What traffic rules are different in different countries
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
Driving regulations can differ significantly when you cross borders from one country to another. Variations include rules for right-hand and left-hand traffic, maximum speed limits, and laws regarding alcohol consumption while driving. Familiarize yourself with the driving regulations in your destination country for a safe and enjoyable travel experience.
The atlas of maps below illustrate just how different the road rules may be in various countries around the world.
Table of Contents
Countries by the handedness of traffic
The choice of whether a country drives on the right-hand side (RHT) or the left-hand side (LHT) of the road is influenced by historical, cultural, and practical factors. In many cases, historical practices and traditions have played a significant role in determining traffic handedness. For instance, medieval European knights on horseback would ride on the left side of the road to have their right arm free for combat, eventually influencing road traffic to favor LHT. Conversely, in countries like the United States, European settlers who drove on the right side of the road contributed to the adoption of RHT.
Colonial influence is another factor, with former colonies often adopting the traffic handedness of their colonizers. Former British colonies, for example, tend to drive on the left side of the road, while former French colonies adopted RHT.
Vehicle manufacturing can also play a role, as countries where vehicles are manufactured with the driver’s seat on a particular side may find it more practical to adopt traffic rules aligned with their vehicle design.
Safety considerations matter as well. Some studies suggest that LHT may reduce head-on collisions, which has influenced the choice of traffic handedness in certain countries.
Transitioning from one traffic handedness to another can be complex and costly, so countries tend to stick with their established system, especially if it’s deeply ingrained in their culture and infrastructure.
International conventions and agreements also play a role, as countries may adopt a particular traffic handedness to facilitate cross-border travel and trade, as seen in continental Europe, where RHT is prevalent.

Highest-posted speed limits around the world
Maximum speed limits in countries worldwide range from 70 to 160 kilometers per hour, which is significant. Especially if you keep in mind that the 1 percent change in speed would lead to a 2 percent change in injury accidents, a 3 percent change in severe injury accidents, and a 4 percent change in fatal accidents.

Drink-driving laws by country
According to the NHTSA, alcohol-impaired driving fatalities accounted for 31% of the total vehicle traffic fatalities and about 1/3 of all traffic-related deaths in the United States. In developing countries, road deaths related to drunk driving are even higher. That is why most countries in the world have strict restrictions on alcohol consumption by drivers.

Seat-belt laws by country
Seat-belts reduce the risk of a fatal injury by ~ 50% for the front seat and ~ 75% for rear seat occupants. In most countries of the world, all road users are required to wear seat belts.
In the map below, countries highlighted in green enforce a national seat-belt law that applies to all vehicle occupants. Countries marked in black have seat-belt laws at a subnational level, and in countries marked in red, there is either no seat-belt law or the law does not apply to all vehicle occupants.

