The World’s Forests Mapped
A forest is an area of land covered by trees. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization, forests cover approximately 3.9 million square kilometers (or 15.1 sq mi), which is about 30% of the Earth’s land surface.
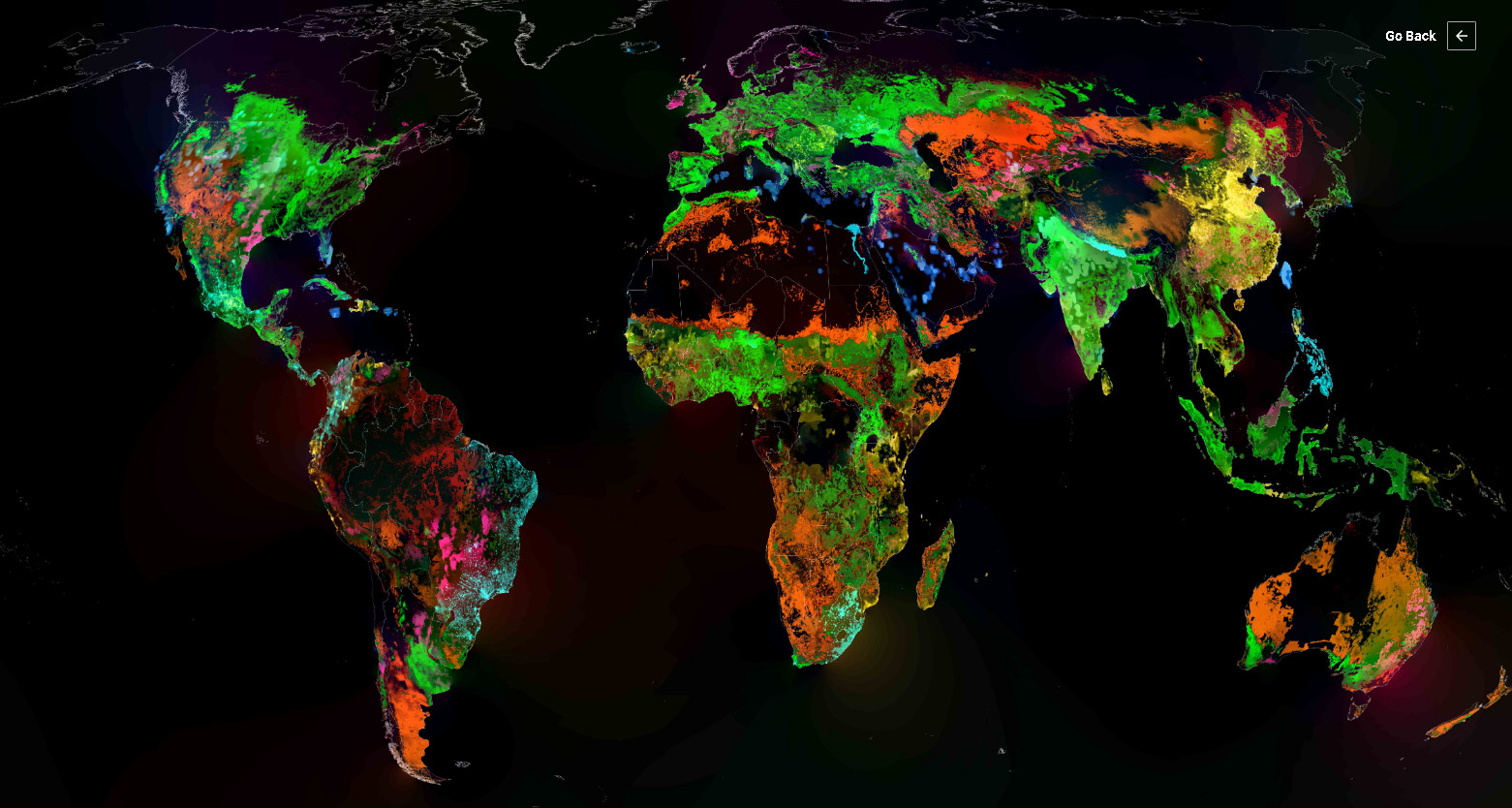
Forests at various latitudes and elevations create precisely diverse biomes: boreal, temperate, and tropical forests. Below is the forest atlas of the world of the main biomes of our planet.
World
Amongst world regions, Europe (including the European part of Russia) estimates for 1/4 of the total forest area, accompanied by South America and then North and Central America. South America is the continent with the highest percentage of forest cover, and Asia is the continent with the lowest rate of forest cover (less than 20 percent of land area).
Below is the world map of various forest types.

Needleleaf forests
Needleleaf forests spread primarily in areas that have lengthy, severe winters. These forests spread over Canada, northern Europe, and Russian Siberia.
Scarce needle-leaf forests grow in warmer territories. For instance, the Southeastern U.S. has vast forests of pines, such as Pinus taeda and Pinus palustris.

Evergreen broadleaf forests
Evergreen broad-leaved forests abound in our planet’s subtropical, tropical, and equatorial regions.

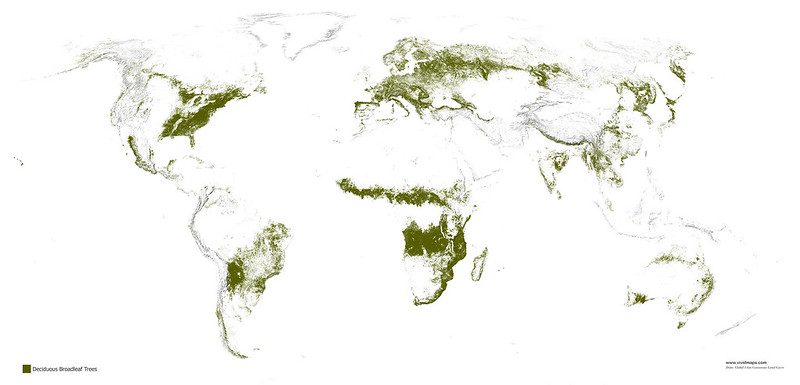
Deciduous broadleaf forests
Deciduous broadleaf forests are a type of temperate forest ‘dominated’ by trees that drop their leaves every year. They are growing in regions with mild, humid summers and chilly winters.
Mixed forests
Mixed forest is a vegetational transition between needle-leaf forests and broadleaf deciduous forests.

