Unemployment in Italy
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
Italy has historically struggled with relatively high levels of unemployment, particularly in comparison to some of its European counterparts. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the country had been grappling with unemployment rates that often exceeded the European Union average.
Several factors contributed to Italy’s unemployment challenges, including a sluggish economy, a relatively high public debt burden, a complex labor market with varying regulations, and a lack of robust economic growth. Additionally, structural issues such as a high youth unemployment rate and a prevalence of temporary and part-time employment contracts were persistent concerns.
The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in early 2020, had a significant impact on Italy’s labor market. Lockdown measures and restrictions imposed to contain the virus led to a sharp economic contraction, resulting in job losses across various sectors. Tourism, hospitality, and retail were among the hardest-hit industries due to the decrease in travel and consumer spending.
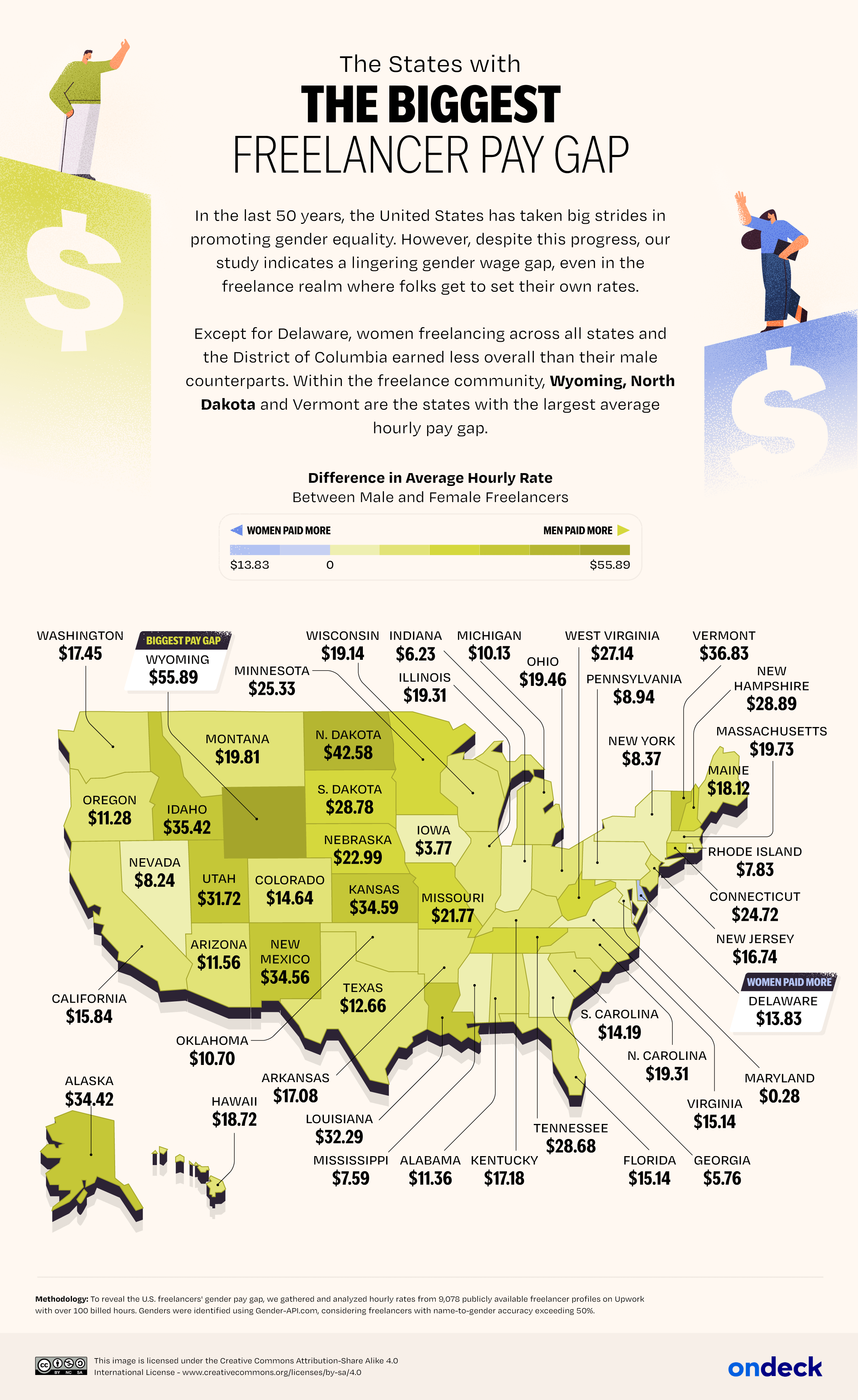
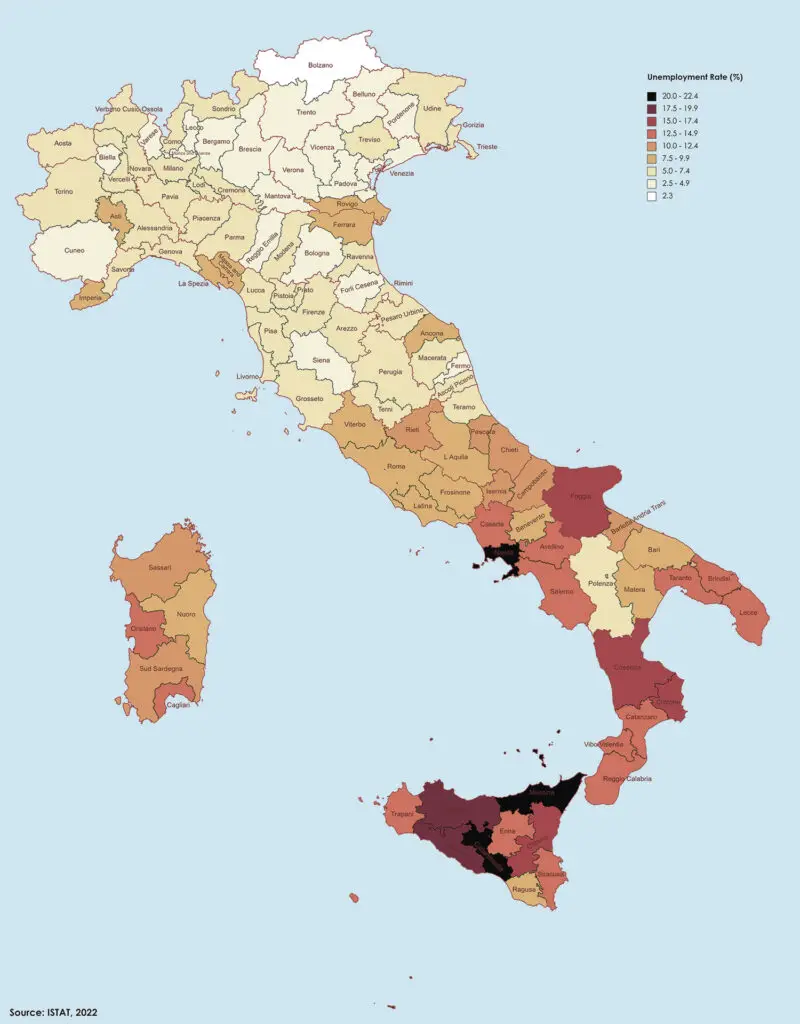
Unemployment rates can vary significantly across different provinces in Italy due to various factors, including regional economic disparities and industry concentrations.
Italy has a noticeable North-South economic divide, with generally lower unemployment rates in the northern regions and higher rates in the southern regions. Provinces in the north tend to have more diversified economies and higher levels of industrialization.
Historically, regions in southern Italy, such as Calabria, Sicily, Campania, and Puglia, have faced higher unemployment rates compared to the rest of the country. These regions have often struggled with lower economic development and fewer job opportunities.
The map below shows unemployment rates in Italian provinces.
In response to the pandemic’s economic impact, the Italian government implemented measures such as furlough schemes and financial support to help businesses retain their employees and navigate the crisis. These interventions aimed to mitigate the rise in unemployment.
To learn more about Italy, have a look at the following books: