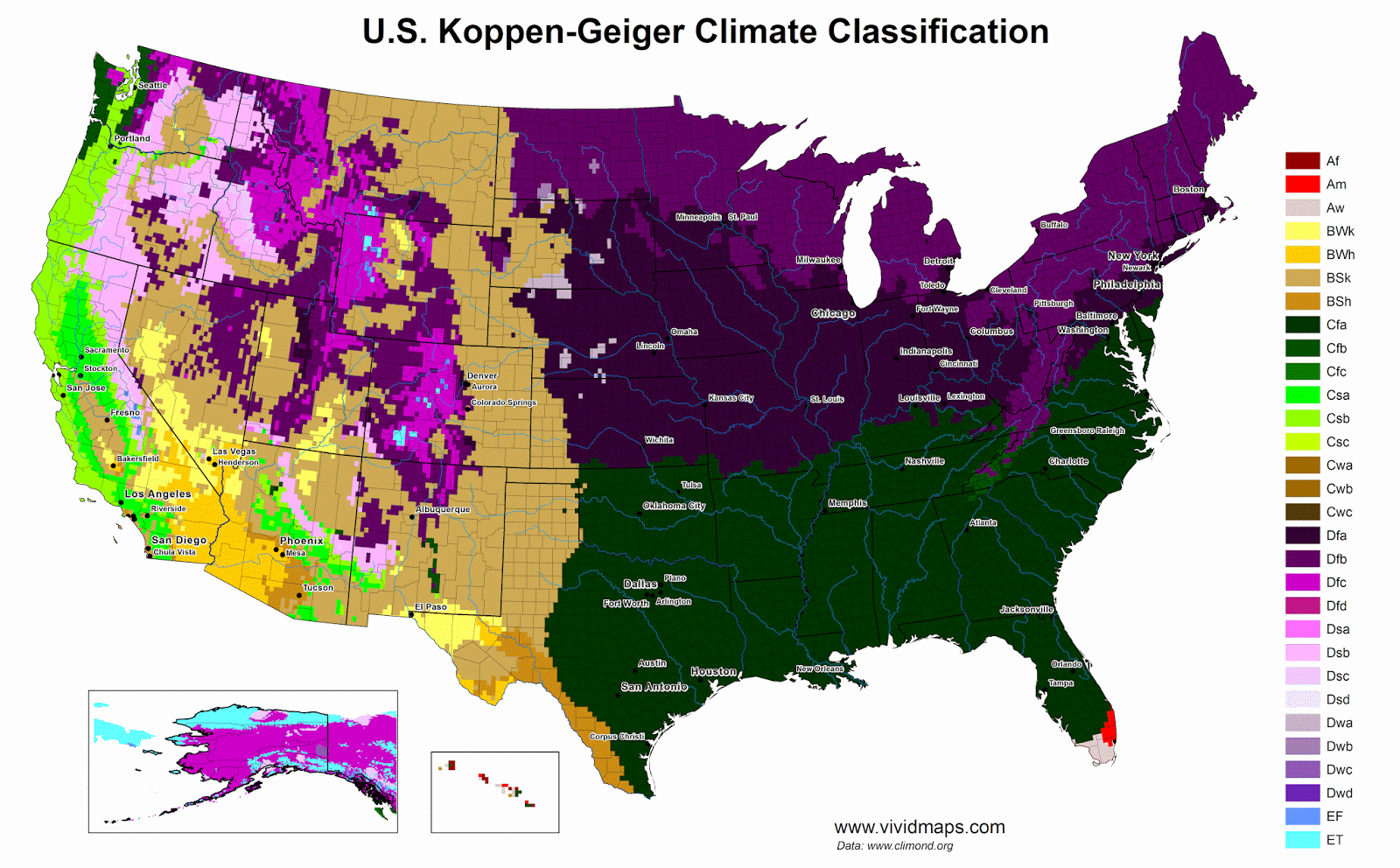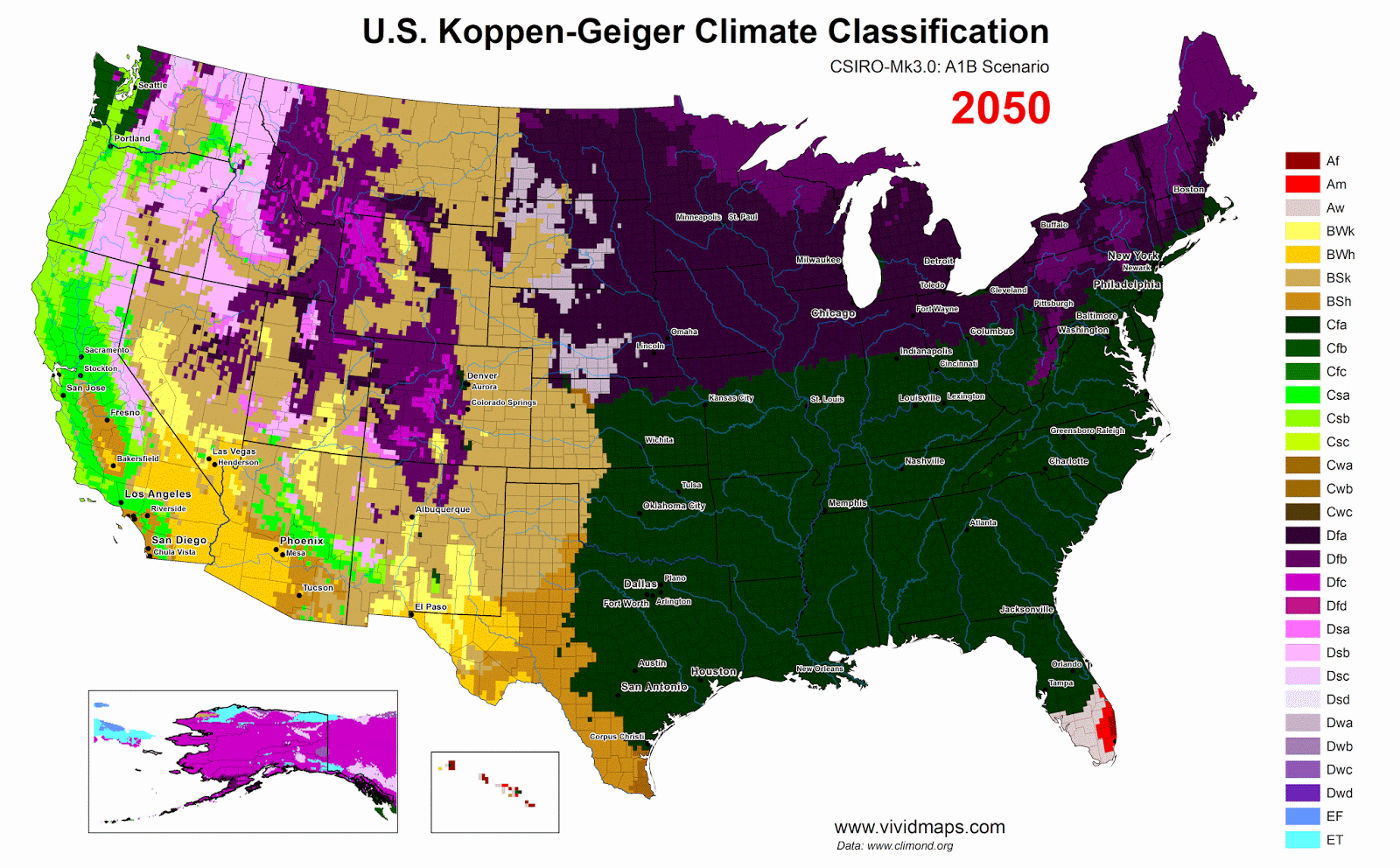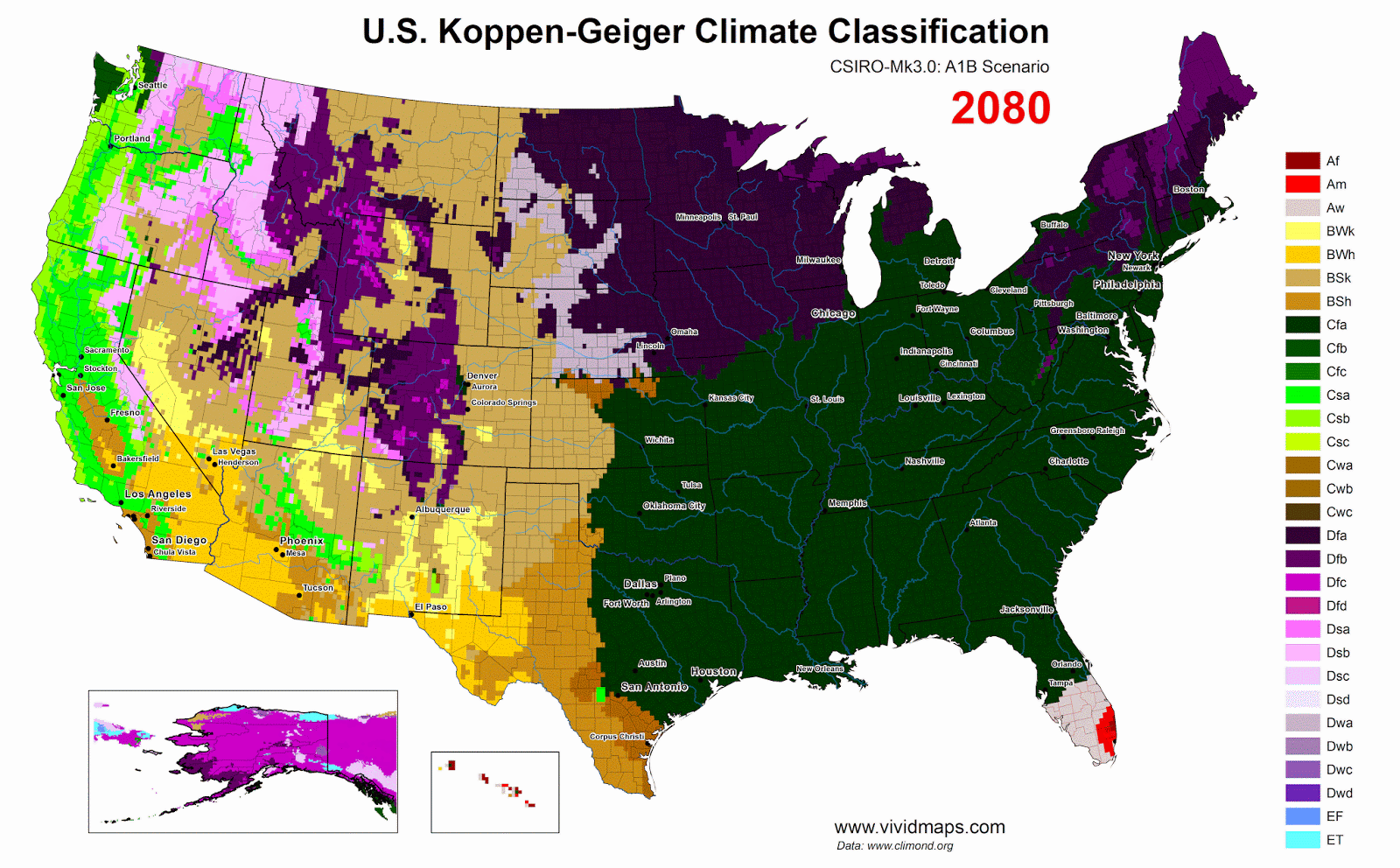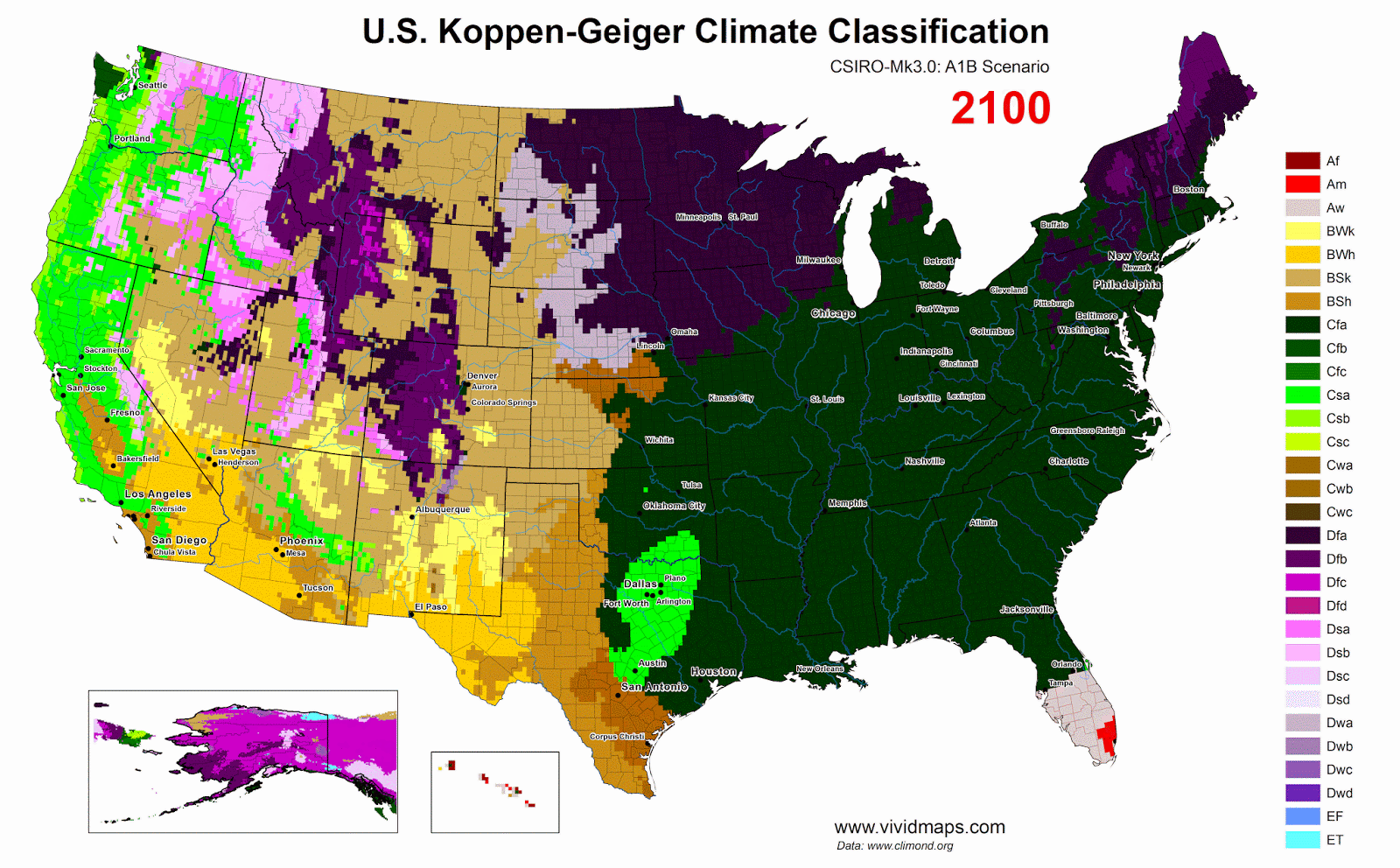
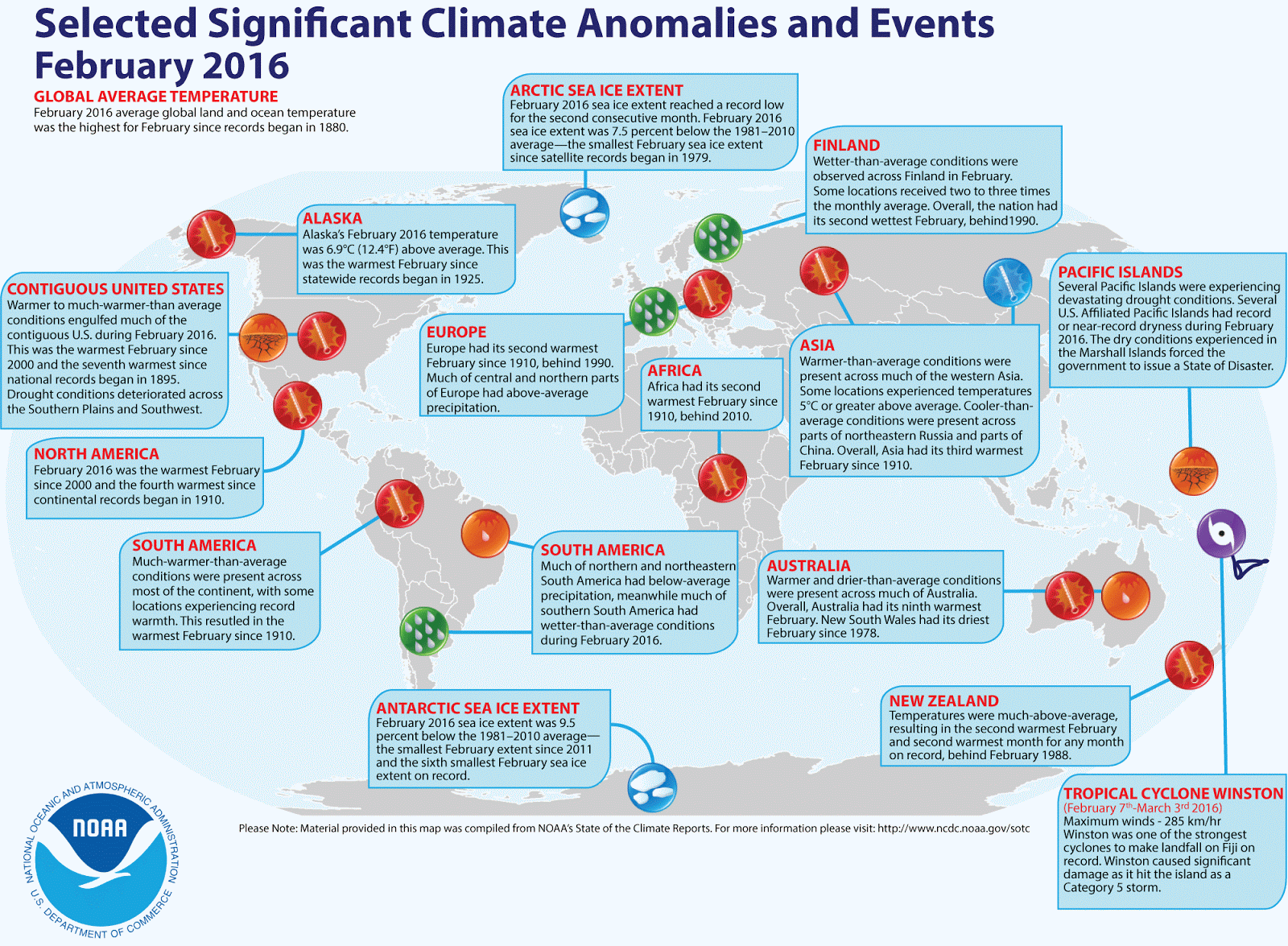
The heating of Arctic as a mountain
Over the past 30 years, the Arctic has warmed at roughly twice the rate as the entire globe, a phenomenon known as Arctic amplification. Most scientists agree that this rapid warming is a signal of human-caused climate change.
Arctic sea ice extent has decreased notably in all months since satellite measures began in 1979. Polar sea ice approaches its minimum every September. September Arctic sea ice is now reducing at a rate of 13 percent per decade, related to the 1981 to 2010 average.
According to the World Meteorological Organization’s report on the State of the Global Climate, recent years are becoming record-breakingly warm, with the most striking warmth being seen in the Siberian Arctic, where temperatures are raised more than five °C above average.
The hottest temperature ever (+ 38.6°C or 101.48°F) registered above the Arctic circle was recorded in Verkhoyansk in Siberia in June 2020. A recent Oxford University-led research reveals artificial climate change due to carbon emissions made six hundred times more likely this Siberian heatwave.
Half of that heat is generated in the Arctic itself, which is already hastening global warming. We observe less ice cover and snow, and the exposed dark areas and darker ocean water have accumulated that heat.
The brilliant map below created by Reddit user: g_fiske, using KNMI Climate Explorer data, visualizes the heating of the Arctic as a mountain.
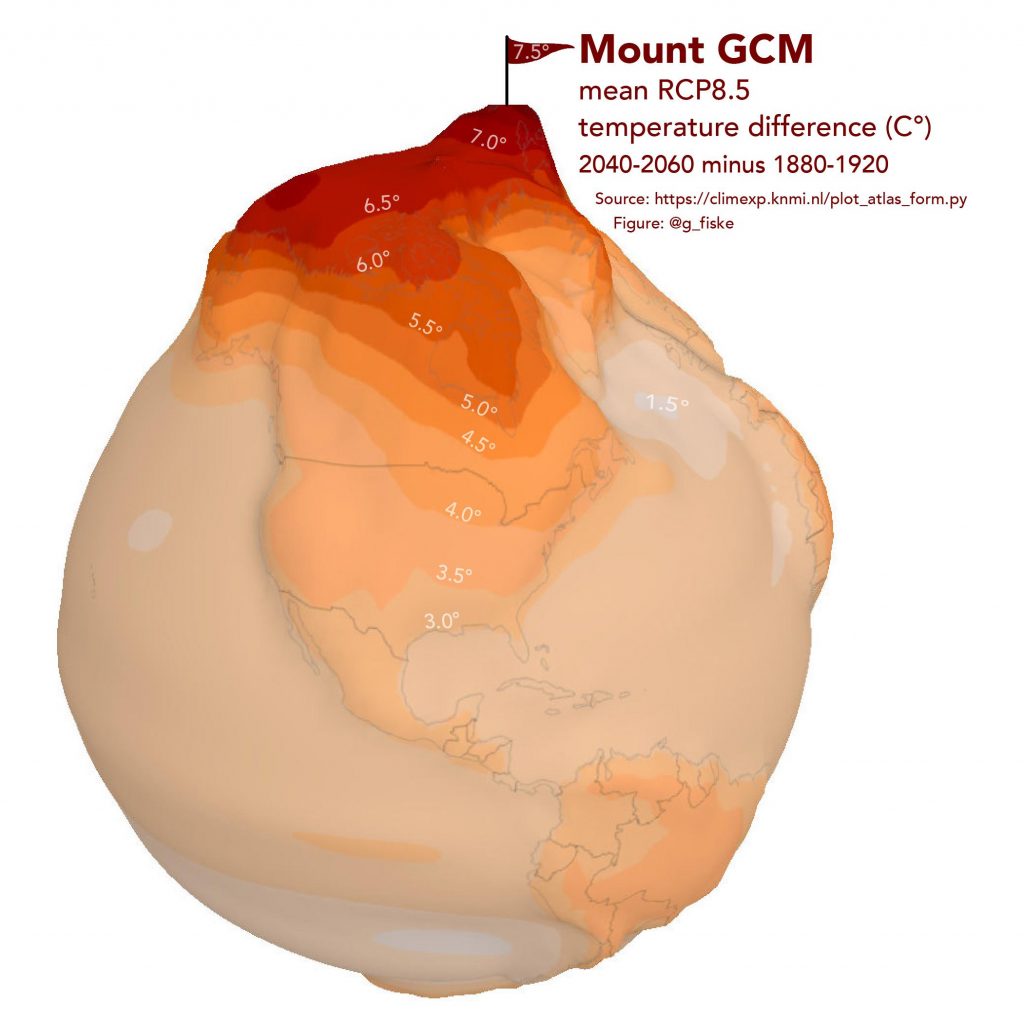
GCM – General Circulation Model describes natural processes in the atmosphere, ocean, land surface, and cryosphere.
RCP – Representative Concentration Pathway. These are a variety of possible scenarios – RCP2.6, RCP4.5, RCP6, and RCP8.5 – for changing the planet’s climate based on the level to which humankind reduces its greenhouse gas emissions. The number of RCP match how many extra watts per square meter of radiative forcing we can expect from the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which in turn depends on how much greenhouse gas is really in the atmosphere of our planet. RCP8.5 is the most severe scenario, essentially with the assumption that we do entirely nothing to stop greenhouse gas emission and continue business-as-usual.
Without meaningful cuts to carbon emissions and land-use changes, humankind is currently on the path to an RCP8.5-like scenario unless large intergovernmental efforts are put into place.
RCP 8.5 evaluation an ~4.5°C global warming by 2100, the Paris agreement only gets us down to ~3°C, still well over the 1.5-2°C that is recommended for the long-term conservation of modern levels of human civilization.
According to this scenario, the Arctic will be ice-free. Greenland is carved out to leave the blue Mediterranean-like but cold seas in the interior. Sea level will rise 34 cm by 2050 and 111cm by 2100, comparatively to the level in 2000.
Related post:
– How hot cities could be in 2050