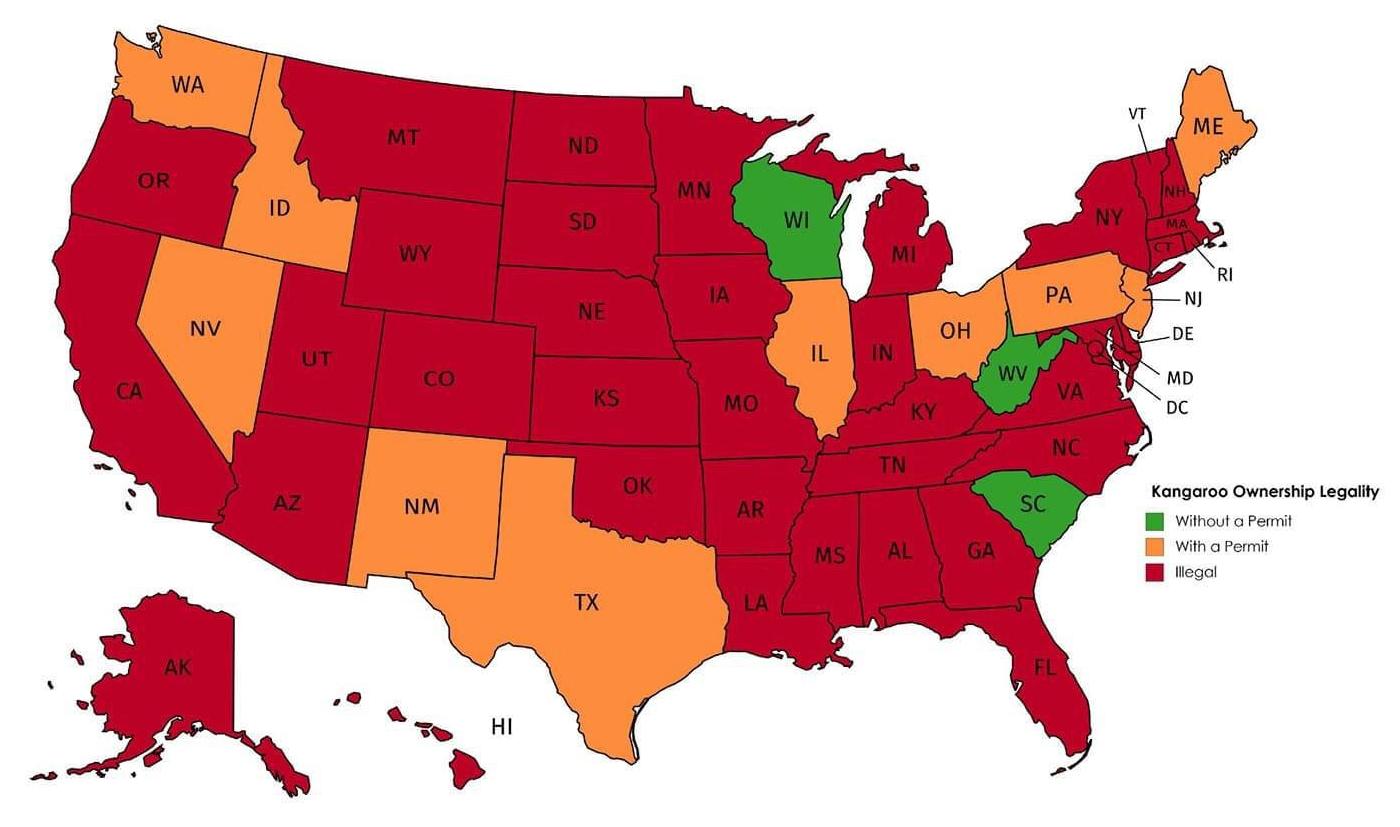
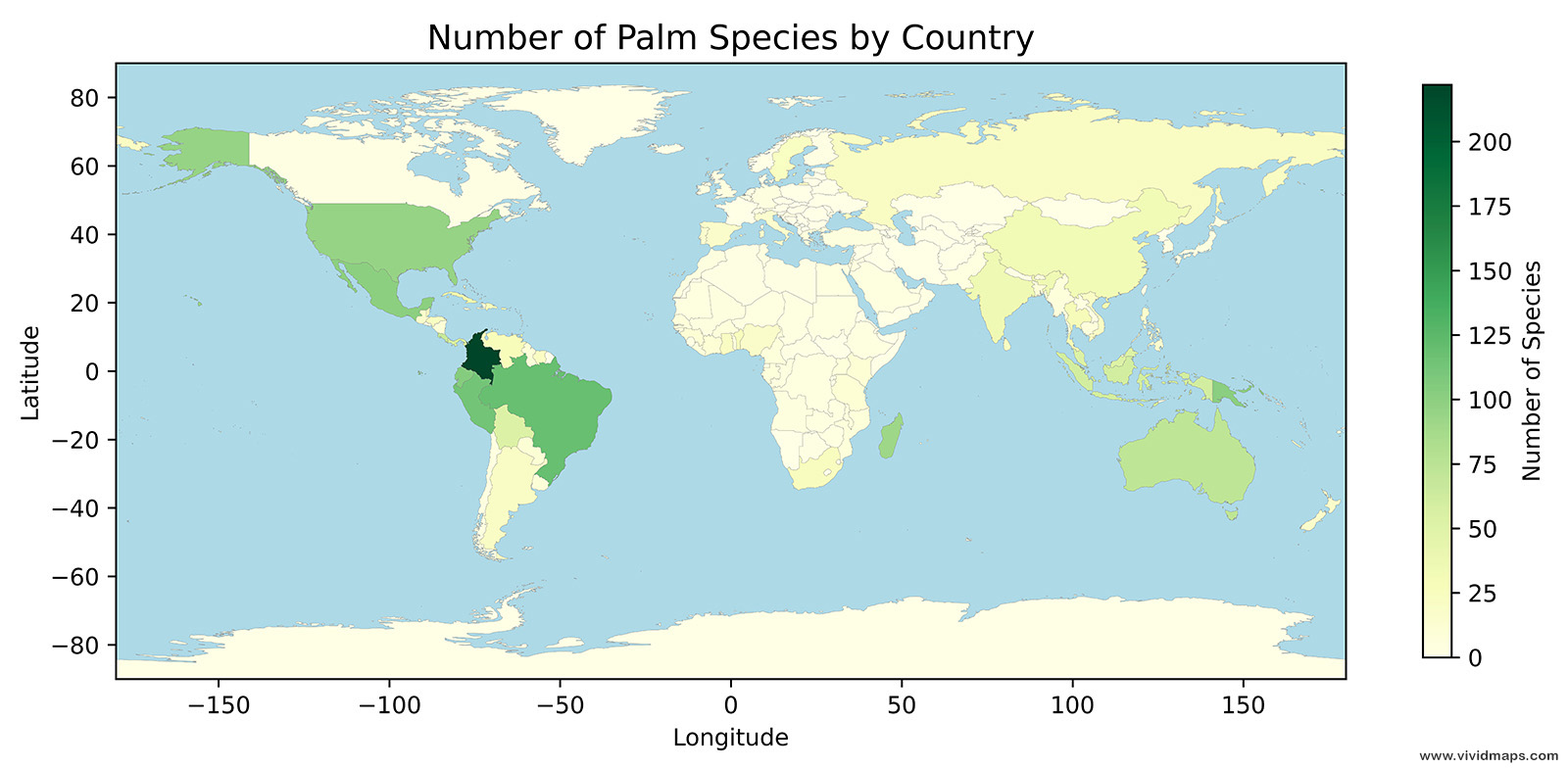
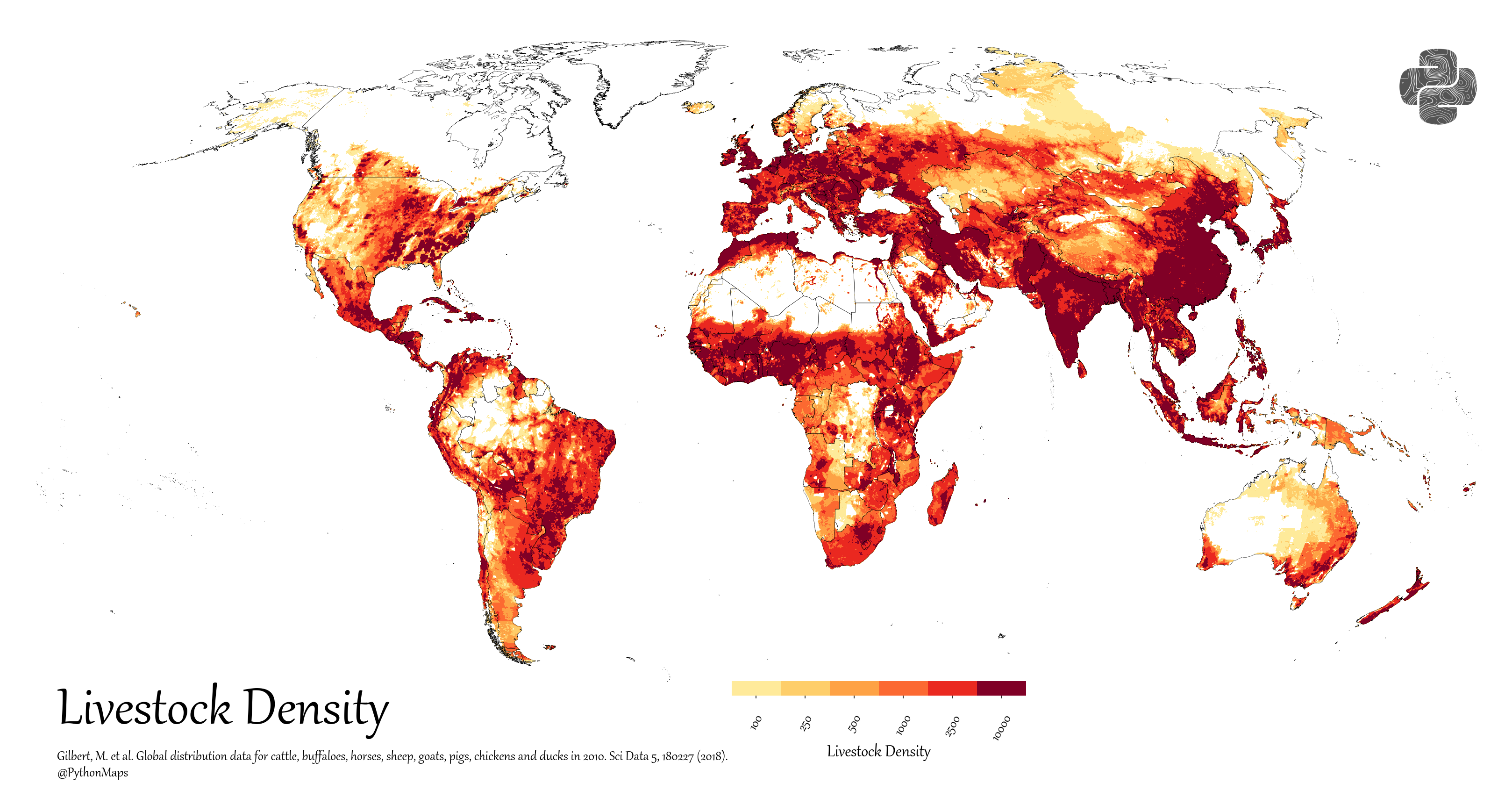
Historic ranges of various domestic animals wild ancestors

Turkeys were domesticated in ancient Mexico, for food in 180 CE.
The guppy is the most popular freshwater aquarium fish species native to Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Brazil, Guyana, Jamaica, the Netherlands Antilles, Trinidad and Tobago, Virgin Islands, and Venezuela. Guppies were first described in 1859.
The guinea pig originated in the Andes of South America. The guinea pig was domesticated in 5000 BCE.
A domestic rabbit is any of the domesticated varieties of the European rabbit species. Rabbits were first exploited by the Romans as sources of food and fur in 600 CE.
Domestic sheep descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia. Sheep was domesticated in 8700 BCE.
The donkey is a domesticated member of the horse family (Equidae). The wild ancestor of the donkey is the African wild donkey. The donkey has been used as a working animal sience 5000 BCE.
The laboratory rats descended from hooded rats and all the laboratory rats descended from a single Japanisee ancestor. The first time laboratory rats was brought into a laboratory for a study in 1828.
The chicken is a subspecies of the red junglefowl native to Southeast Asia. Chicken was domesticated in 6000 BCE.