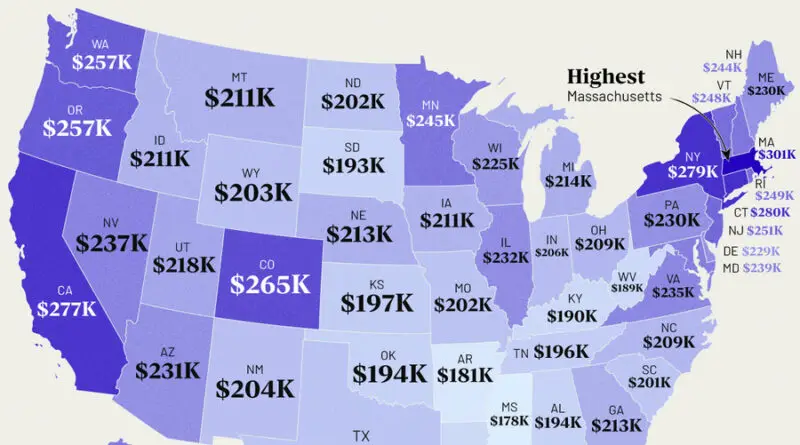
The Income Needed for a Comfortable Lifestyle in Every U.S. State
Outside of major cities, many Americans find life to be more affordable. However, years of high inflation have increased costs for almost everyone. To maintain a comfortable lifestyle, the 50/30/20 budget rule suggests spending about 50% of your income on necessities like food and housing, 30% on wants, and saving or paying off debt with the remaining 20%.
Read More