Maps of other types of vegetation

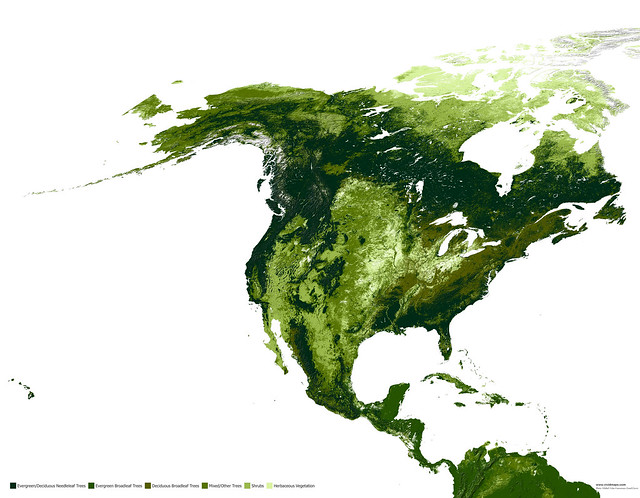
North America
North America has approximately 15.5% of the world’s entire forest cover (~850 million hectares).
The forests of North America contain arborescent representatives of 158 genera; 142 genera occur in the Atlantic and 50 genera in the Pacific region. Of the Atlantic genera, 48 are not represented in the United States outside the semi-tropical region of Florida. In the U.S. grow more than 640 various tree species.
The United States has about 301.5 million hectares of forest or 72% of the original forest cover that grew before European settlement. Canada has about 402.7 million hectares of forest, or 91% of its original forest cover, more than any other nation in the world.

Needleleaf forests of North America
North America’s boreal forest is formed of such evergreen conifers as fir and spruce.
The coastal forest is a unique needle-leaf evergreen forest of the Pacific Northwest coastal belt, covering in latitudes from northern California to southern Alaska. Here, in a gathering of a large percentage of precipitation, moderate temperatures and high humidity are the densest of all needle leaf forests, with impressive spruce, fir, and cedar specimens. At the farthest southern end, the coastal needle leaf forest comprises the planet’s most giant trees – Sequoia sempervirens.

Evergreen broadleaf forests of North America
Small woodlands of evergreen broadleaf tree species like evergreen oak and magnolia are found in the U.S. in Florida and along the Gulf Coast.

Deciduous broadleaf forests of North America
North America’s deciduous broad-leaf forests stretch across 25 U.S. states from Florida up to New England and Canada and reach as far west as Minnesota and Texas. These forests cover approximately 2.5 million square kilometers.

Mixed forests of North America

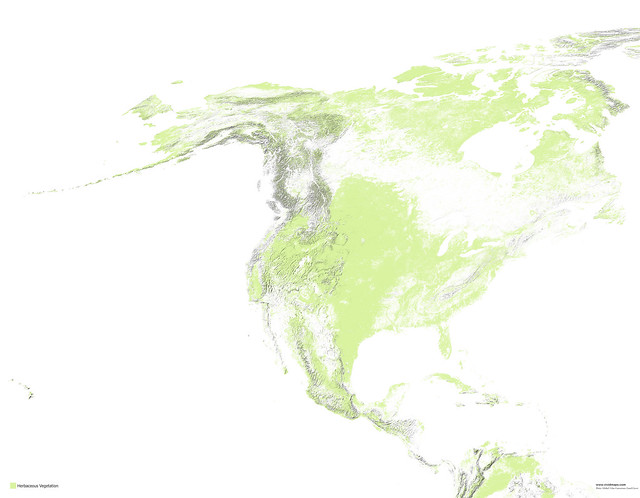
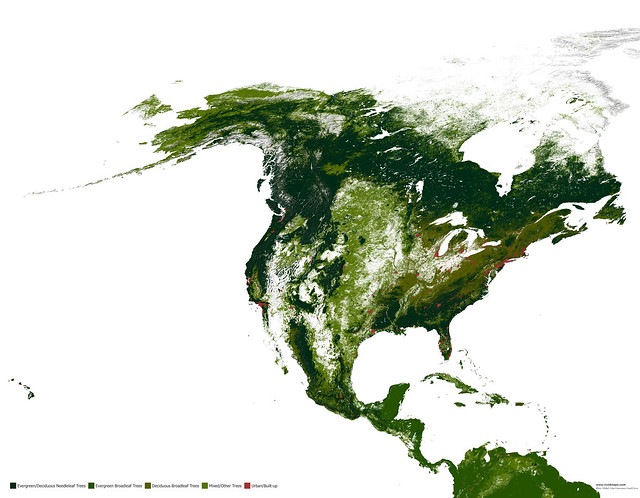
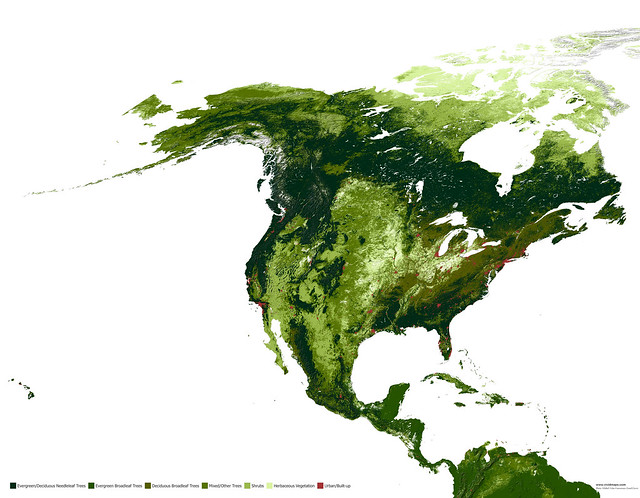
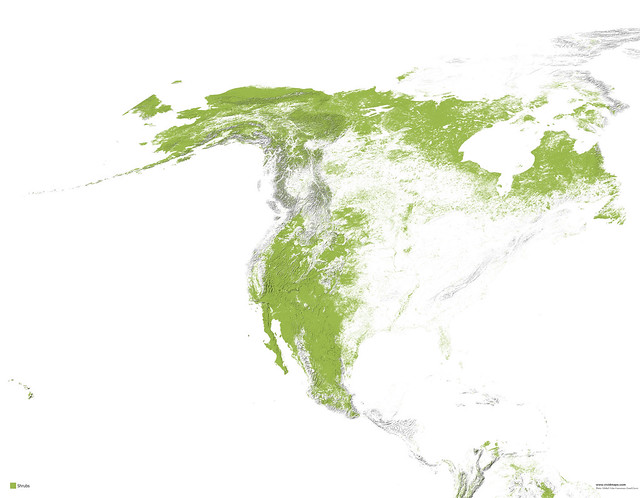
Maps of other types of vegetation in North America
South America
South America’s total forest area is about 3 million square miles (7.8 million square kilometers) and occupies about 21 percent of the continent, representing around 27 percent of the global forest area.