Minimum Age to Drive a Vehicle
One of the primary reasons for setting a minimum driving age is safety. Younger individuals, particularly teenagers, tend to have less experience and maturity when it comes to operating a vehicle. By setting a minimum age requirement, authorities aim to ensure that drivers have had enough time to develop the necessary skills, judgment, and responsibility to navigate the road safely.
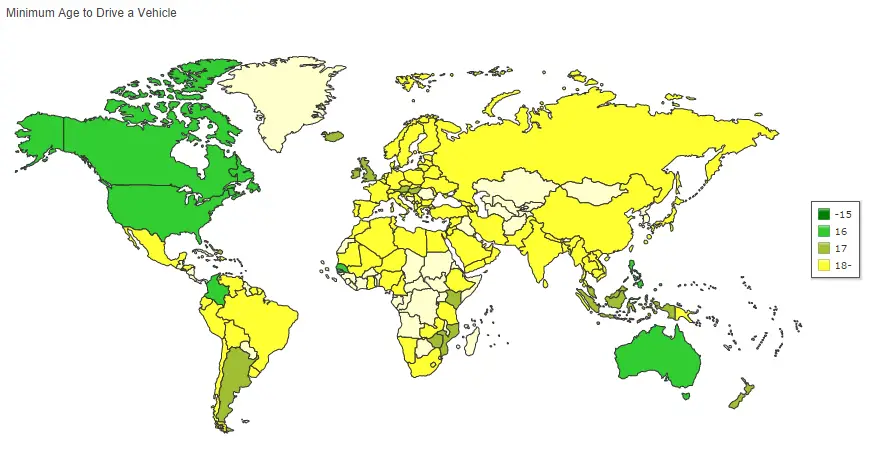
Statistics often show that younger drivers are at a higher risk of accidents and traffic violations. By setting a minimum age, governments hope to reduce the overall risk on the road and minimize the potential for accidents caused by inexperienced or immature drivers.
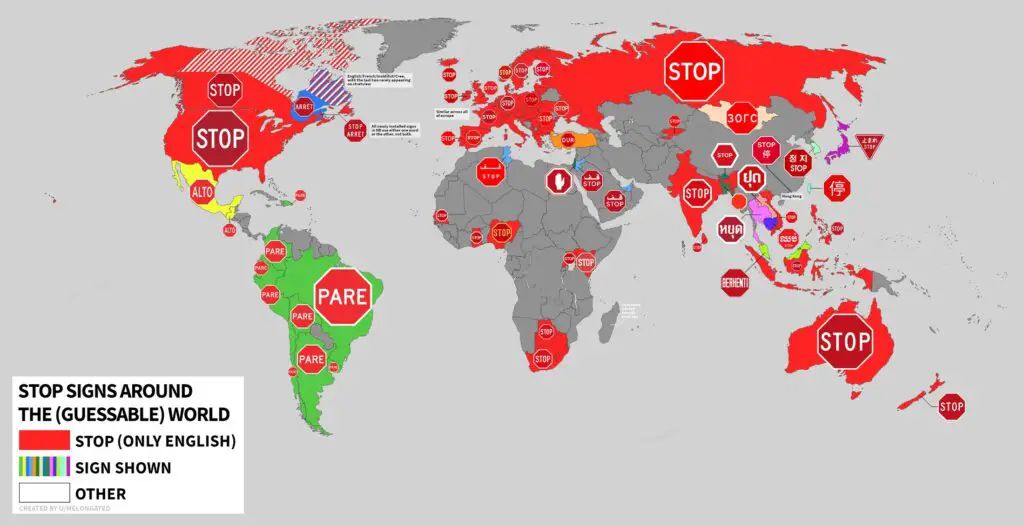
Stop signs around the world
Stop signs are a ubiquitous traffic control device used worldwide. They typically feature a red octagonal shape with the word “STOP” in white letters. The purpose of a stop sign is to instruct drivers to come to a complete halt at intersections, ensuring safety by allowing right-of-way determination. While the design is consistent, the specific rules and regulations governing stop sign use may vary from country to country, but the fundamental concept of stopping remains universal.
Road distances order in Europe
In Europe, road distances order signs are used to provide information about distances to various destinations along a specific road or route. These signs typically display the names of towns, cities, or landmarks along with the respective distances in kilometers or miles. They are crucial for helping drivers navigate and plan their journeys, ensuring they have clear information about how far they are from their intended destinations.

Traffic light sequences in Europe
Traffic light sequences in Europe typically follow a standardized pattern of colors: red, amber (or yellow), and green. Red signals stop, green signals go, and amber is a warning to prepare to stop. The sequences usually include a brief period when all lights are red (the “all-red” phase) to allow for a safe transition between conflicting traffic movements. While the colors and meanings are consistent, the duration and timing of each phase can vary depending on local traffic management and road conditions, but they generally adhere to international standards to ensure uniformity and safety across European road systems.
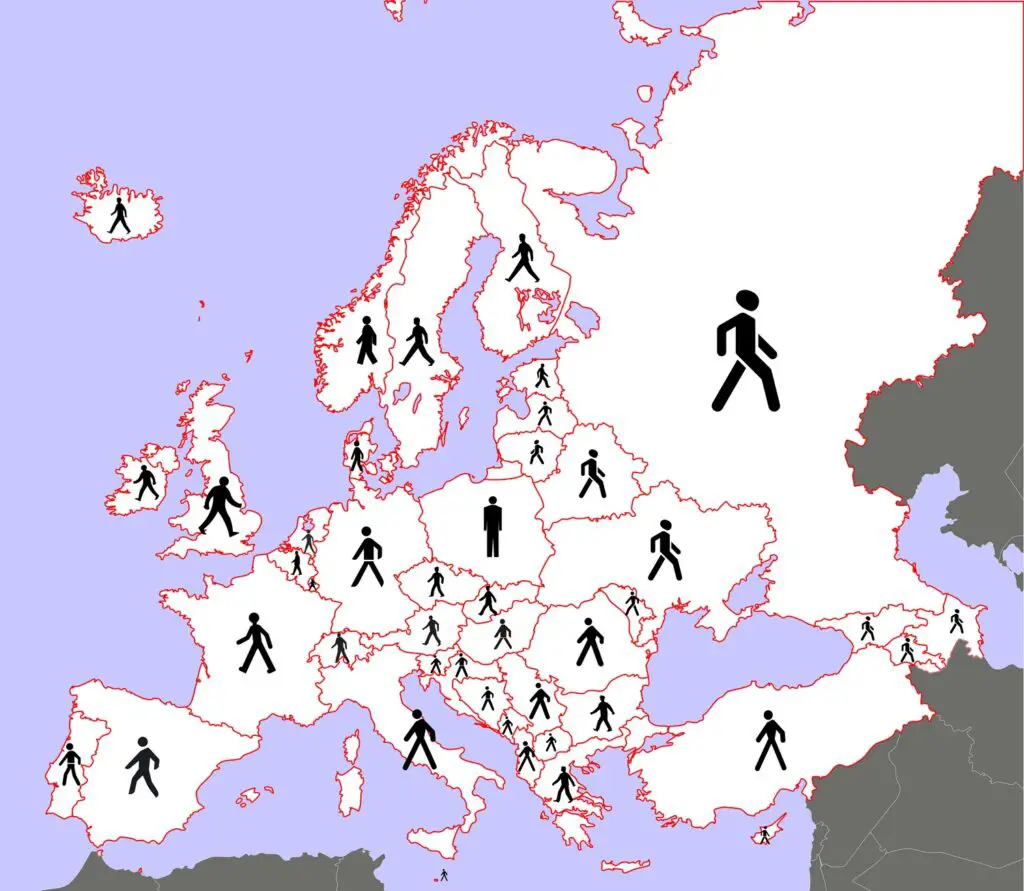
What pedestrians look like across Europe?
Pedestrian signs around the world are designed to enhance pedestrian safety and facilitate smooth interactions between pedestrians and vehicular traffic. These signs typically include symbols of pedestrians walking, crossing, or using crosswalks. Common variations include “Pedestrian Crossing” signs, “Yield to Pedestrians” signs, and “Pedestrian Zone” signs. While the design and wording of these signs may differ, the objective remains consistent: to alert drivers to the presence of pedestrians, promote safe crossing, and encourage drivers to yield the right-of-way to those on foot.
You can learn about traffic rules from the following books:
- Traffic Signs Every Driver Should Know But Don’t: A Driver Education Manual To Help New and Old Drivers Learn Traffic Signs And Their Meaning To Ace Their Driving Tests
- Road Signs Flash Cards with Detailed Explanations and Safe Driving Tips – Stocking Stuffers for Teens, Teen Boy Gifts, Gifts for Teen Boys, Teenage Boy Gift









That is so weird. Wonder why the difference?