The Changing World Population, by Country (1960 – 2022)
From 1960 to 2022, the population of various countries around the world has undergone significant changes. These changes have been influenced by a multitude of factors, including birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration.
In 1960, the world’s population stood at 3 billion. In just under three decades, by 1987, it had surged past the 5 billion mark. Fast forward another three decades, and we reached a global population of 8 billion. Notably, since 1975, the world’s population has consistently increased by approximately one billion every 12 years.
Asia’s distinction as the world’s most populous continent has deep historical roots, extending back for centuries. The interplay of factors such as robust birth rates, an expansive landmass, and a mosaic of diverse cultures has solidified Asia’s sustained reign as the most densely populated continent on our planet.
Europe, meanwhile, maintained its position as the second most populous continent for the majority of the 20th century, relinquishing this status around 1992. In that pivotal juncture, Africa emerged as the new contender, driven by remarkable population growth rates stemming from elevated birth rates and improved healthcare. Since the early 1990s, this shift in the population ranking has endured, with Africa firmly holding its place as the world’s second most populated continent, trailing only behind Asia.
| Rank | Continent | Population in 1960 (millions) | Population in 2022 (million) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Asia | 1 700 | 4 722 |
| 2 | Africa | 257 | 1 470 |
| 3 | Europe | 606 | 743 |
| 4 | North America | 240 | 602 |
| 5 | South America | 218 | 437 |
| 6 | Australia/Oceania | 36 | 46 |
| – | Total | 3 057 | 8 020 |
China’s long-standing status as the world’s most populous nation dates back to 221 BC when the Qin Dynasty’s unification marked its ascent. Over the millennia, China consistently maintained this demographic supremacy. In 2022, China’s population reached a pinnacle of 1.412 billion before embarking on a gradual decline. Remarkably, by the close of the same year, India assumed the mantle of the world’s most populous nation, surpassing China in terms of population.
The top 10 most populated countries 1960 vs 2022