Evergreen broadleaf forests of South America
Evergreen broadleaf forests are growing in the Amazonian lowlands, from Rio Grande do Norte state in the north to the Rio Grande do Sul state in the south of Brazil (the Atlantic Forest).
Plant families mainly include Anareadiaceae, Bignoniaceae, Bombacaceae, Bromeliaceae, Malpighiaceae and Malvaceae.

Deciduous broadleaf forests of South America
Tropical deciduous forests are located in the Pacific watershed of Ecuador, in Venezuela, and on the Brazilian coast from about 7°S to the Tropic of Capricorn.

Temperate deciduous forests are found on low-altitude coastal mountains in southern Brazil, Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile.
Mixed forests of South America

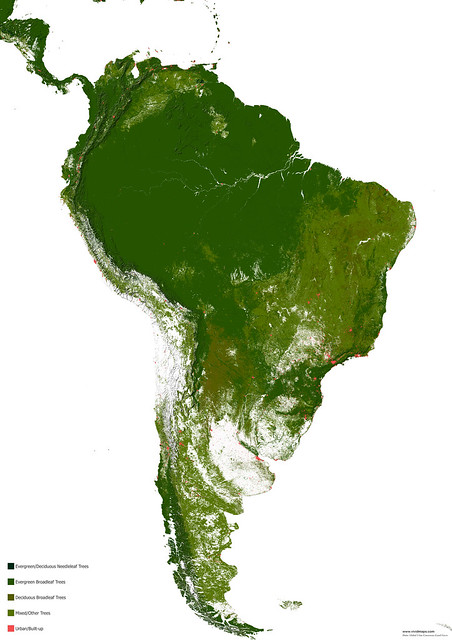
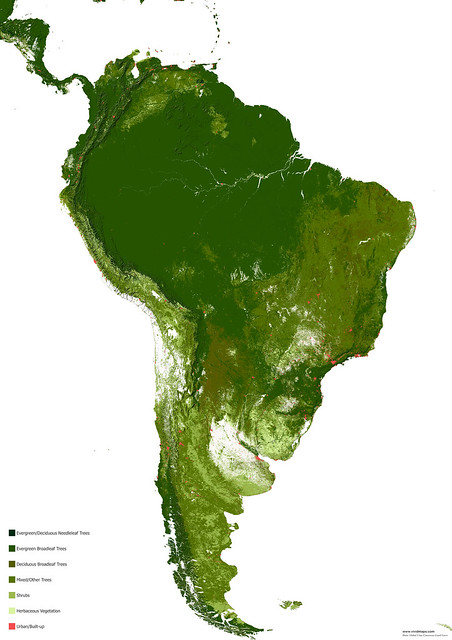
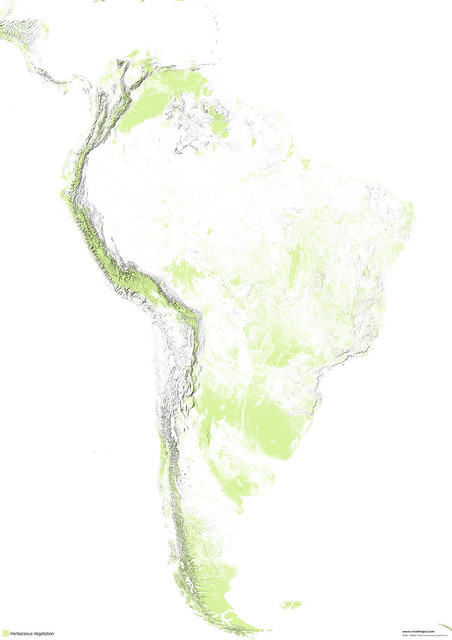
Maps of other types of vegetation in South America
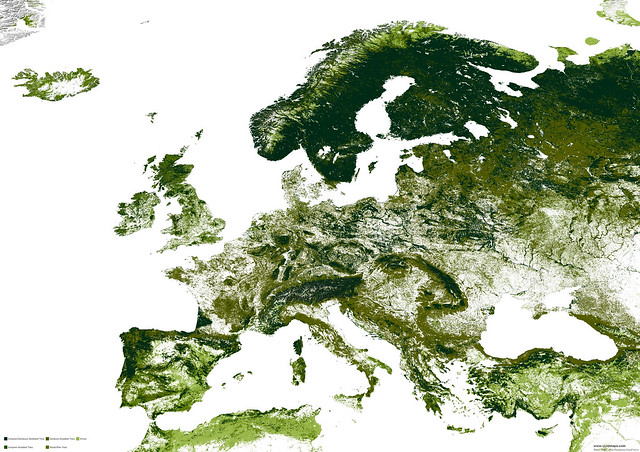
Europe
Nowadays, forests amount to around 1.8 million kilometers, making the European continent one of the most forest-rich territories globally, with more than forty percent of the area covered by forests.

Needle-leaf forests of Europe
In Europe, needle-leaf forests are predominantly found on all mountain ridges in northern Europe. Coniferous forests cover about 29.6% of Europe.

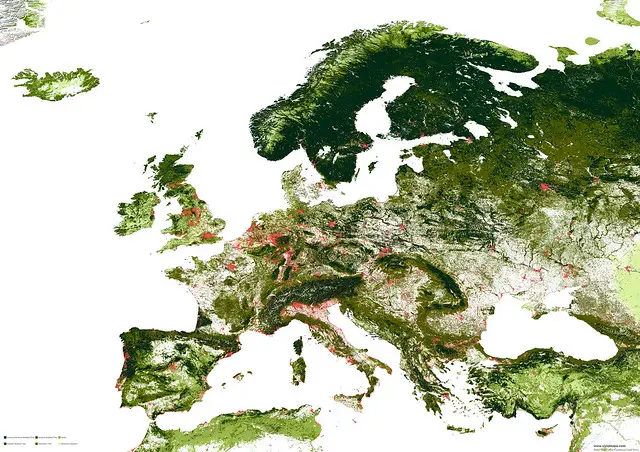
Deciduous broad-leaf forests of Europe
Deciduous forests of Europe include forests dominated by mixtures of Carpinus betulus, Quercus petraea, Quercus robur, Fraxinus (Fraxinus excelsior, Fraxinus angustifolia), Acer (Acer campestre, Acer pseudoplatanus), and Tilia cordata.

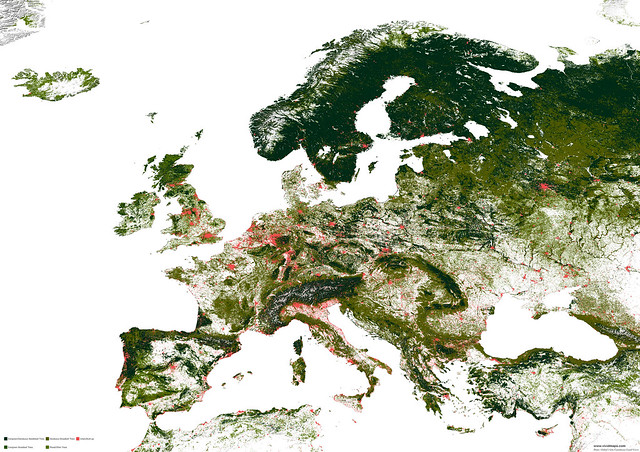
Mixed forests of Europe

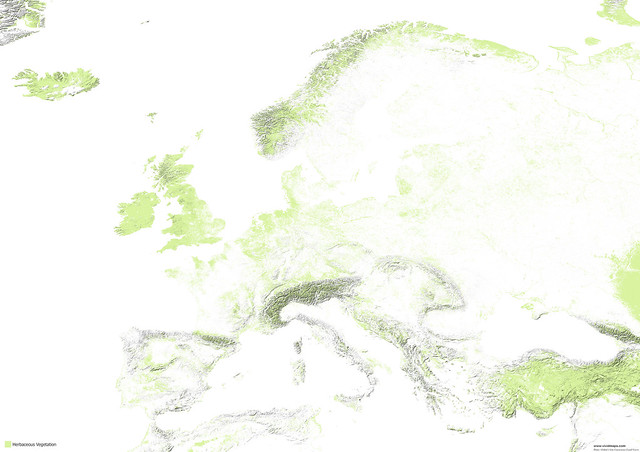
Maps of other types of vegetation in Europe
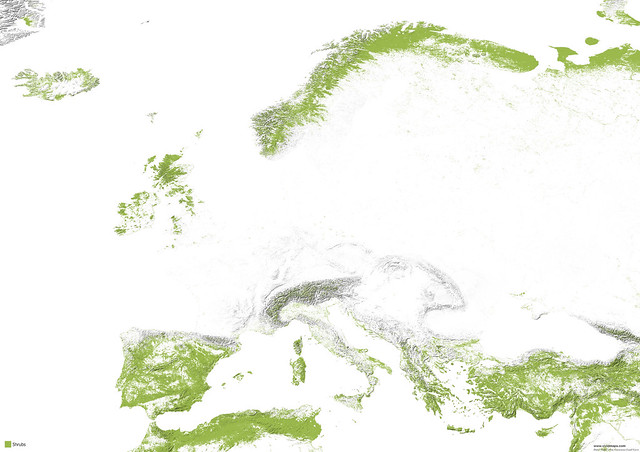
Middle East
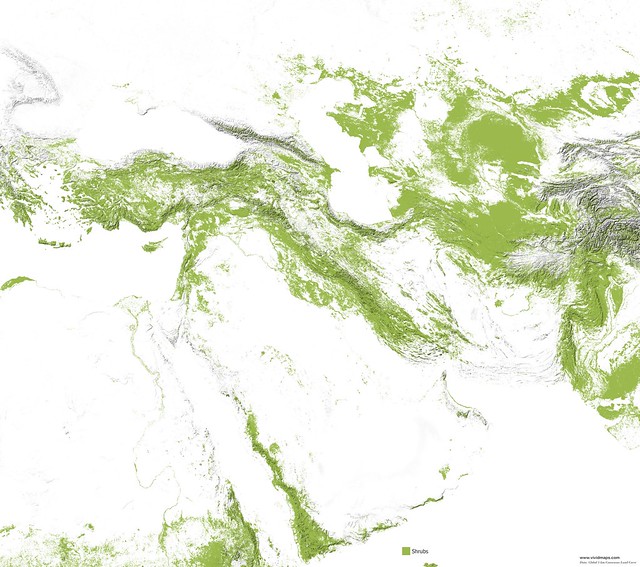
While the Middle East is usually associated with deserts, burning sun, and water deficiency, it has had dense forests and grasslands in ancient times. They have decreased during the last centuries. Nowadays, the Middle East has become drier, but forests, however, survive.

