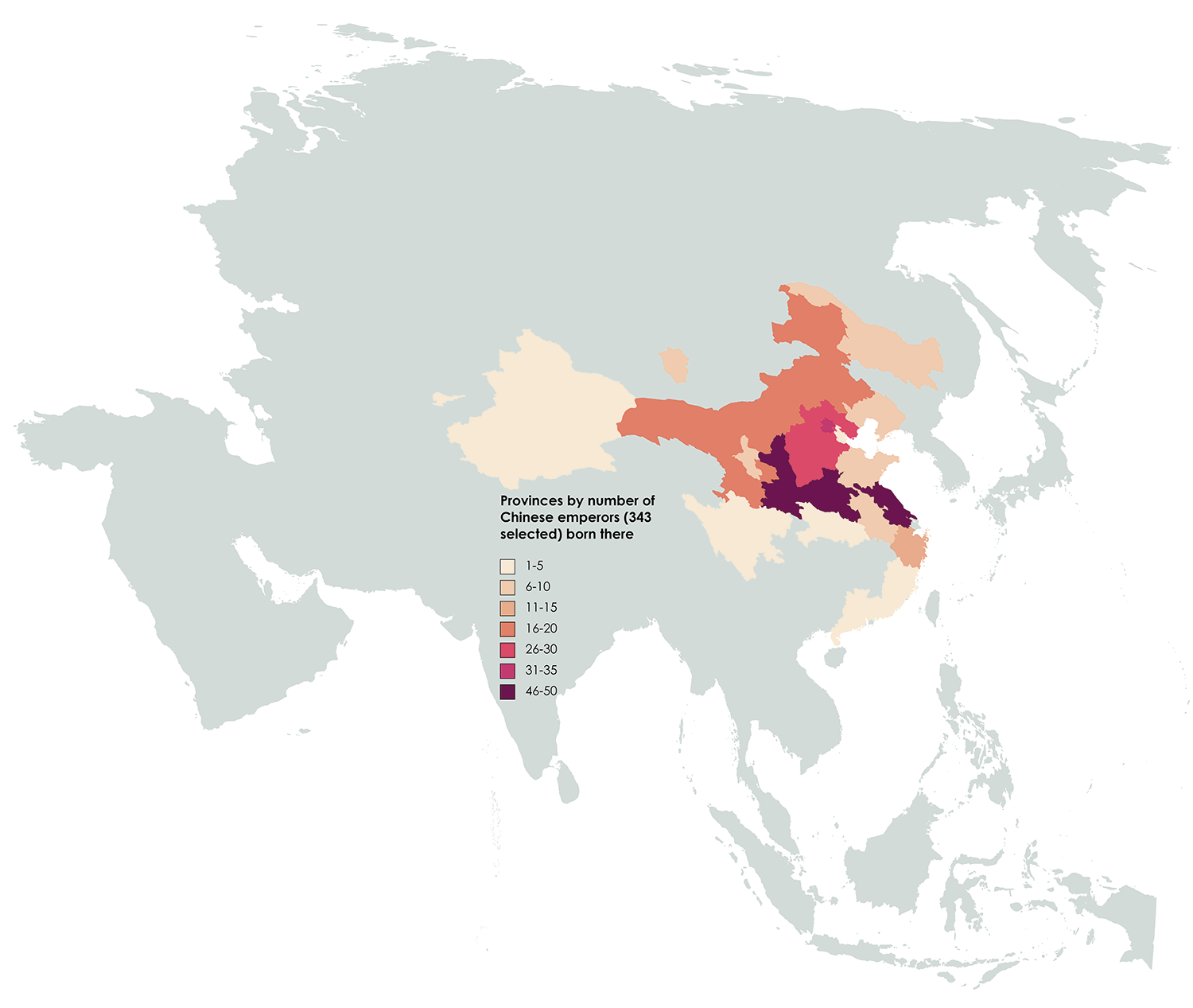
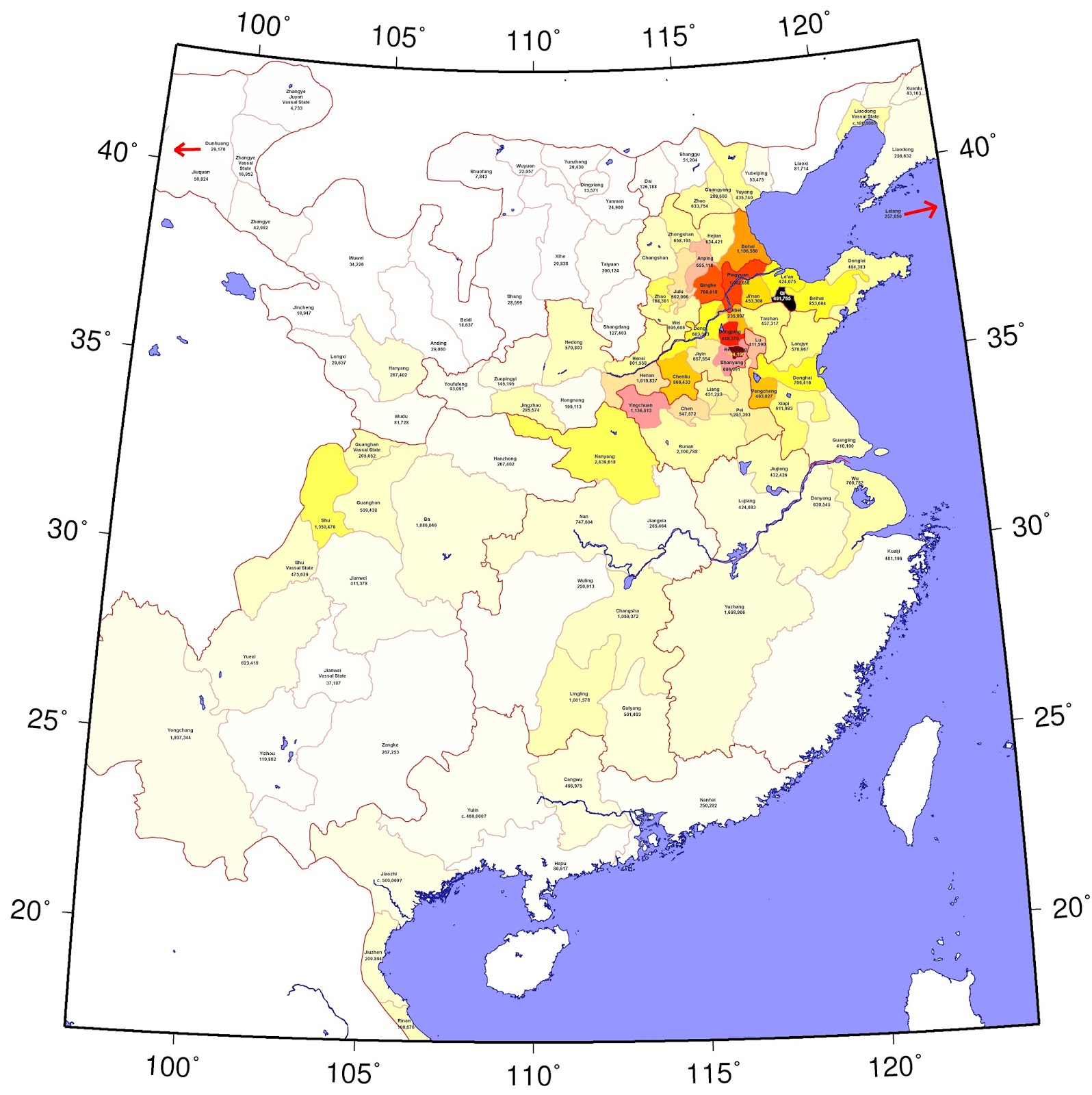
Population map of ancient China mapped
As beginning as 2 C.E. during the Han dynasty, China had about 60 million citizens. It is almost 1/4 of the globe’s population at that time. Historical changes of increase and drop had China’s population between 37 and 60 million for at least the following one thousand years before starting to grow fast.
Population map of ancient China, per an empire-wide census made in 2 AD
In the beginning years of the Ming dynasty in the late 14th century, China’s population started considerably grow that proceed to the present.
Especially accelerated growth happened between 1749 and 1811 during the Qing dynasty when the country’s population doubled from 177.5 million to 358.6 million.
The first modern Chinese census in 1953 showed a population of 583 million, which has more than doubled in less than fifty years to 1.25 billion people in 1999.