| Rank 1960 | Country | Population in 1960 (millions) | Rank 2022 | Country | Population in 2022 (millions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 667 | 1 | India | 1 417 |
| 2 | India | 446 | 2 | China | 1 412 |
| 3 | United States | 181 | 3 | United States | 333 |
| 4 | Russia | 120 | 4 | Indonesia | 276 |
| 5 | Japan | 93 | 5 | Pakistan | 236 |
| 6 | Indonesia | 88 | 6 | Nigeria | 219 |
| 7 | Brazil | 73 | 7 | Brazil | 215 |
| 8 | Germany | 73 | 8 | Bangladesh | 172 |
| 9 | United Kingdom | 52 | 9 | Russia | 144 |
| 10 | Bangladesh | 50 | 10 | Mexico | 128 |
The maps provided below showcase the population of countries worldwide in both 1960 and 2022, based on data sourced from the World Bank.
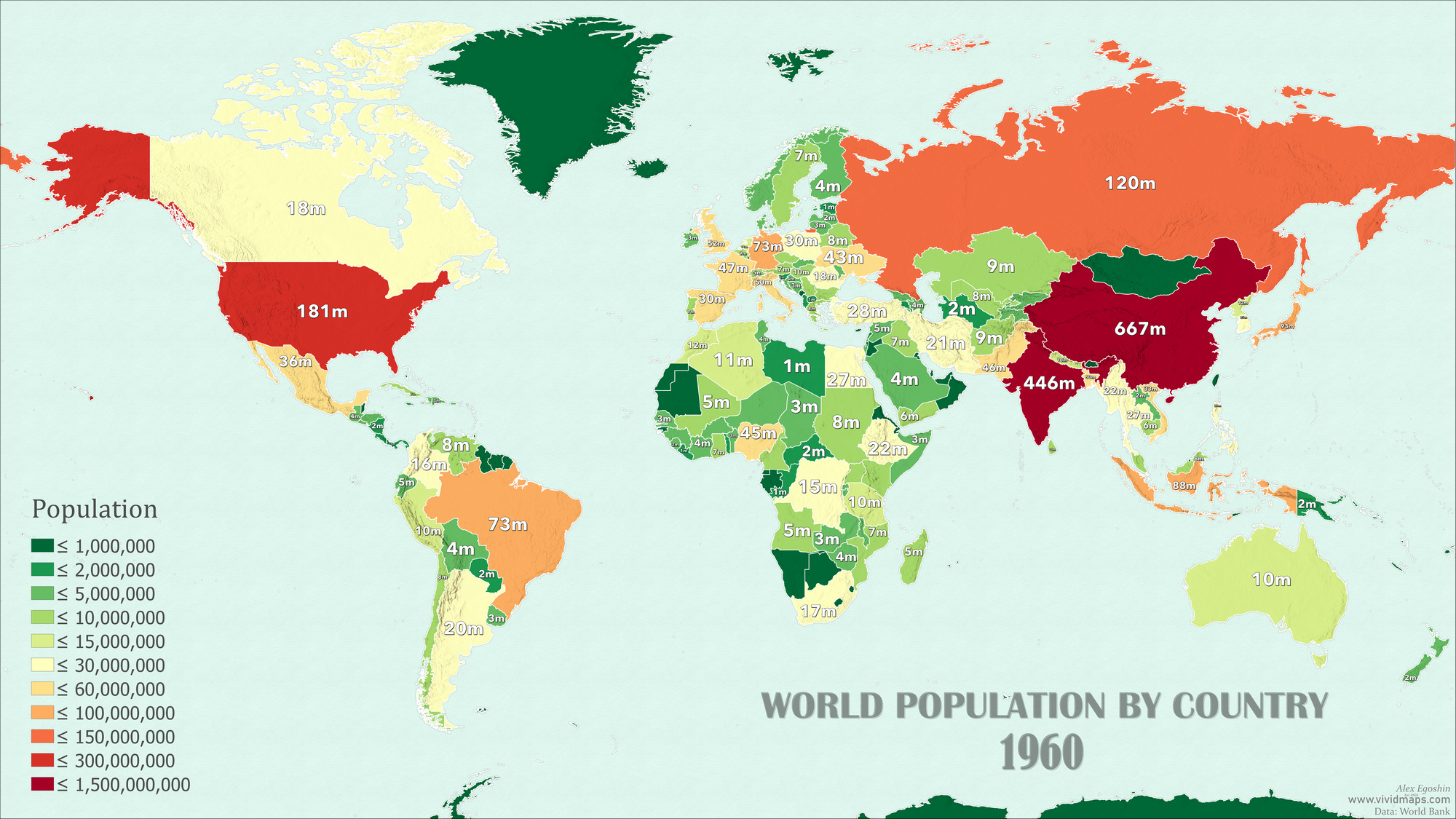

From 1960 to 2022, the country with the most significant population growth in terms of percentage increase is Qatar (+7307%). Qatar’s population growth is driven by economic development, immigration, and labor force migration.
A significant percentage increase in population also is a notable feature also shared by several countries in the Middle East (United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, and Jordan).
The country that experienced the most significant population decline as a percentage from 1960 to 2022 is Bulgaria (-17.8%). Bulgaria has faced notable demographic challenges, including low birth rates, high emigration, and an aging population, which have contributed to a decline in its population during this period.
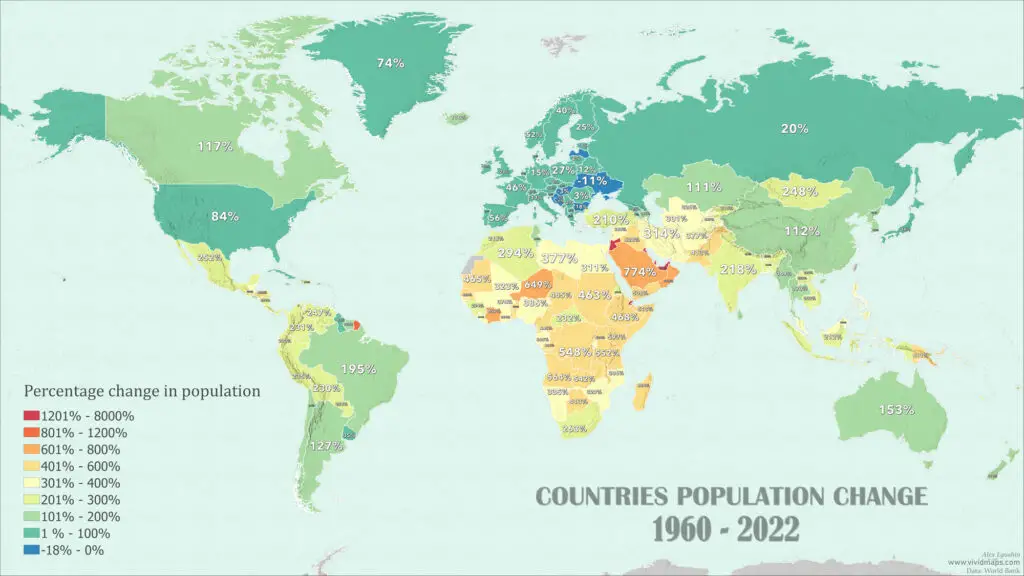
Below is an animated version of the world map.
In many countries of the world, a decline in the number of births per woman has led to reduced fertility, while the timing of deaths has shifted towards old age, resulting in high life expectancy.
Globally, birth and death rates have exhibited a consistent decrease over time, decreasing from 34 births and 13 deaths per 1000 people in 1965 to fewer than 18 births and less than 17.6 deaths per 1000 in 2022. Sub-Saharan Africa, where both birth and death rates remain relatively high, exhibits a considerable gap between these rates, resulting in rapid population growth. Conversely, Europe and Central Asia experienced a low death rate as early as 1960, which has remained consistently low over the years.