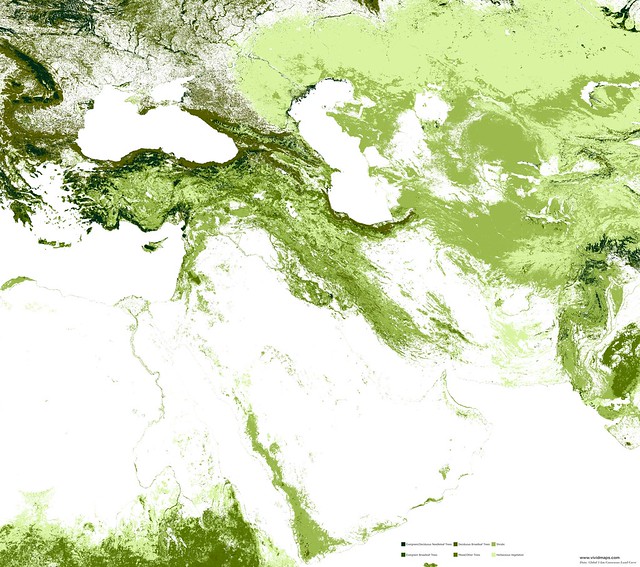
Needle-leaf forests of the Middle East

Deciduous broad-leaf forests of the Middle East

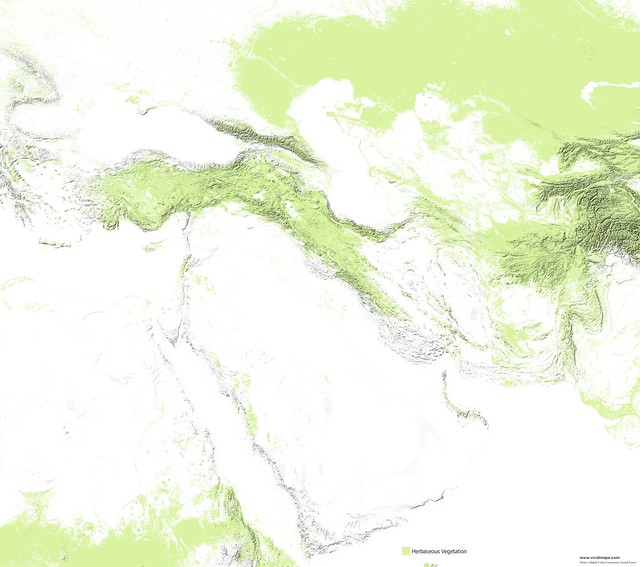
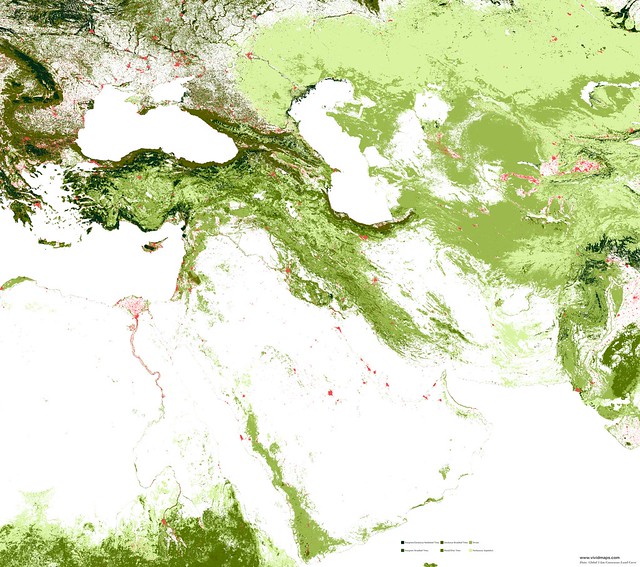
Maps of other types of vegetation of the Middle East
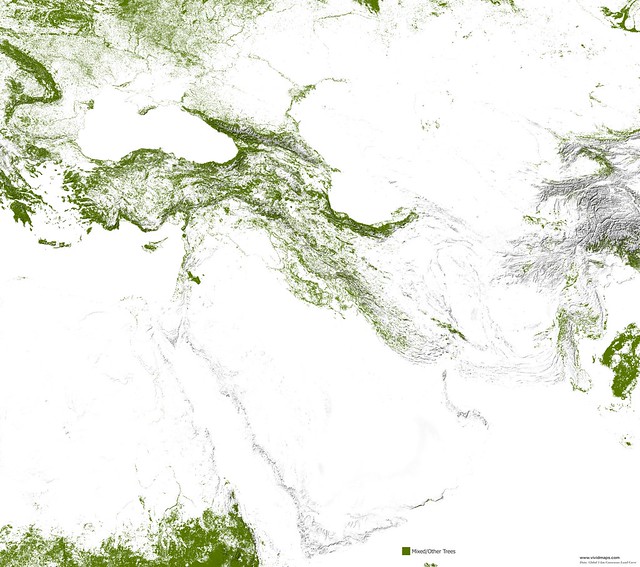
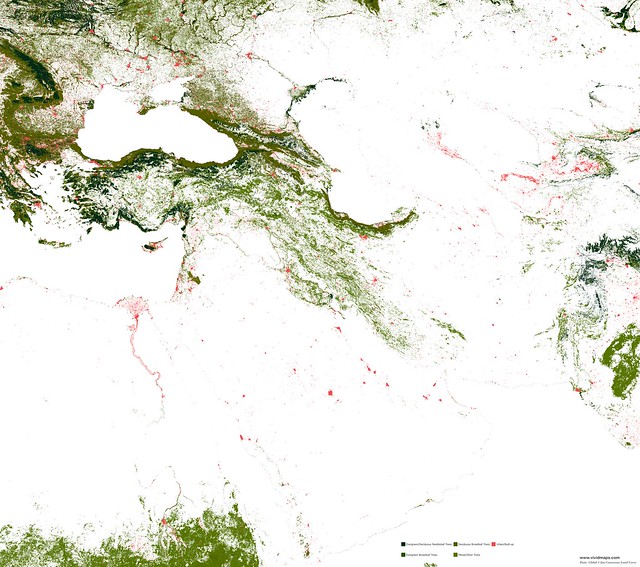
Asia
East Asia has the largest forest area (~2.4 million km2), 16% of these forests are listed as primary forests, with no noticeable marks of human activities. It is lower than the global mean of 36% due to high population density. At the same time, 18% are intensively regulated forests of indigenous species, and 9% are listed as forest plantations with alien species.

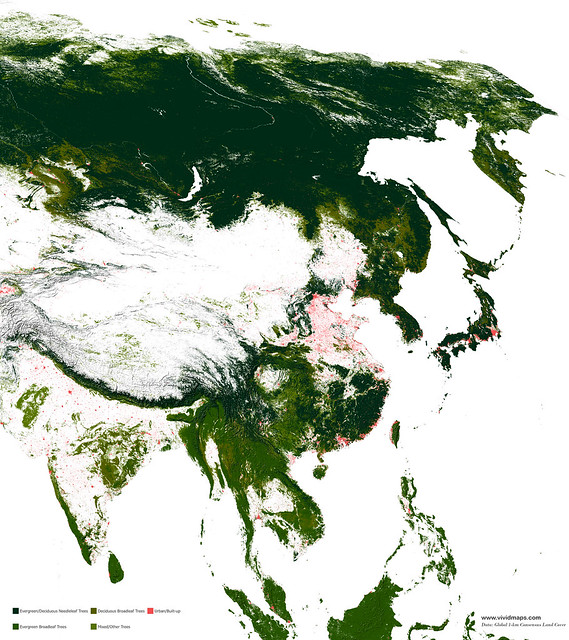
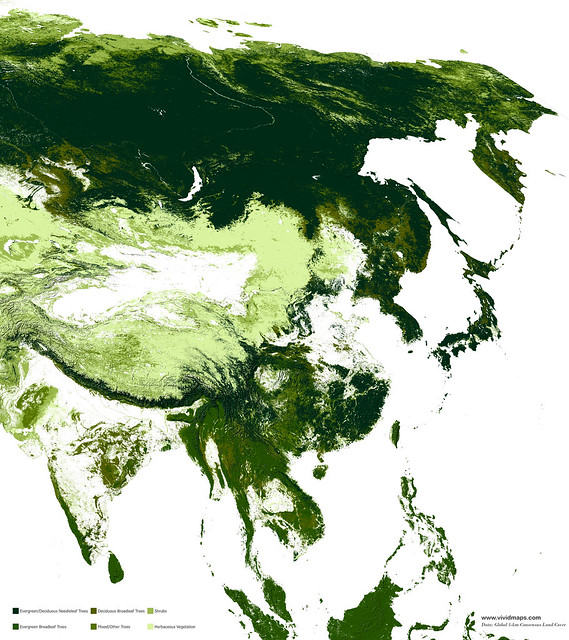
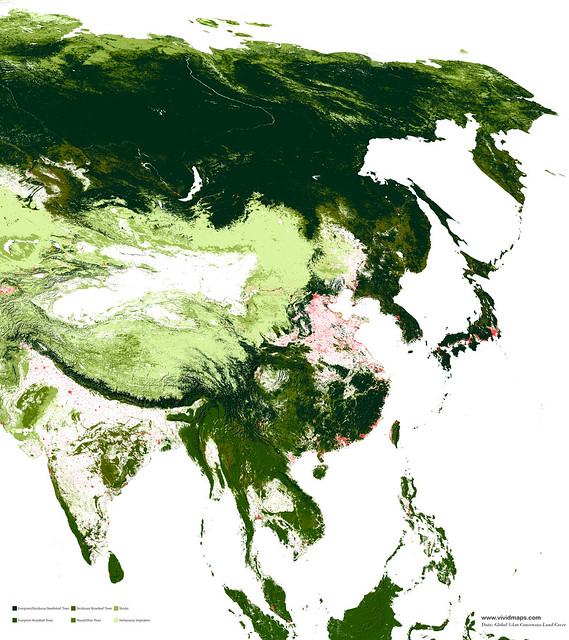
Needle-leaf forests of Asia
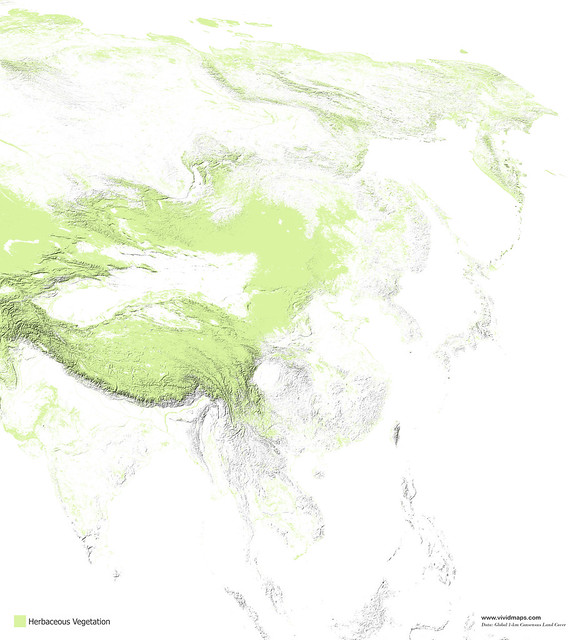
Coniferous forests in Asia are mainly found in Siberia, mountainous regions, and territories with a monsoon climate.

Evergreen broadleaf forests of Asia
Most evergreen broadleaf forests in Asia are growing in Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia.

Deciduous broad-leaf forests of Asia
In China, intensive agriculture has cleared the natural presence of broad leaves, while in Southwest Asia, this forest is fragmented. Oaks dominate the upper layer are frequently mixed with alders, ashes, maples, and poplars.
In Japan, the deciduous broadleaf forests are presented by maple (Acer carpinofolium), beeches (Fagus crenata, Fagus japonica), and oak (Quercus crispula) wich mingle with ashes, cherries, and magnolias.

Mixed forests of Asia

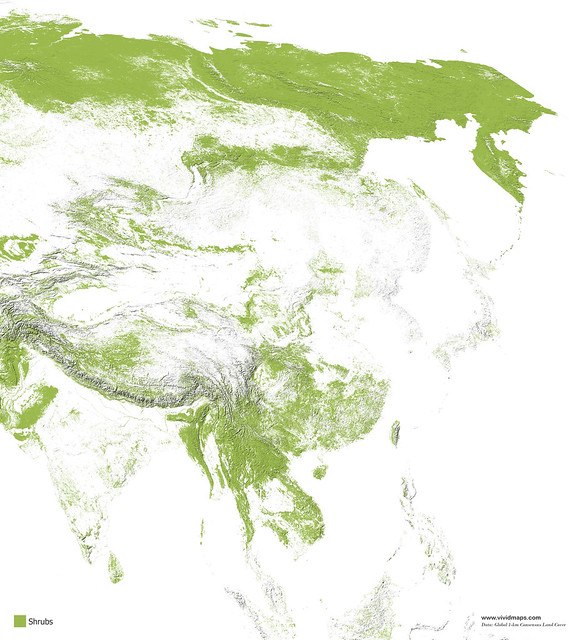
Maps of other types of vegetation in Asia
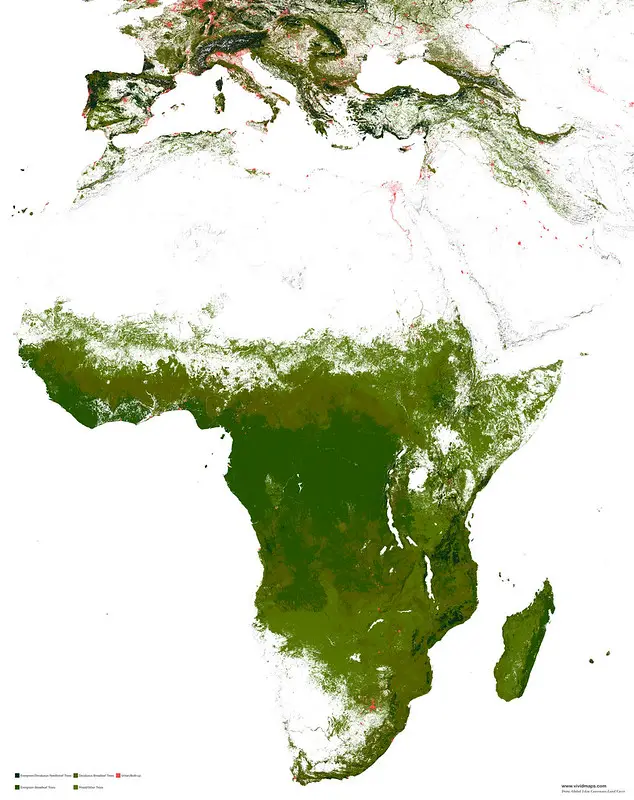
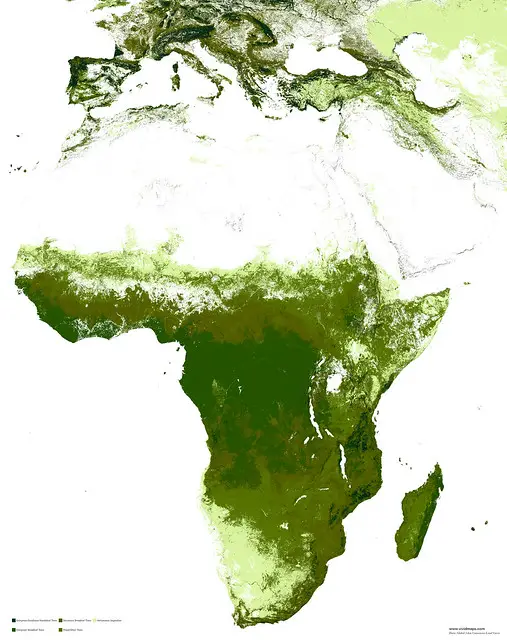
Africa
The forests of Africa show a complicated image. The most impressive picture appears that only Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo yet preserve more than half of their primary forest cover; most of the other 32 nations have less than 1/5 remaining.

Needleleaf forests of Africa
In Africa, needle-leaf forests are represented mainly by Mediterranean pines, cypresses, and cedar (Cedrus atlantica) on the Atlante Range.

Evergreen broadleaf forests of Africa
Tropical forests occupy Central Africa with outliers in West Africa and Madagascar but have lower diversity than South American and Southeast Asia forests. Commonly widespread plants are within the Lauraceae, Myristicaceae, Myristicaceae, Myrtaceae families, and oil palms (Elaeis guineensis, Raphia vinifera).
The Congo Basin, covering about 1800041 square kilometers, is Africa’s most extensive contiguous forest and the 2nd-largest tropical evergreen broadleaf forest on Earth.

Deciduous broad-leaf forests of Africa
In Africa, the deciduous forest is composed of Leguminosae. The main species that occur are Brachystegia, Colophospermum mopane, Isoberlinia, Parinari, and Uapca.

Mixed forests of Africa

Maps of other types of vegetation

Australia and New Zealand
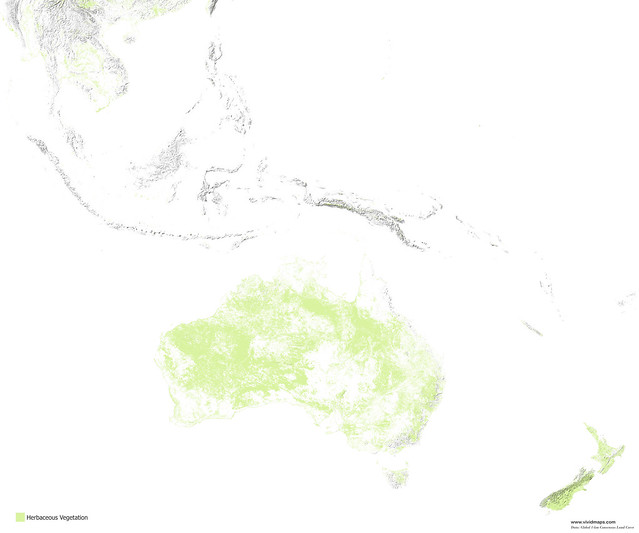
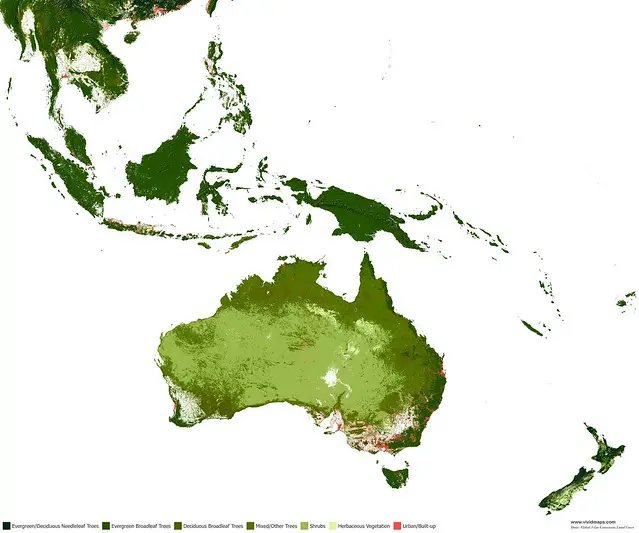
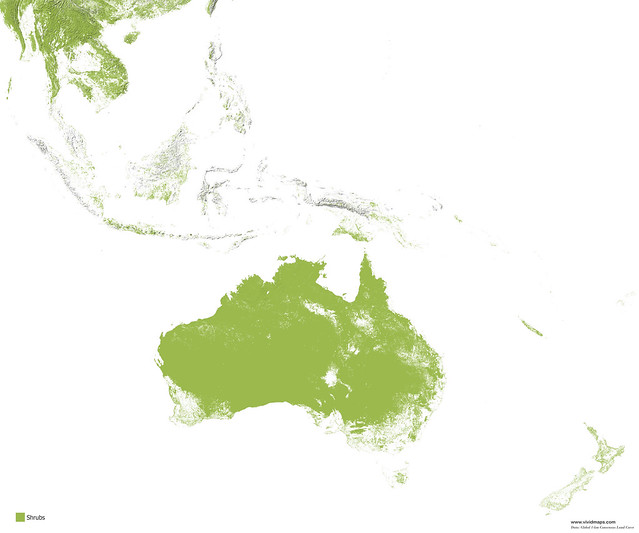
Australia has about 1.46 million kilometers of indigenous forest, representing approximately 19 percent of Australia’s territory. The preponderance of Australia’s trees typically eucalypts.

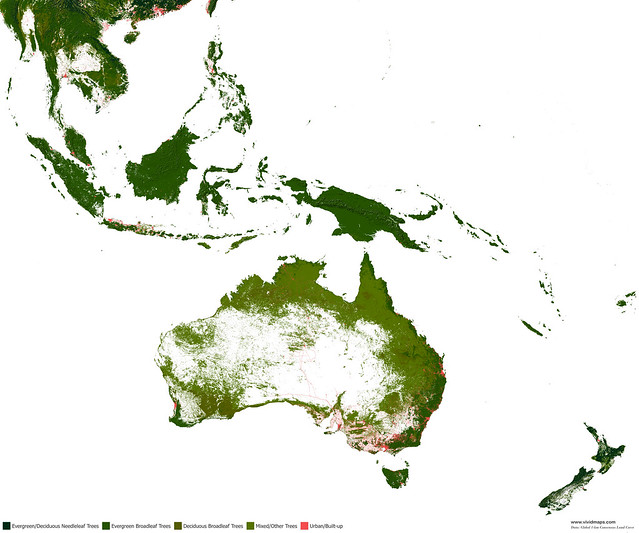
Needle-leaf forests of Australia and New Zealand
The region’s conifers are predominantly found in New Zealand. New Zealand’s native needle-leaf species belong to 4 families (Araucariaceae, Phyllocladaceae, Cupressaceae, Podocarpaceae), ten genera, and 20 species.

Evergreen broadleaf forests of Australia and New Zealand
Australia has barely any native deciduous trees. Most Australian species evergreens.
Only a few native species to Australia are deciduous (Toona ciliata, Melia azedarach, Adansonia gregorii).

Deciduous broad-leaf forests of Australia and New Zealand

Mixed forests of Australia and New Zealand

Maps of other types of vegetation of Australia and New Zealand







Loved the article. Wish all regions showed their world share of forest percentage